- Pediatric skin conditions are the third most common reason for presentation in the ED for children
- Suspected Rocky Mountain spotted fever should be treated immediately, before laboratory confirmation, as untreated cases can progress to serious illness or death
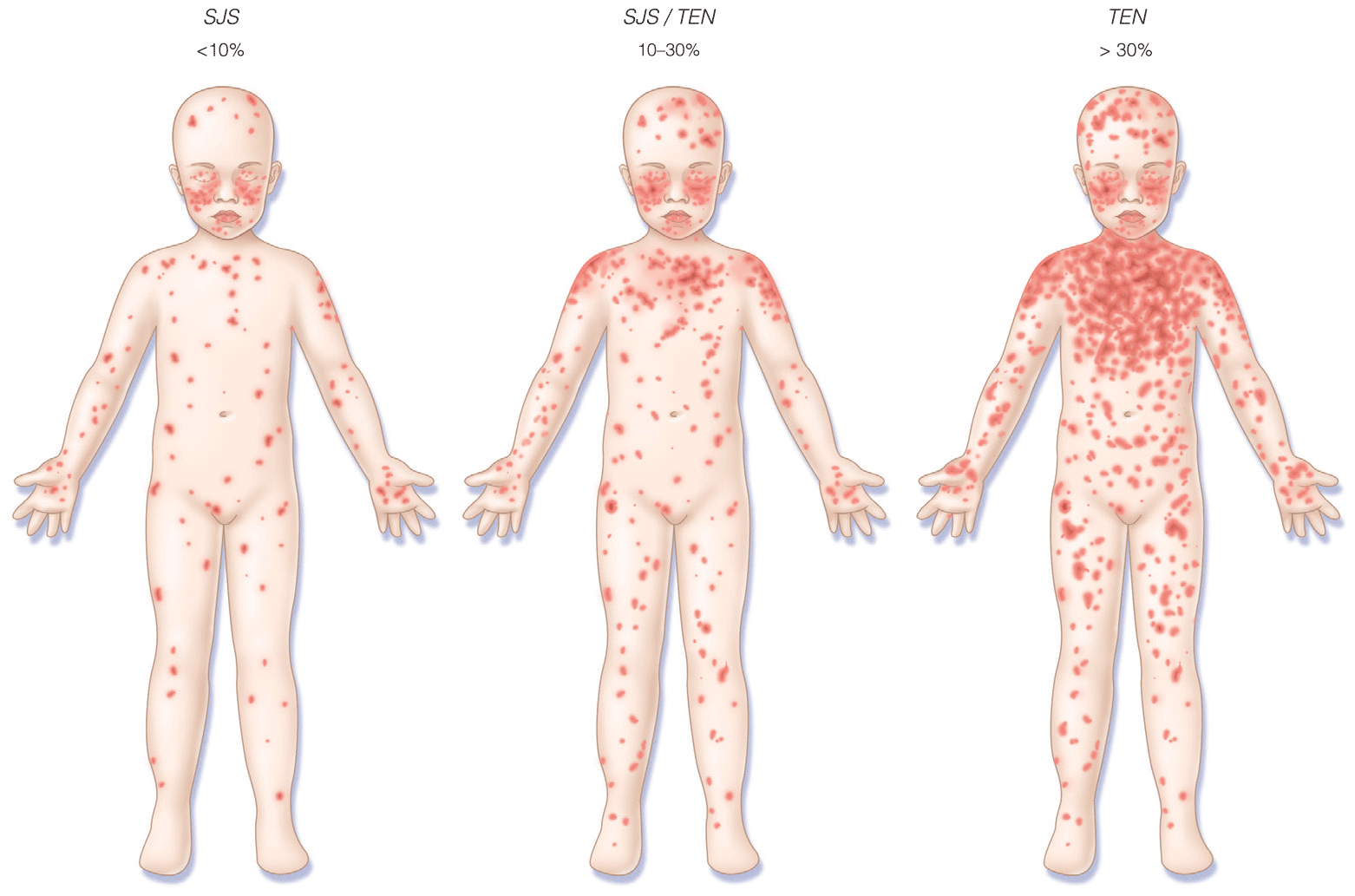
- Clinical scoring systems for necrotizing fasciitis and toxic epidermal necrolysis
Latest Updates
- The DSM-III ushered in the era of criteria-based diagnoses that improved the reliability of the psychiatric diagnostic process.
- The multiaxial diagnostic system was discontinued in the DSM-5 because it had outlived its usefulness and was subject to misuse.
- The DSM-5 emphasized the importance of dimensional assessment, although not as extensively as originally hoped.
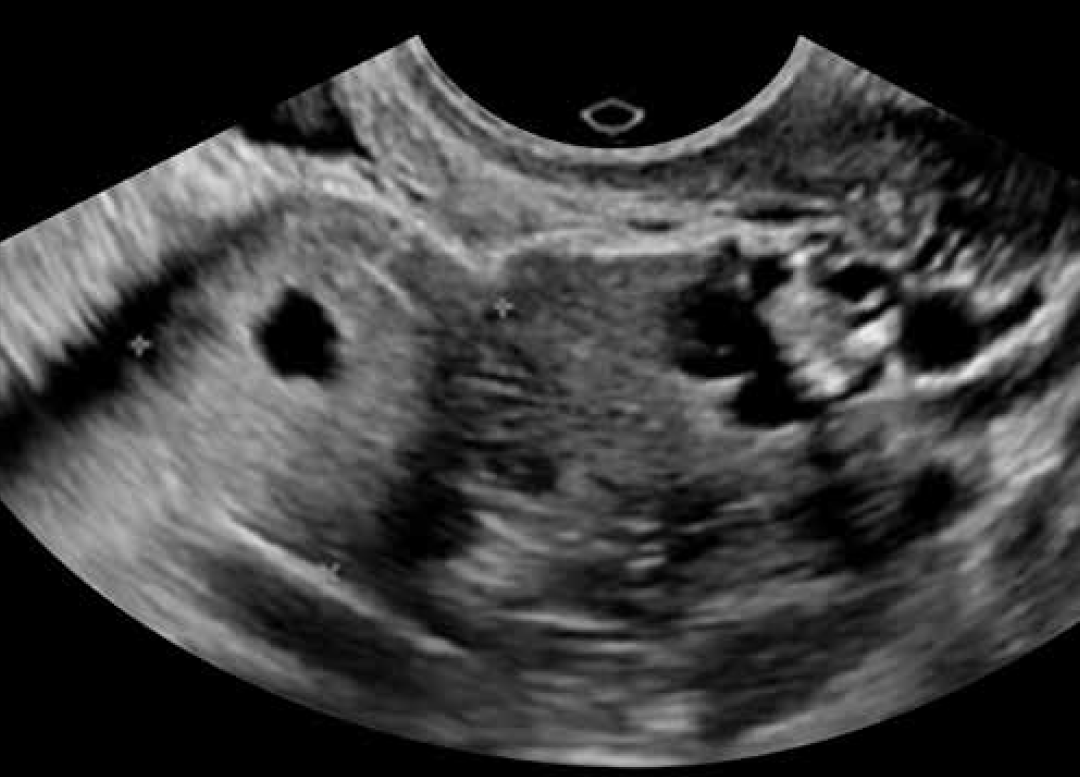
Pregnancy of Unknown Location and Ectopic Pregnancy
- hCG curves have been redefined to help identify abnormal pregnancies, whether in location or viability, and to further broaden the hCG values of a potentially normal pregnancy so as not to inadvertently interrupt a potentially viable pregnancy.
- Risks and benefits of single, two-dose, and multidose methotrexate therapy for medical management of ectopic pregnancy have been studied further and defined.
- Diagnostic accuracy for nontubal ectopic pregnancies is improving, but recommendations regarding treatment options remain controversial.

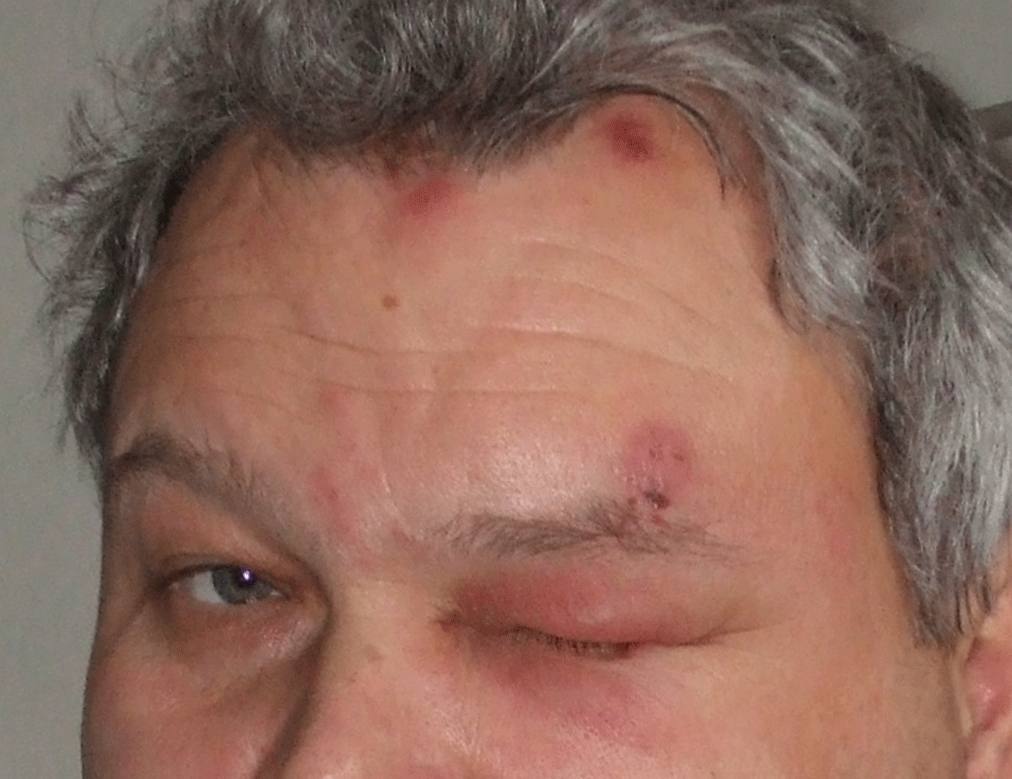
Postherpetic Neuralgia: A Patient’s and a Physician’s Perspective
- Today, most experts in interventional pain management recommend an evidence-based stepladder approach for the management of all patients with PHN that includes an advancing combination of therapeutic strategies as needed on a graduated basis to control pain and anxiety and prevent complications, including suicide.
- The most important immunologic risk factor for herpes zoster and PHN is the decline in cell-mediated immunity to VZV that occurs over time as people age, with an onset around 50 years of age. Although possible, second episodes of zoster are uncommon due to the boosting or anamnestic effect of the first episode of zoster.
- The nonpharmacologic treatment options for PHN include combinations of acupuncture, cryotherapy, heat therapy, and transcutaneous and/or percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. The multimodal nonpharmacologic treatment options for PHN are stratified and compared by their evidence levels.
- The eighth edition of the AJCC TNM staging system has presented new stage groups for thyroid cancer subtypes.
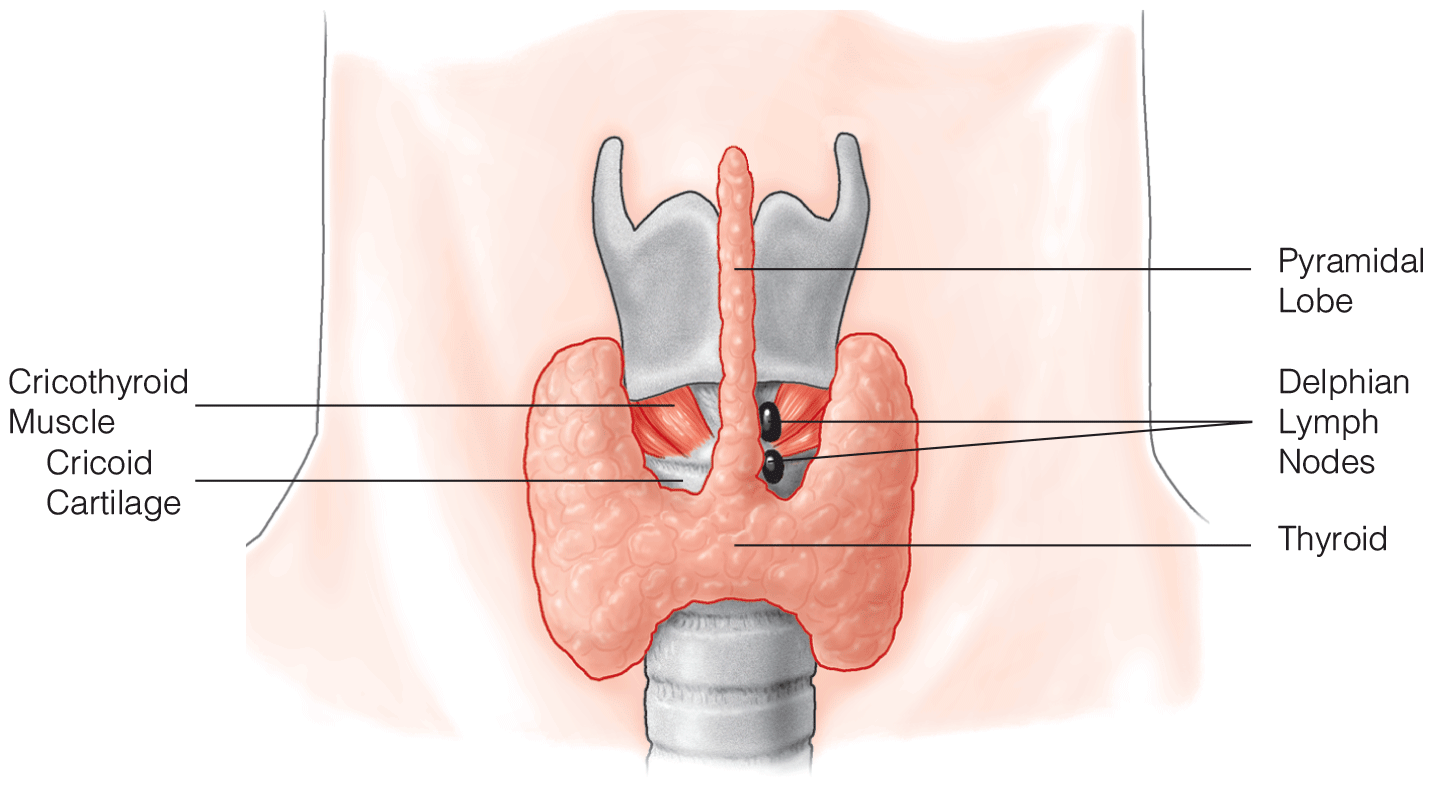
- Intraoperative nerve monitoring is a technique that helps prevent recurrent laryngeal nerve injury during thyroidectomy.
- Minimallyinvasive video-assisted thyroidectomy and minimally invasive nonendoscopic thyroidectomy are new techniques that can be performed with or without gas insufflation; patient perceptions of cosmesis are often improved by the smaller incisions used.

- The eighth edition of the AJCC TNM staging system has presented new stage groups for thyroid cancer subtypes.
- Intraoperative nerve monitoring is a technique that helps prevent recurrent laryngeal nerve injury during thyroidectomy.
- Minimallyinvasive video-assisted thyroidectomy and minimally invasive nonendoscopic thyroidectomy are new techniques that can be performed with or without gas insufflation; patient perceptions of cosmesis are often improved by the smaller incisions used.
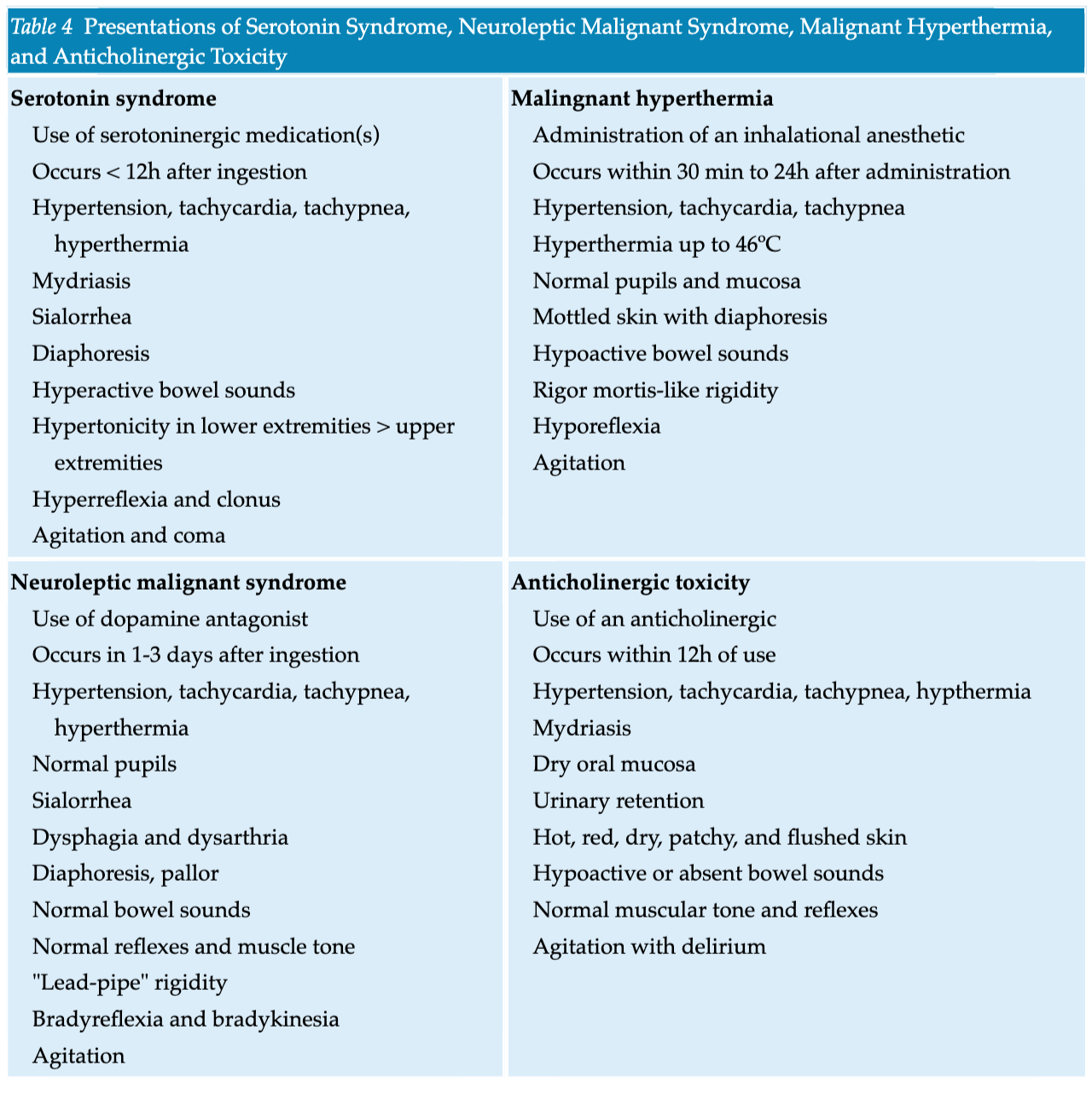
- Currently, there is a belief that the incidence of SS is congruent with the increasing number of serotoninergic agents prescribed and nutraceutical agents, such as St. John’s wort. In 2002, the Toxic Exposure Surveillance System reported 26,633 incidences of exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) that caused significant adverse events in 7,349 patients, with a total of 93 deaths within the year.
- The Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria are simpler, more sensitive, and more specific compared with Sternbach’s criteria. The Hunter criteria require a patient to have taken a serotoninergic agent and to meet one of the following conditions: spontaneous clonus; inducible clonus with agitation or diaphoresis; ocular clonus with agitation or diaphoresis; tremor with hyperreflexia; hypertonia with temperature above 38ºC (100.4°F) with ocular clonus or inducible clonus.
- In the setting of severe hyperthermia (temperature greater than 41°C [105.8°F]), immediate sedation with neuromuscular paralysis and intubation should occur to eliminate excessive muscle activity and thus prevent further complications. Nondepolarizing agents (e.g., vecuronium or atracurium) should be used for paralysis prior to intubation.
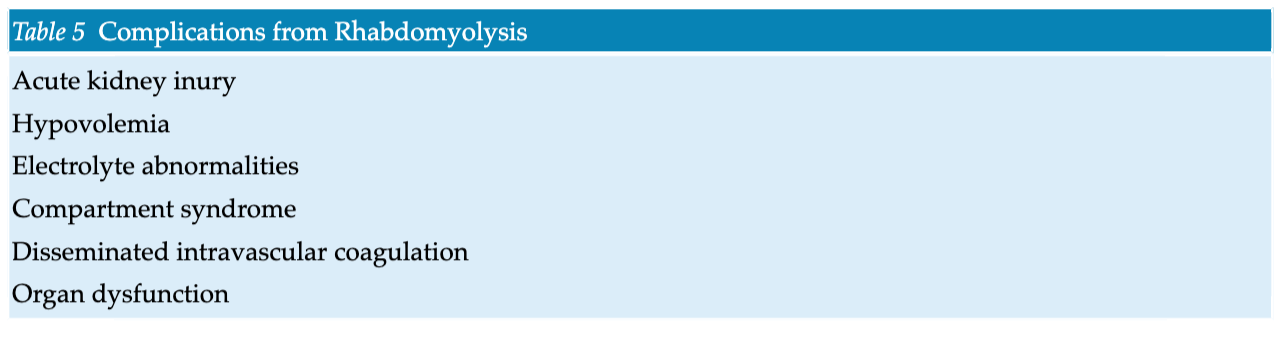
- Development of a model to predict risk of severe AKI or death for patients admitted to hospital with rhabdomyolysis
- Growing consensus for treatment of rhabdomyolysis with isotonic crystalloid solution at a high rate
- Exploration of early initiation of renal replacement therapy for patients with rhabdomyolysis-induced AKI in the absence of conventional indications to allow for faster renal recovery


.png)






