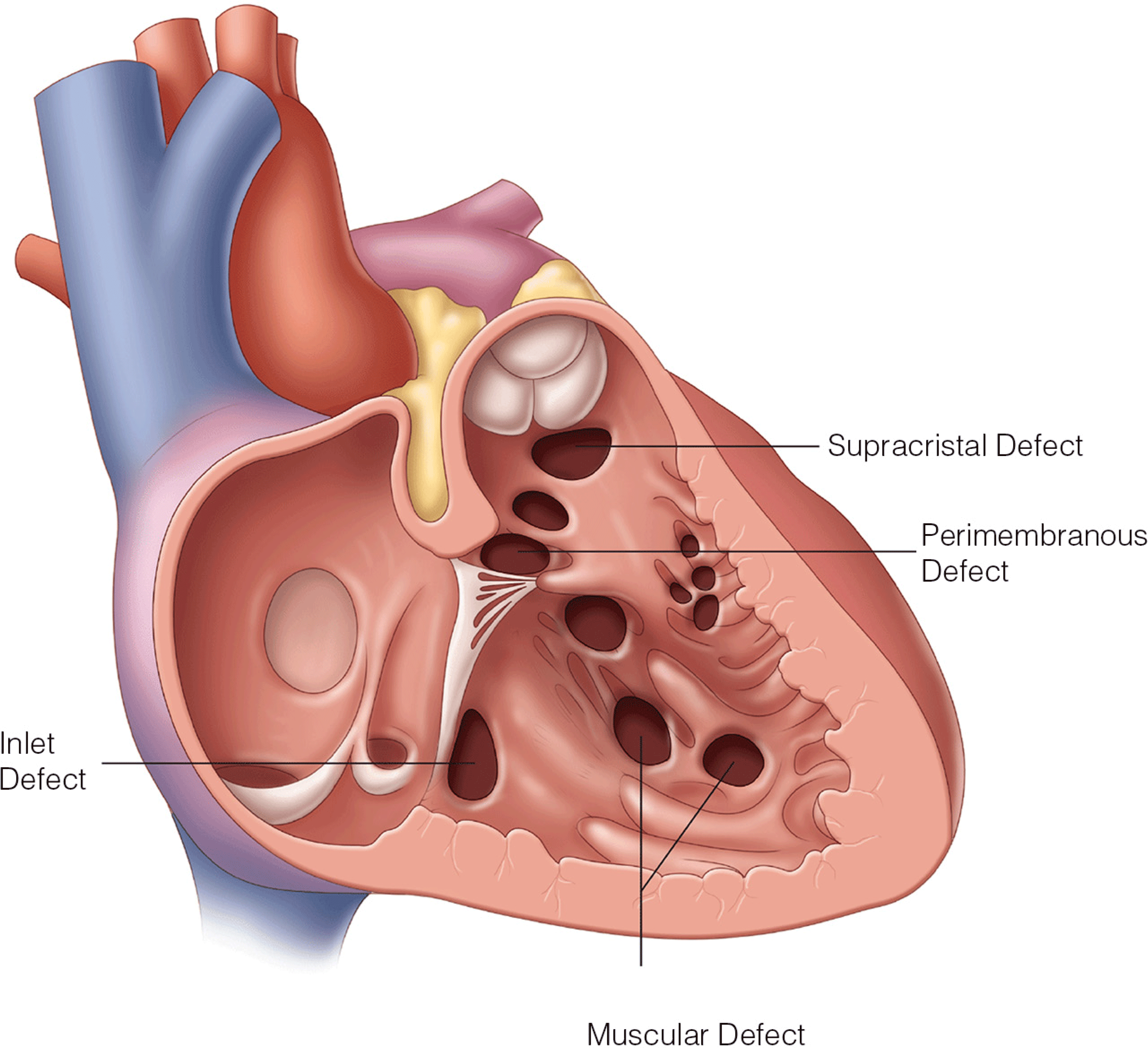
- Contemporary understanding of ventricular mechanics with identification of the structure and function of the ventricular myocardial band
- Detailed description of the anatomic proximity of cardiac structures and how knowledge of this proximity helps prevent intraoperative complications and damage to critical cardiac structures
- Comprehensive description of aortic root anatomy and mechanics and application of how this anatomy dictates performance of transcatheter aortic valve replacement
Latest Updates
- Updating consensus guideline recommendations up to January 2016
- Adding a duplex scan image showing a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the diagnosis section
- Adding a computed tomographic (CT) scan showing a pulmonary embolism (PE)
- Showing the various types of approved inferior vena cava filters
- Adding five separate flow-chart figures depicting a stepwise management algorithm for the evaluation and treatment of DVT and PE
- Adding a section on catheter-associated upper extremity thrombosis
- Adding a section on extended prophylaxis, the use of non–vitamin K antagonists, updates on stockings
- Writing five new multiple-choice questions based on the review
Iatrogenic Withdrawal Syndromes in Children: A Review of Sedative and Analgesic Weaning
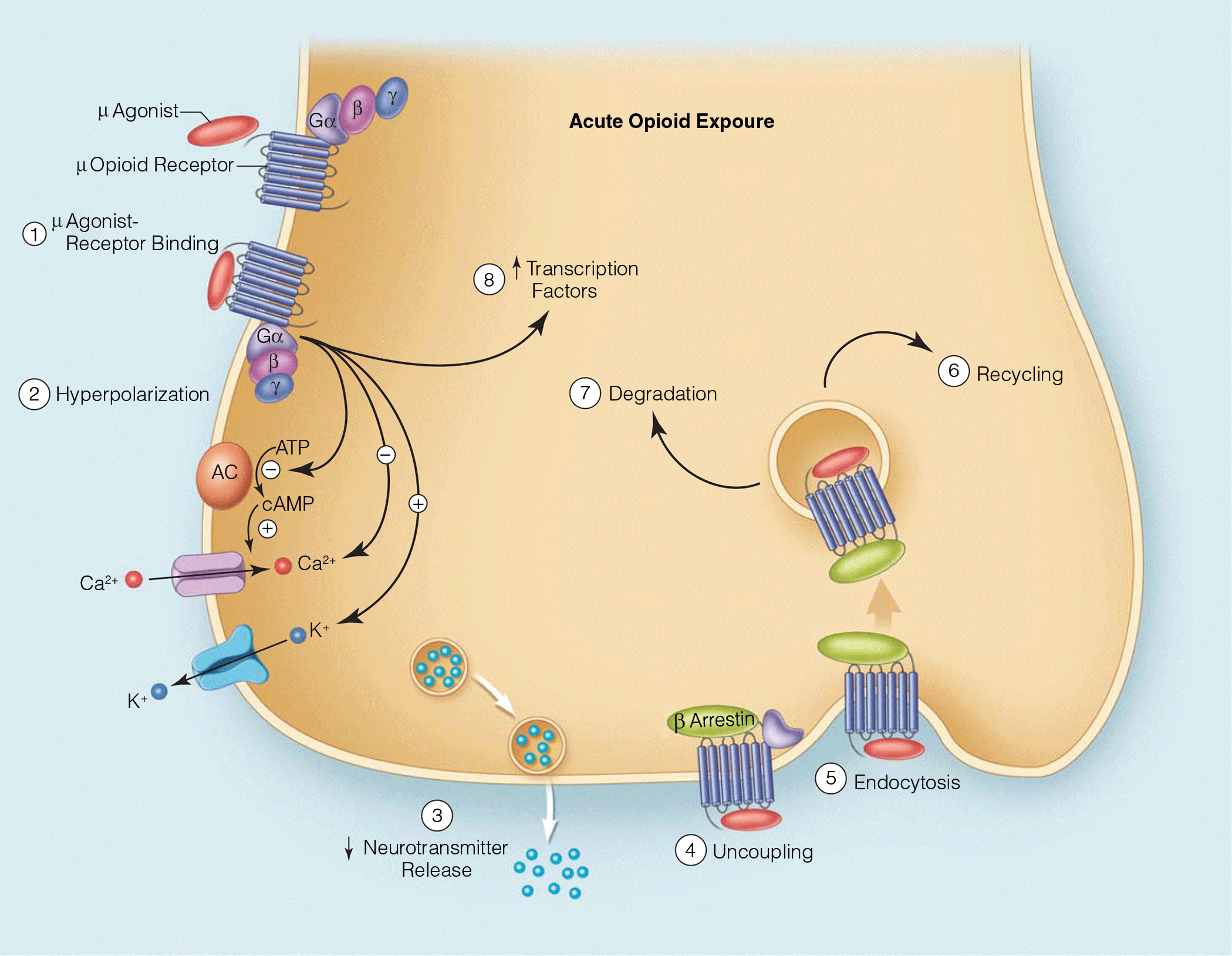
- Many iatrogenic withdrawal syndromes have been identified, the most common of which is opioid or benzodiazepine withdrawal. Generally speaking, the approach to treating opioid and/or benzodiazepine withdrawal is to provide enough medication to saturate target receptors, followed by a period of gradual dose reduction to allow the body to return to a state of homeostasis.
- The Neonatal Abstinence Score (NAS) was designed to assess withdrawal symptoms in infants with multiple drug exposure during pregnancy. Because the NAS was validated in infants, it is not applicable in older children with iatrogenic withdrawal. In recent years, withdrawal assessment tools for pediatrics have been developed for iatrogenic withdrawal to provide an objective assessment of withdrawal.
- There have been no randomized clinical trials that have compared the efficacy of various weaning strategies. However, a recent multicenter clinical trial, named the RESTORE trial, examined the effects of a standardized sedation protocol in pediatric intensive care units.

- Updating consensus guideline recommendations up to January 2016
- Adding a duplex scan image showing a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the diagnosis section
- Adding a computed tomographic (CT) scan showing a pulmonary embolism (PE)
- Showing the various types of approved inferior vena cava filters
- Adding five separate flow-chart figures depicting a stepwise management algorithm for the evaluation and treatment of DVT and PE
- Adding a section on catheter-associated upper extremity thrombosis
- Adding a section on extended prophylaxis, the use of non–vitamin K antagonists, updates on stockings
- Writing five new multiple-choice questions based on the review

Iatrogenic Withdrawal Syndromes in Children: A Review of Sedative and Analgesic Weaning
- Many iatrogenic withdrawal syndromes have been identified, the most common of which is opioid or benzodiazepine withdrawal. Generally speaking, the approach to treating opioid and/or benzodiazepine withdrawal is to provide enough medication to saturate target receptors, followed by a period of gradual dose reduction to allow the body to return to a state of homeostasis.
- The Neonatal Abstinence Score (NAS) was designed to assess withdrawal symptoms in infants with multiple drug exposure during pregnancy. Because the NAS was validated in infants, it is not applicable in older children with iatrogenic withdrawal. In recent years, withdrawal assessment tools for pediatrics have been developed for iatrogenic withdrawal to provide an objective assessment of withdrawal.
- There have been no randomized clinical trials that have compared the efficacy of various weaning strategies. However, a recent multicenter clinical trial, named the RESTORE trial, examined the effects of a standardized sedation protocol in pediatric intensive care units.

Iatrogenic Withdrawal Syndromes in Children: A Review of Sedative and Analgesic Weaning
- Many iatrogenic withdrawal syndromes have been identified, the most common of which is opioid or benzodiazepine withdrawal. Generally speaking, the approach to treating opioid and/or benzodiazepine withdrawal is to provide enough medication to saturate target receptors, followed by a period of gradual dose reduction to allow the body to return to a state of homeostasis.
- The Neonatal Abstinence Score (NAS) was designed to assess withdrawal symptoms in infants with multiple drug exposure during pregnancy. Because the NAS was validated in infants, it is not applicable in older children with iatrogenic withdrawal. In recent years, withdrawal assessment tools for pediatrics have been developed for iatrogenic withdrawal to provide an objective assessment of withdrawal.
- There have been no randomized clinical trials that have compared the efficacy of various weaning strategies. However, a recent multicenter clinical trial, named the RESTORE trial, examined the effects of a standardized sedation protocol in pediatric intensive care units.
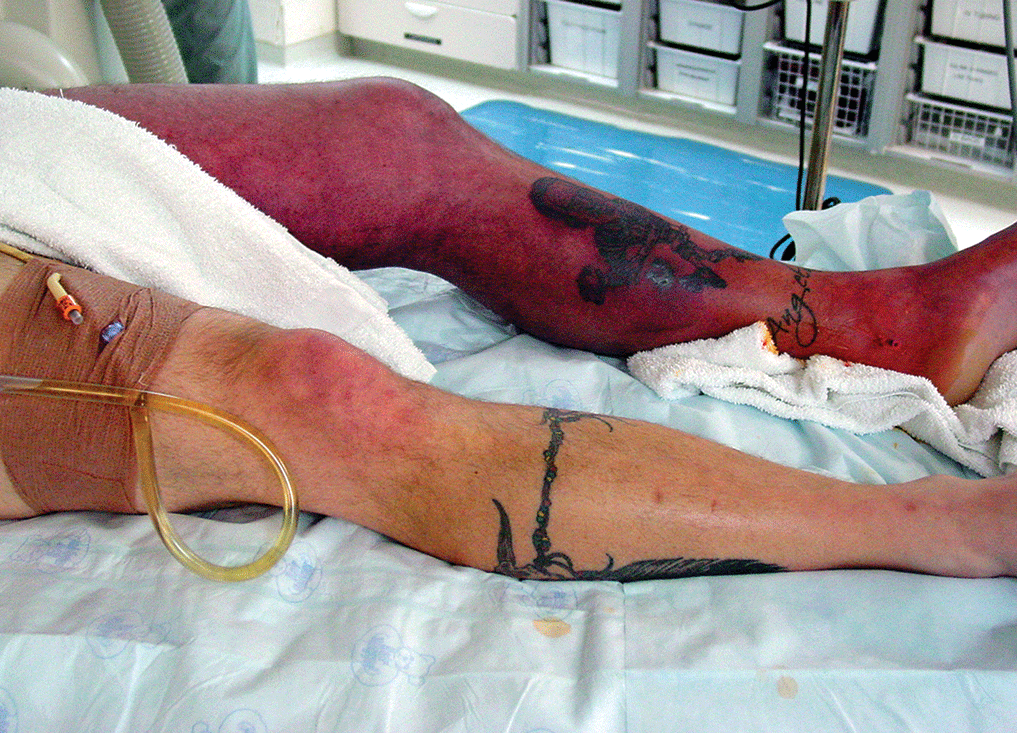
- Early recognition of shock is difficult but essential for preservation of cellular and organ function and survival. The earliest clinical signs are nonspecific, with the initial inflammatory response including tachycardia, fevers, or cool or clammy skin.
- The approach to shock ultimately requires understanding and correcting its etiology (eg, antibiotics and source control for sepsis, thrombectomy after massive pulmonary embolus, hemorrhage control after trauma, and so forth). However, until these are diagnosed and addressed directly, clinicians ultimately have three approaches in their armamentarium: volume expansion, vasopressors, and cardioactive agents.
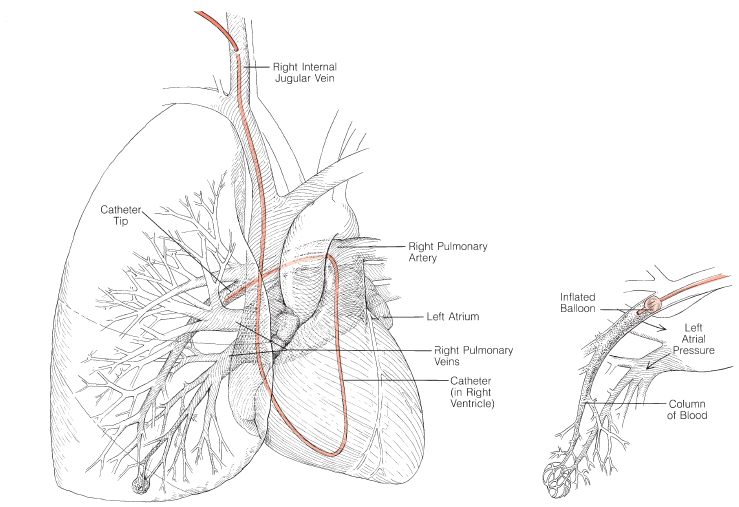
- The PAC was introduced in 1970. Its use increased over the next 3 decades and eventually was considered the standard of care for most critically ill patients. However, the use of PACs declined rapidly after the results of the randomized, controlled trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine revealing no benefit in high-risk surgical patients.
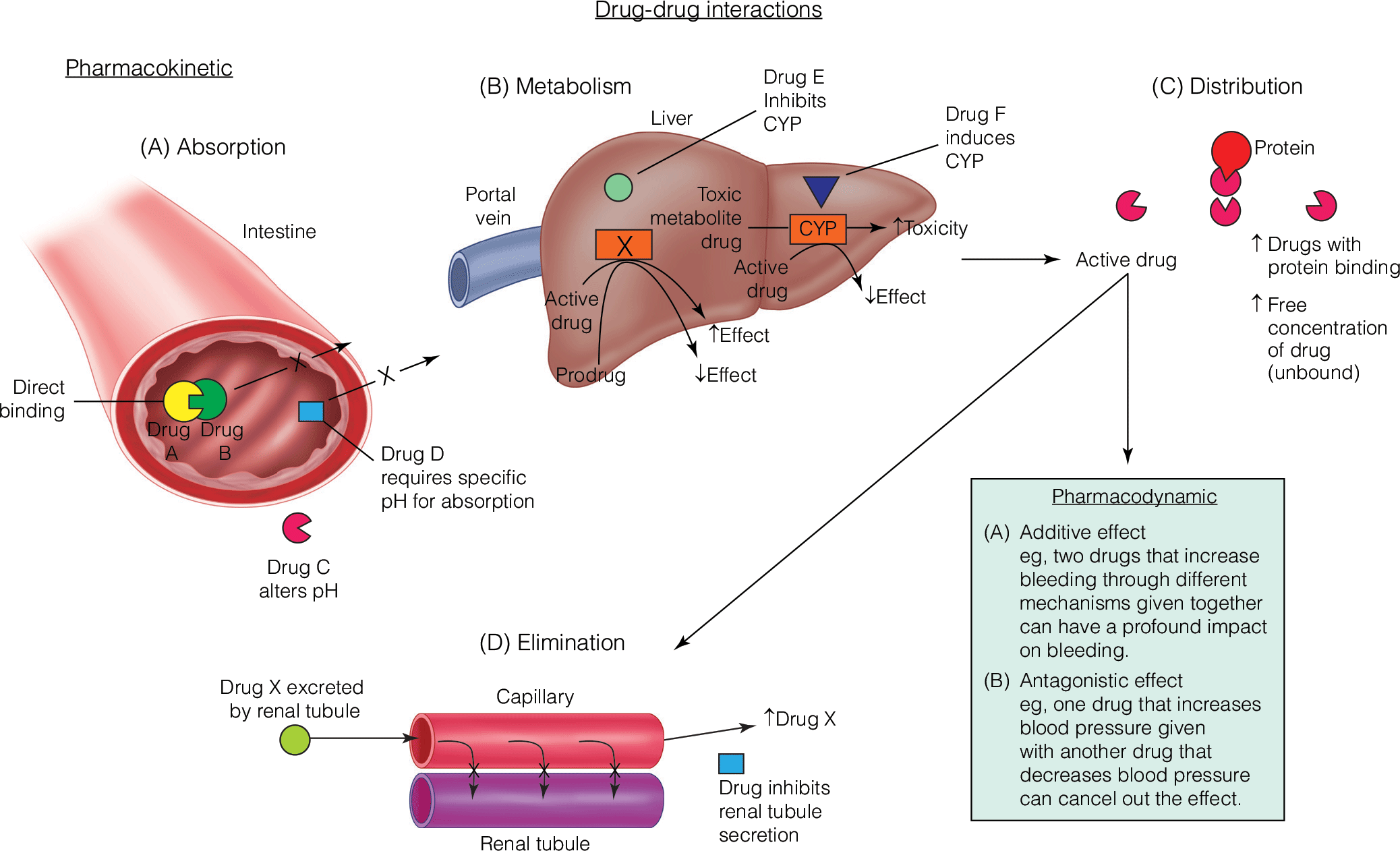
Management of Drug Interactions between Anti-infectives and Common Anesthetics
- Rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade is potentiated by a synergistic effect of gentamicin and clindamycin, which may delay recovery.
- Penicillins form a complex with sugammadex, which may interfere with the therapeutically intended sugammadex-rocuronium complex.
- Ondansetron can decrease the analgesic efficacy of acetaminophen at high doses.
- Anesthesiologists are positioned to manage interactions between anesthetic agents and antimicrobials in the operating room.


.png)







