Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions
- The treatment of simple exanthematous eruptions is generally supportive. For example, oral antihistamines used in conjunction with soothing baths may help relieve pruritus. Topical corticosteroids are indicated when antihistamines do not provide relief. Systemic corticosteroids are used only in severe cases. Discontinuance of the offending agent is recommended in most cases.
- Sulfonamide antibiotics can cause hypersensitivity syndrome reactions in susceptible persons. The primary metabolic pathway for sulfonamides involves acetylation of the drug to a nontoxic metabolite and renal excretion. An alternative metabolic pathway, quantitatively more important in patients who are slow acetylators, engages the cytochrome P-450 mixed-function oxidase system.
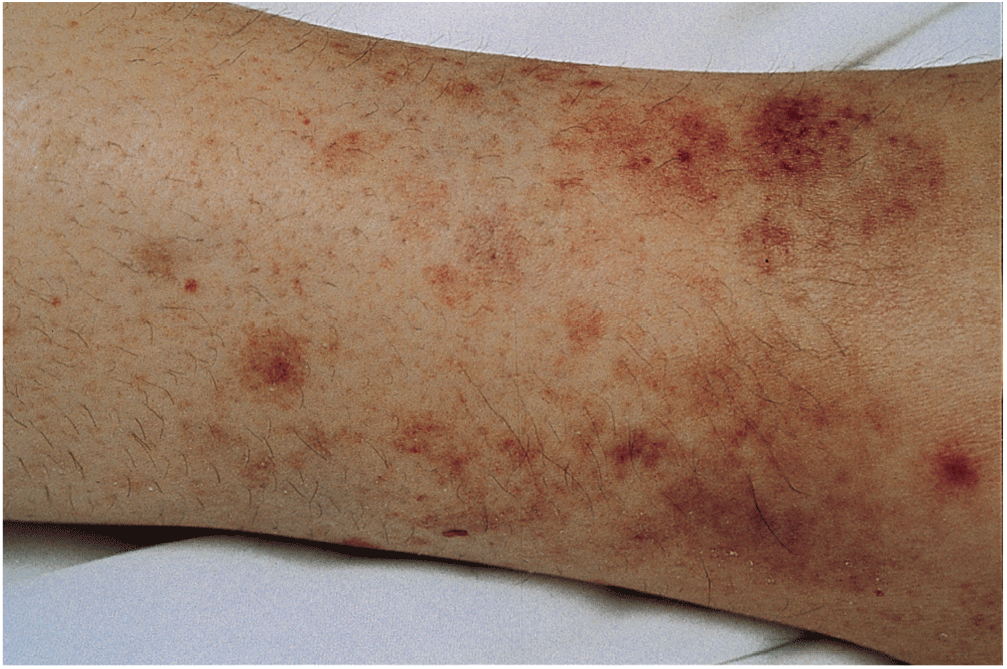
- Differentiation within the spectrum of SJS and TEN depends on the nature of the skin lesions and extent of body surface area involvement. Clinically, reactions of SJS/TEN spectrum are characterized by the presence of the triad of mucous membrane erosions, target lesions, and epidermal necrosis with skin detachment.62 Detachment of less than 10% of the total body surface area is part of the definition of SJS, whereas TEN occurs when there is greater than 30% body surface involvement; intermediate cases have been called SJS/TEN overlap (10 to 30%).


.png)







