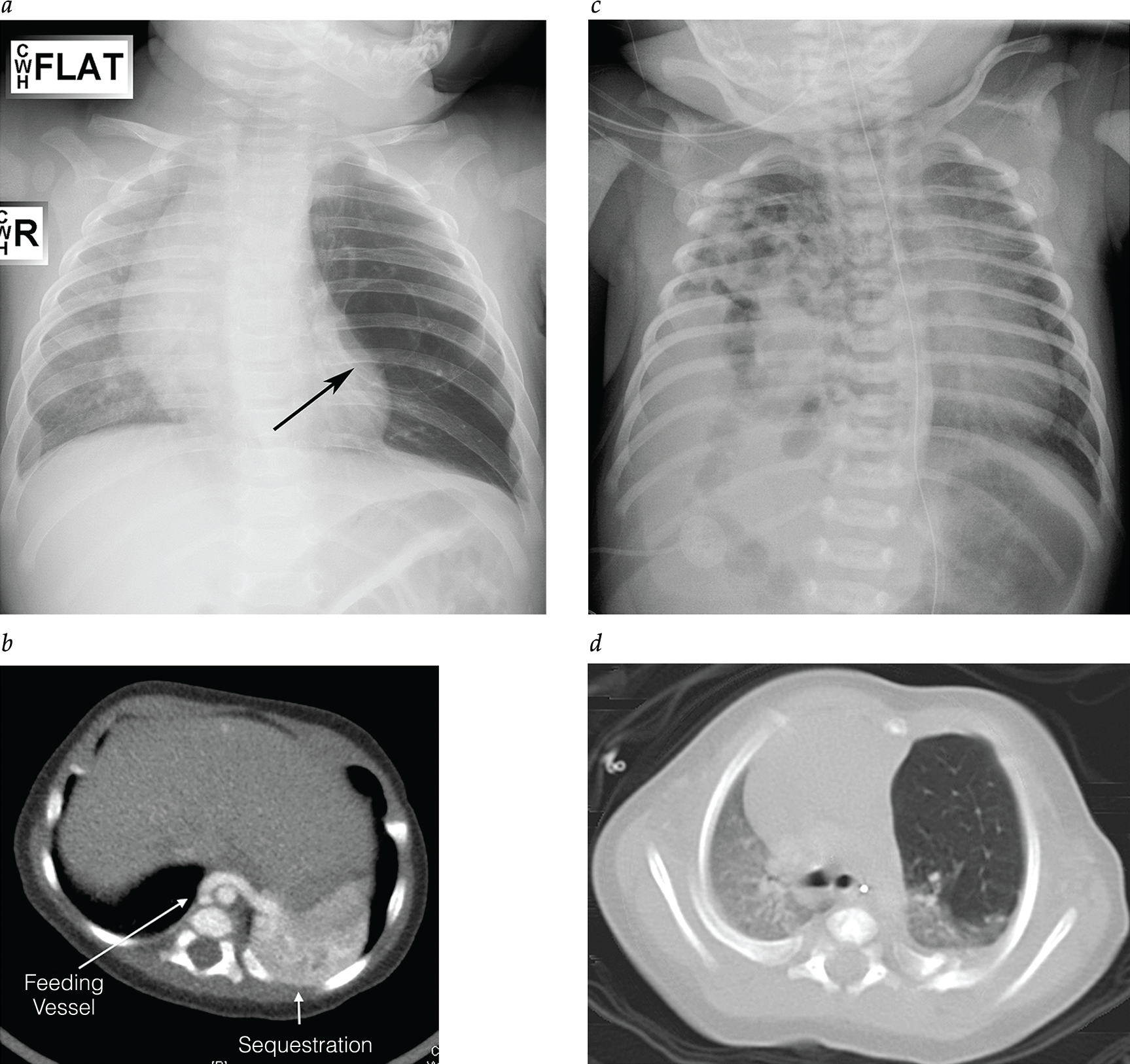
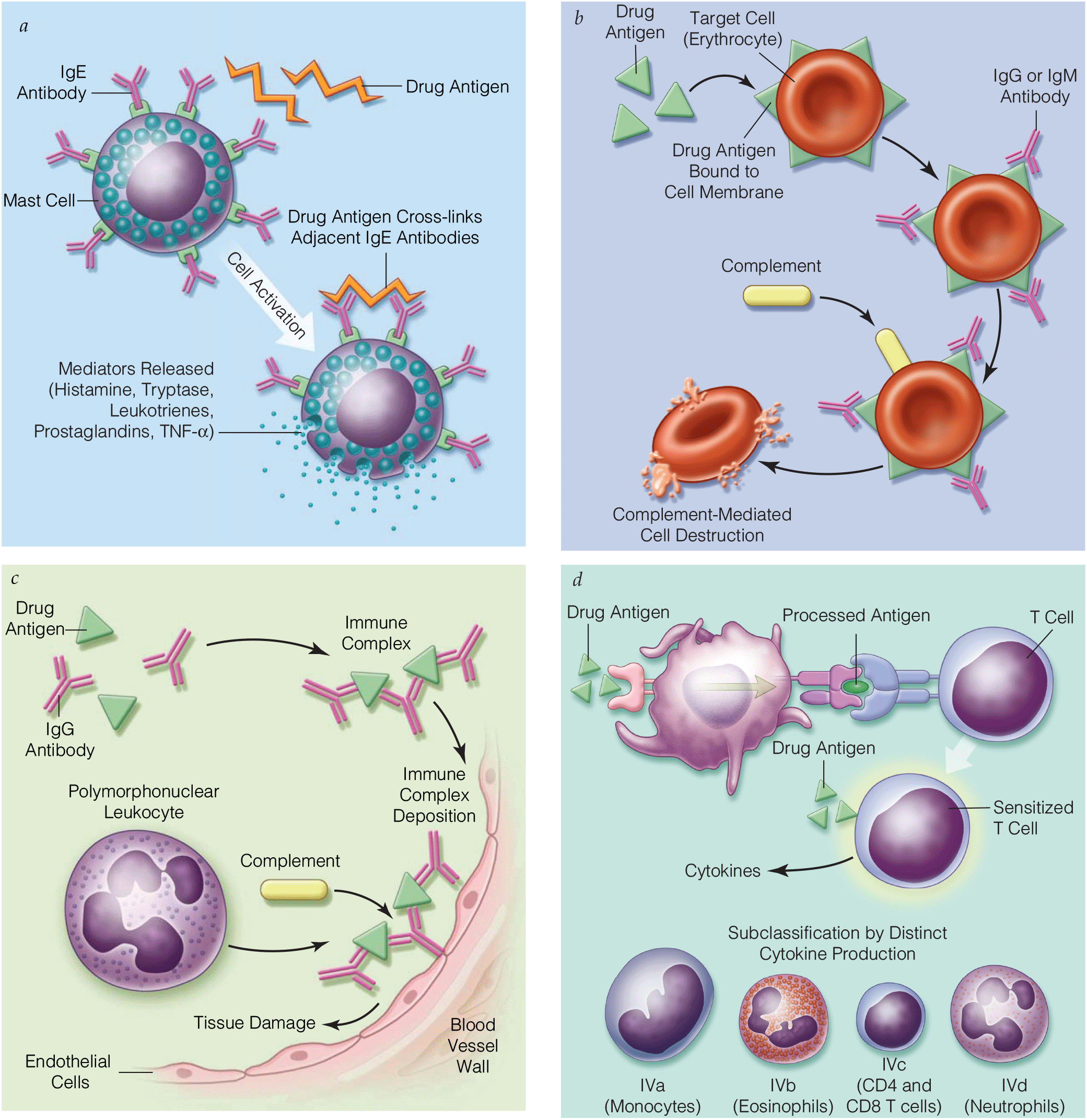
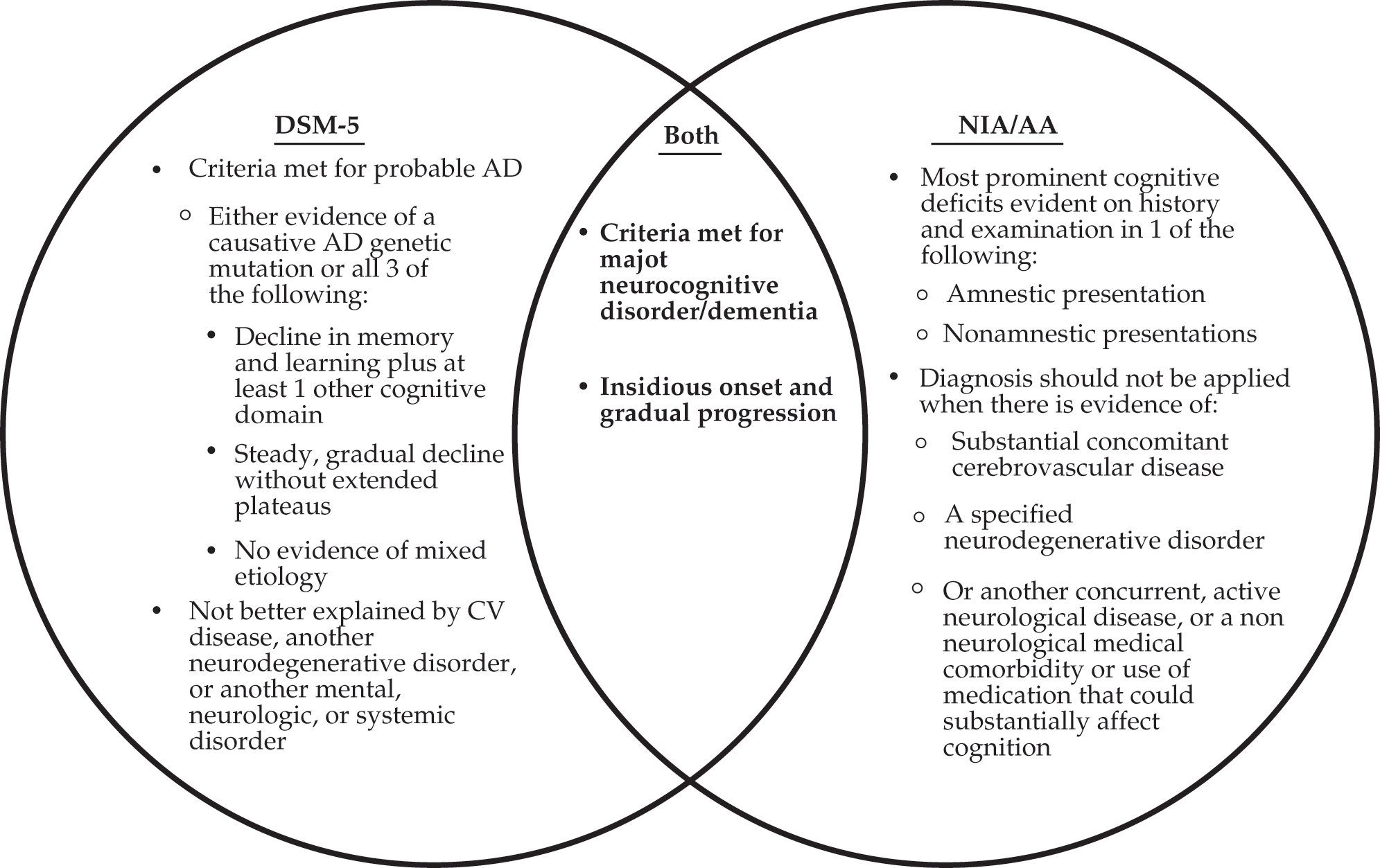
The Pediatric Surgical Patient
- Nasogastric tube feedings are often employed for the early stages of postoperative feeding in infants to ensure adequate nutrition. In general, feeding is begun after the resolution of postoperative ileus. Initially, small volumes of rehydration fluid are given orally or via a gastrostomy tube. If these are tolerated, the feedings are increased gradually until the nutritional goals are reached.
- The laparoscopic approach for abdominal testes is safe and cost-effective; it allows for both localization and surgical treatment, minimizing the use of preoperative imaging for localization of the testicle. Orchiopexy is performed in one or two stages depending on the anatomic localization of the testicle and feasibility of mobilization of the spermatic vessels. Orchiectomy is indicated when an atrophic or hypoplastic testicle is encountered.
- Babies with CDH require immediate resuscitation, correction of acidosis, and, in most cases, endotracheal intubation. Placement of an orogastric tube can help decompress the GI tract. Once the patient is relatively stable, surgical intervention should be delayed to allow time for the pulmonary hypertension to improve.



.png)






