Subjective Cognitive Impairment and Mild Cognitive Impairment (Predementias)
- One in seven Americans is above the age of 65, and in the next 40 years, that number is expected to jump to nearly one in four. Older adulthood is a period when many individuals begin to exhibit difficulties in cognitive functioning, especially with memory and performing activities of daily living.
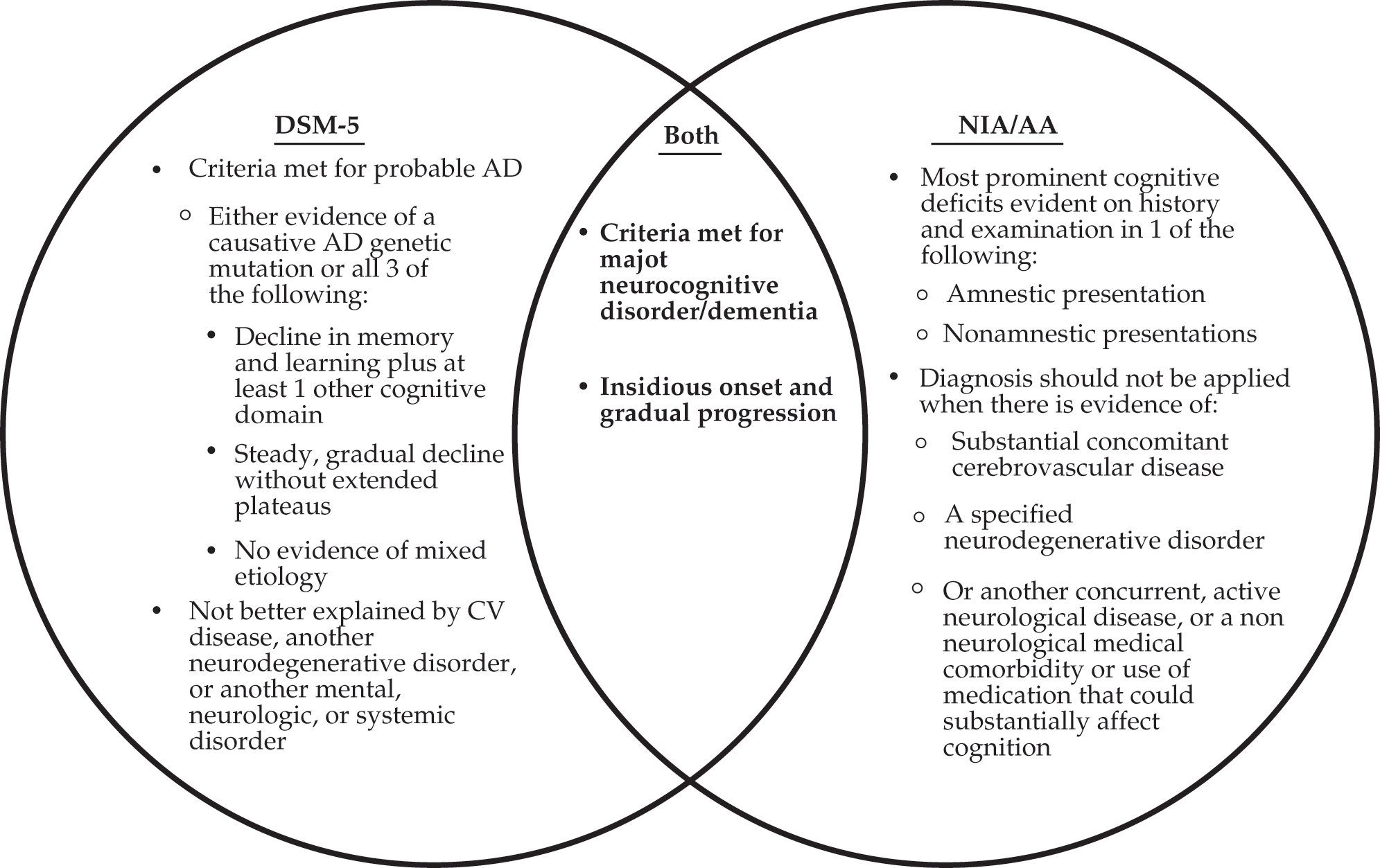
- With the introduction of the DSM-5, changes were made to the nomenclature of the NCDs, as highlighted here. Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) was replaced by the new term mild neurocognitive disorder. Dementia was replaced by the new term major neurocognitive disorder.
- AD is the most prevalent variant of the major NCDs, comprising 60 to 80% of all cases. In addition to the NIA/AA and DSM-5 criteria for dementia or major NCD, patients with AD need to exhibit evidence of a causative genetic mutation from family history/genetic testing or present with all of the following: (1) clear evidence of decline in memory and learning and at least one other cognitive domain, (2) steady, progressive decline in cognition without extended plateaus, and (3) no evidence of mixed etiology.


.png)







