Management of Depression, Part 2: Treatment Options
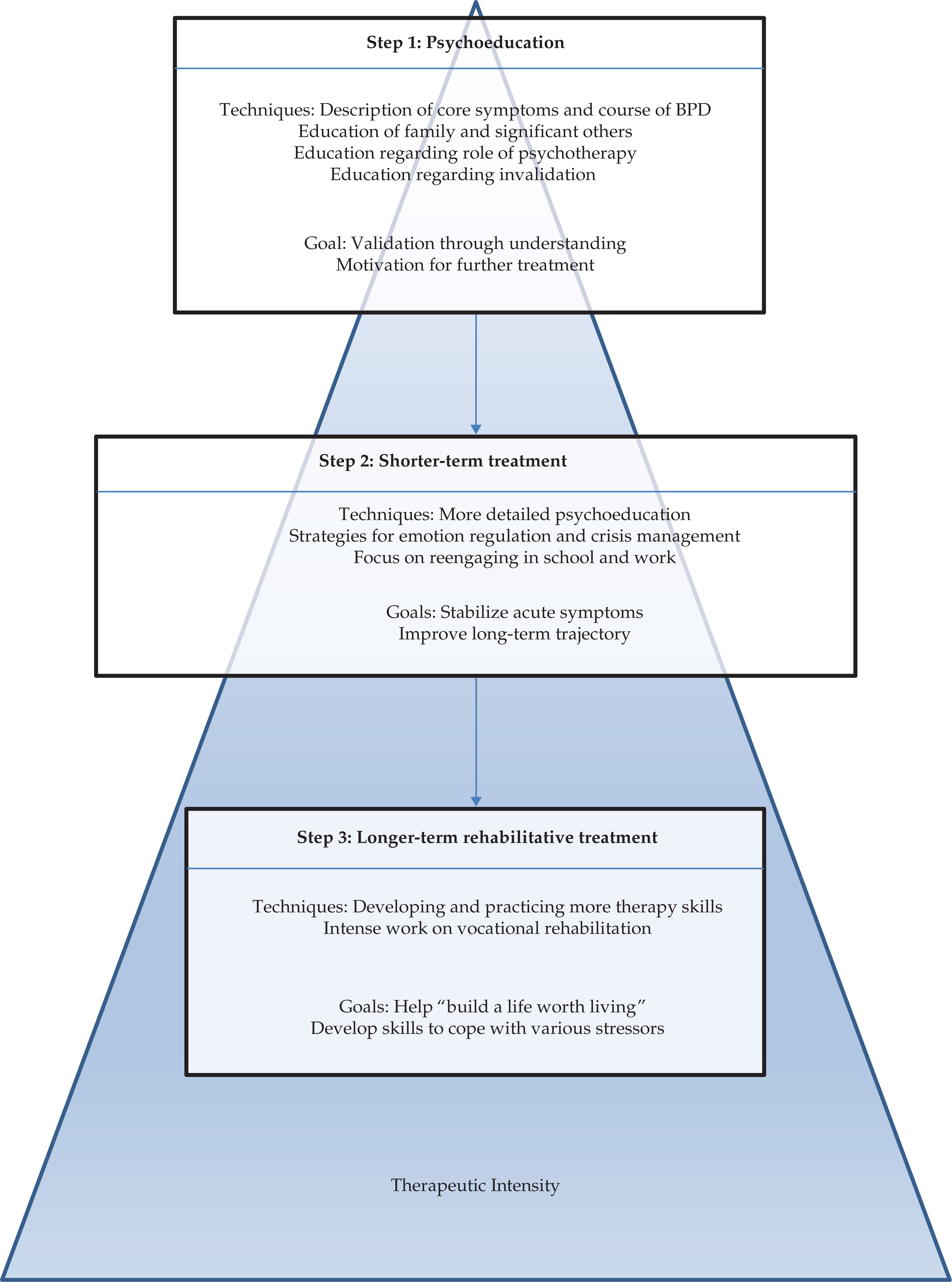
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is typically more structured and shorter duration and centers on identifying thoughts and beliefs and how they impact feelings and behaviors. The therapist helps individuals label and challenge these thoughts and beliefs, and often homework is assigned to identify and counter these as they occur in their daily life.
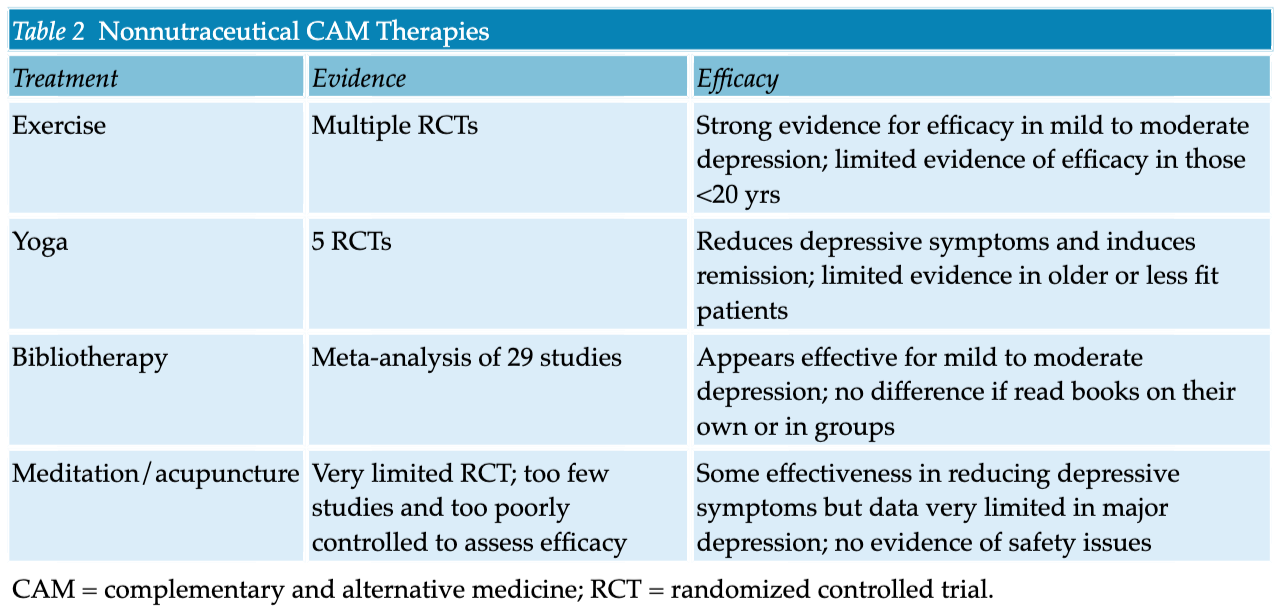
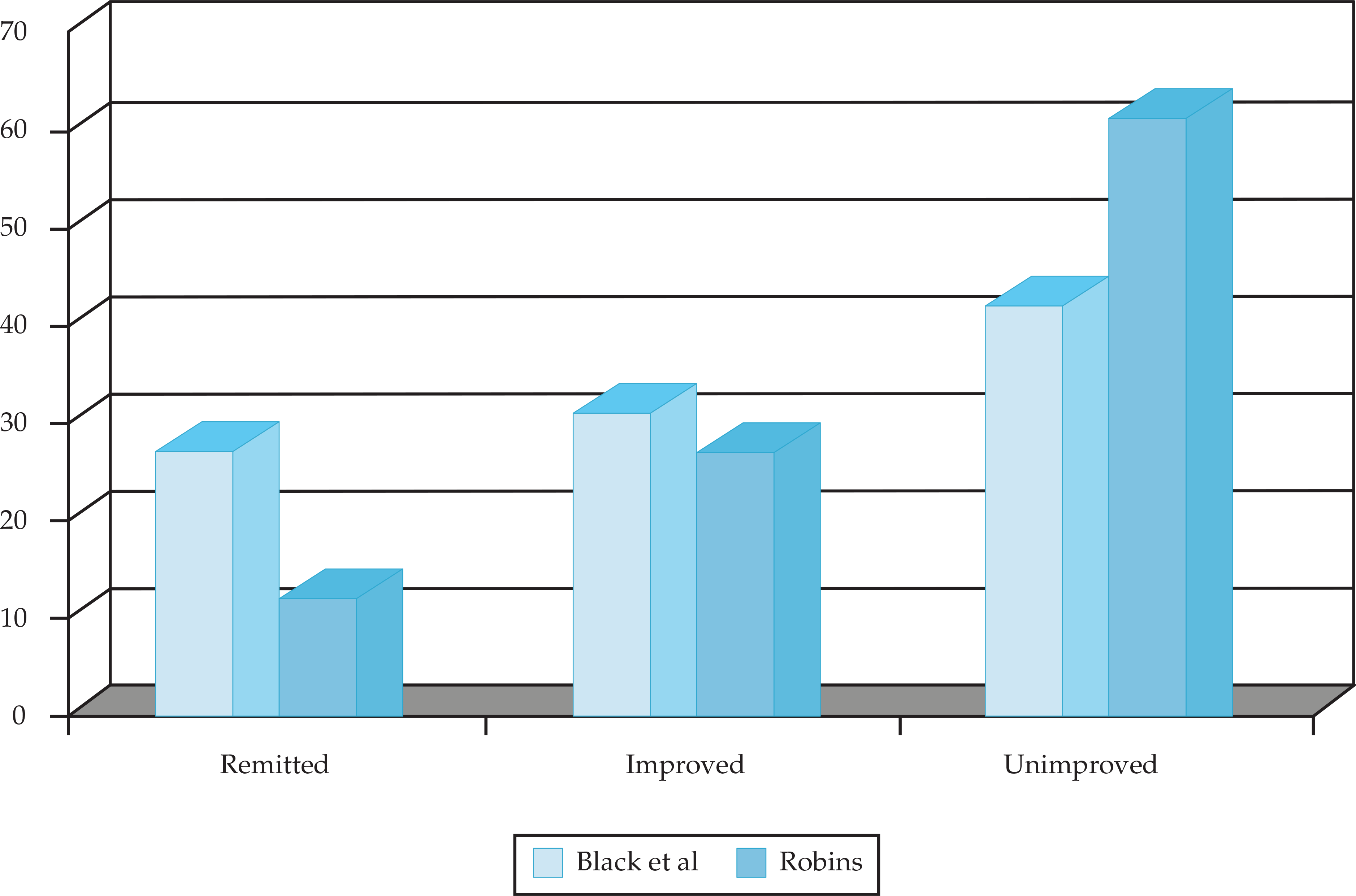
- All guidelines agree that an antidepressant trial should be a minimum of 4 weeks and up to 8 to 12 weeks at an adequate duration and dose. Even with dozens of antidepressant therapies on the market, overall response rates are still suboptimal, and remission rates remain low.
- There are few data on long-term use of antidepressants. Studying relapse and prevention therapies is challenging because of the heterogeneity of the disease and difficulty retaining subjects in long-term antidepressant studies.


.png)







