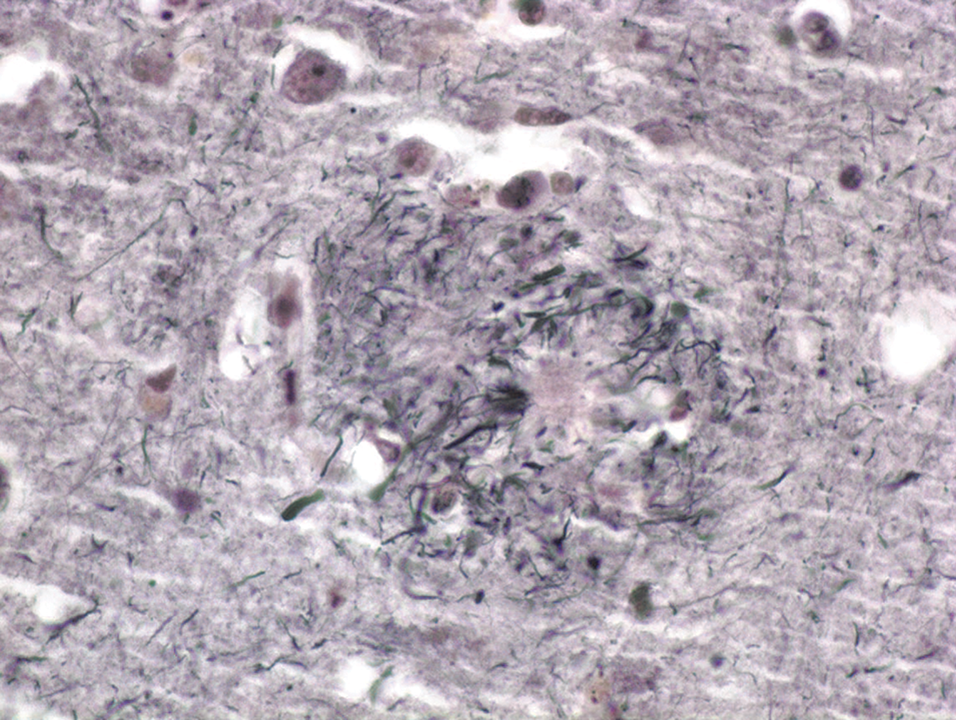
Pathophysiology of Alzheimer Disease
- Amyloid positron emission tomography (PET) has greatly expanded our knowledge of Alzheimer disease (AD), from its preclinical to its clinical manifestations.
- Tau PET has become available as a research tool and is providing new insights into the evolution of AD.
- A conceptual scheme that classifies the imaging and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of AD into amyloid, tau, and neurodegeneration has been adopted.



.png)






