- The directed neurologic examinations for neuromuscular disease focus heavily on the motor and sensory examinations and the cranial nerves involved in motor function, although valuable information may still be learned from other subsections of the neurologic examination. Most neuromuscular diseases do not primarily impact cognitive function, so the mental status testing included in the screening examination is usually sufficient. However, there are exceptions, such as the frontotemporal executive dysfunction that can occur in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, the generalized cognitive dysfunction that can occur in some of the muscular dystrophies, and the alteration in consciousness that can occur in association with respiratory failure due to neuromuscular weakness.
Latest Updates

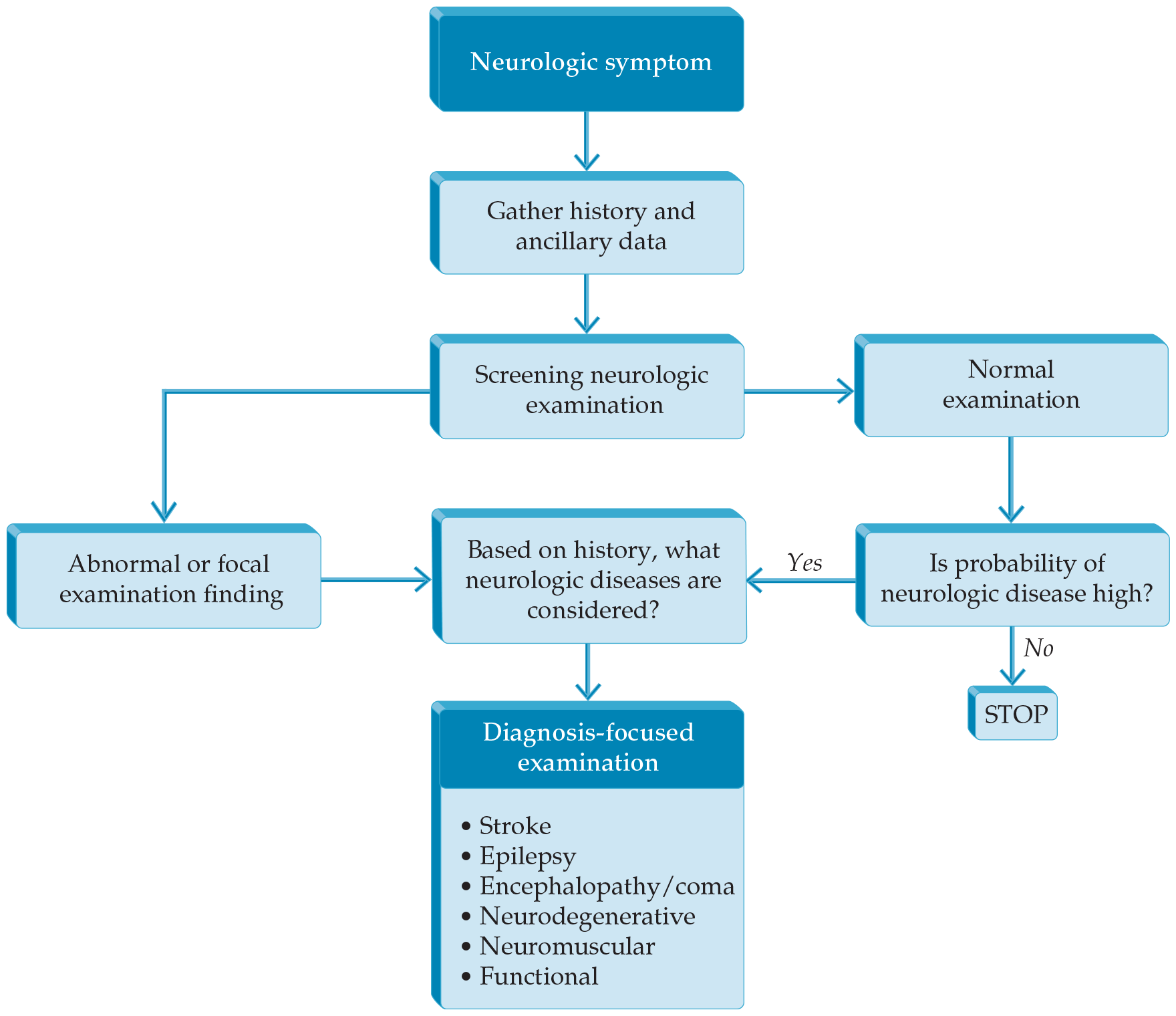

- The directed neurologic examinations for neuromuscular disease focus heavily on the motor and sensory examinations and the cranial nerves involved in motor function, although valuable information may still be learned from other subsections of the neurologic examination. Most neuromuscular diseases do not primarily impact cognitive function, so the mental status testing included in the screening examination is usually sufficient. However, there are exceptions, such as the frontotemporal executive dysfunction that can occur in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, the generalized cognitive dysfunction that can occur in some of the muscular dystrophies, and the alteration in consciousness that can occur in association with respiratory failure due to neuromuscular weakness.

- The directed neurologic examinations for neuromuscular disease focus heavily on the motor and sensory examinations and the cranial nerves involved in motor function, although valuable information may still be learned from other subsections of the neurologic examination. Most neuromuscular diseases do not primarily impact cognitive function, so the mental status testing included in the screening examination is usually sufficient. However, there are exceptions, such as the frontotemporal executive dysfunction that can occur in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, the generalized cognitive dysfunction that can occur in some of the muscular dystrophies, and the alteration in consciousness that can occur in association with respiratory failure due to neuromuscular weakness.
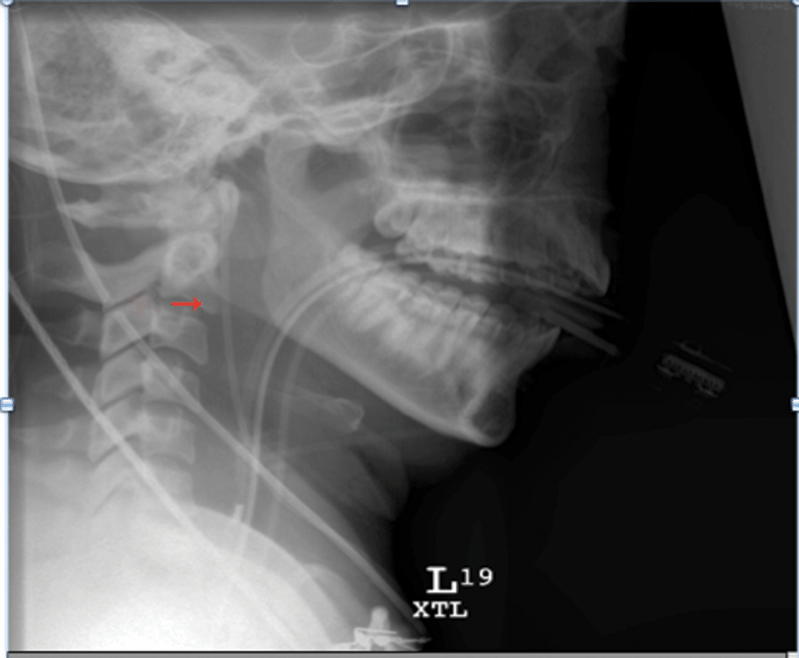
- Cerebral edema and intracranial hypertension are the major cause of early mortality in acute liver failure (ALF)
- Liver transplantation is the only proven liver replacement therapy to reduce mortality
- N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) should be administered to all patients with ALF due to acetaminophen
- New methods for predicting prognosis, such as the Acute Liver Failure Study Group Index, may offer improved sensitivity in predicting the need for liver transplant or death in ALF.
- Correction of coagulopathy with fresh frozen plasma in the absence of bleeding or procedures does not improve survival and may precipitate complications.
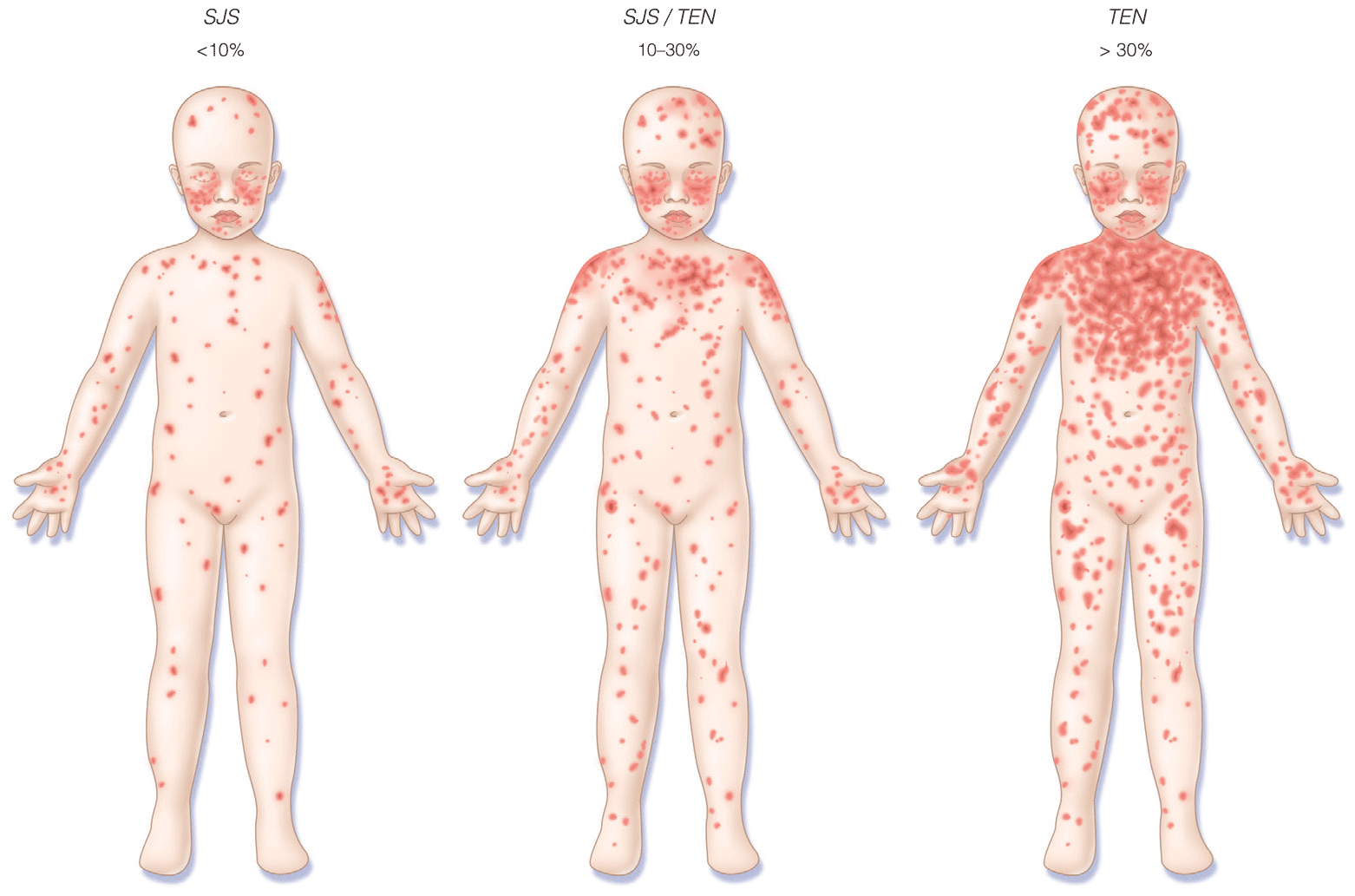
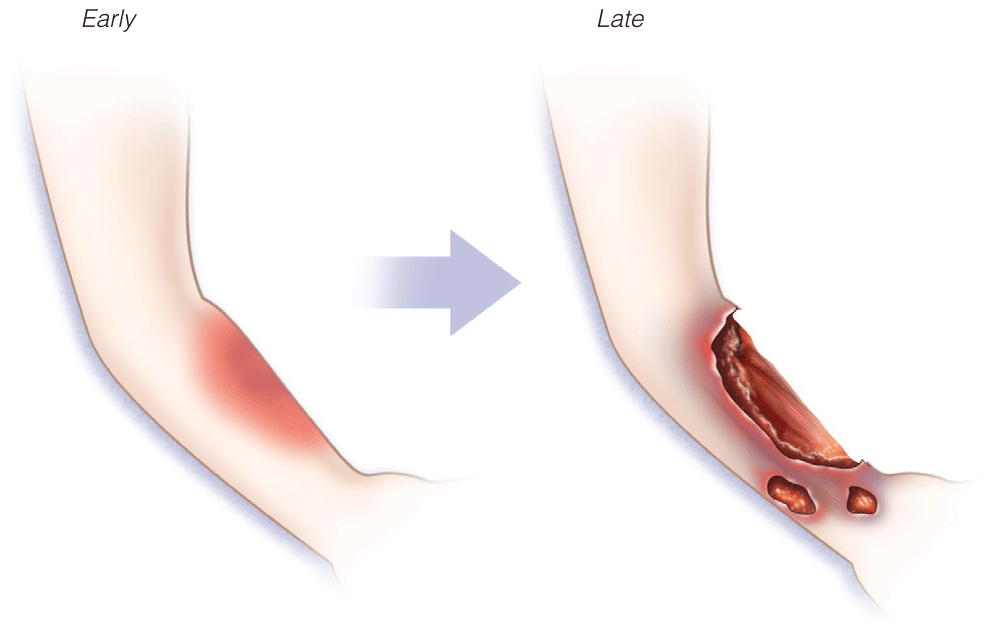
- Pediatric skin conditions are the third most common reason for presentation in the ED for children
- Suspected Rocky Mountain spotted fever should be treated immediately, before laboratory confirmation, as untreated cases can progress to serious illness or death
- Clinical scoring systems for necrotizing fasciitis and toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Pediatric skin conditions are the third most common reason for presentation in the ED for children
- Suspected Rocky Mountain spotted fever should be treated immediately, before laboratory confirmation, as untreated cases can progress to serious illness or death
- Clinical scoring systems for necrotizing fasciitis and toxic epidermal necrolysis
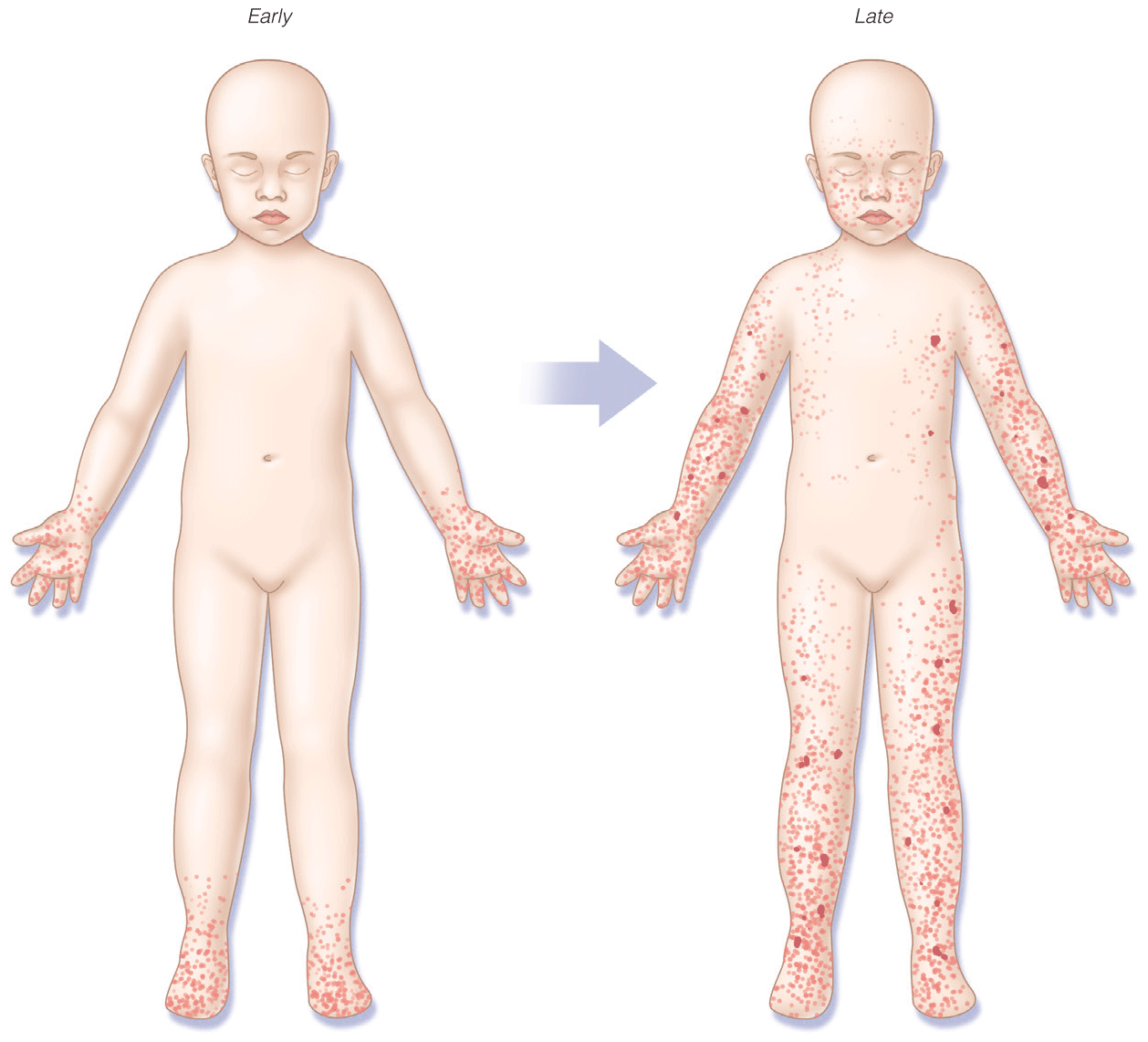
- Pediatric skin conditions are the third most common reason for presentation in the ED for children
- Suspected Rocky Mountain spotted fever should be treated immediately, before laboratory confirmation, as untreated cases can progress to serious illness or death
- Clinical scoring systems for necrotizing fasciitis and toxic epidermal necrolysis

- Pediatric skin conditions are the third most common reason for presentation in the ED for children
- Suspected Rocky Mountain spotted fever should be treated immediately, before laboratory confirmation, as untreated cases can progress to serious illness or death
- Clinical scoring systems for necrotizing fasciitis and toxic epidermal necrolysis


.png)






