Clinical Management of Anxiety Disorders
- Identification of major anxiety disorders observed in adults according to the DSM-5
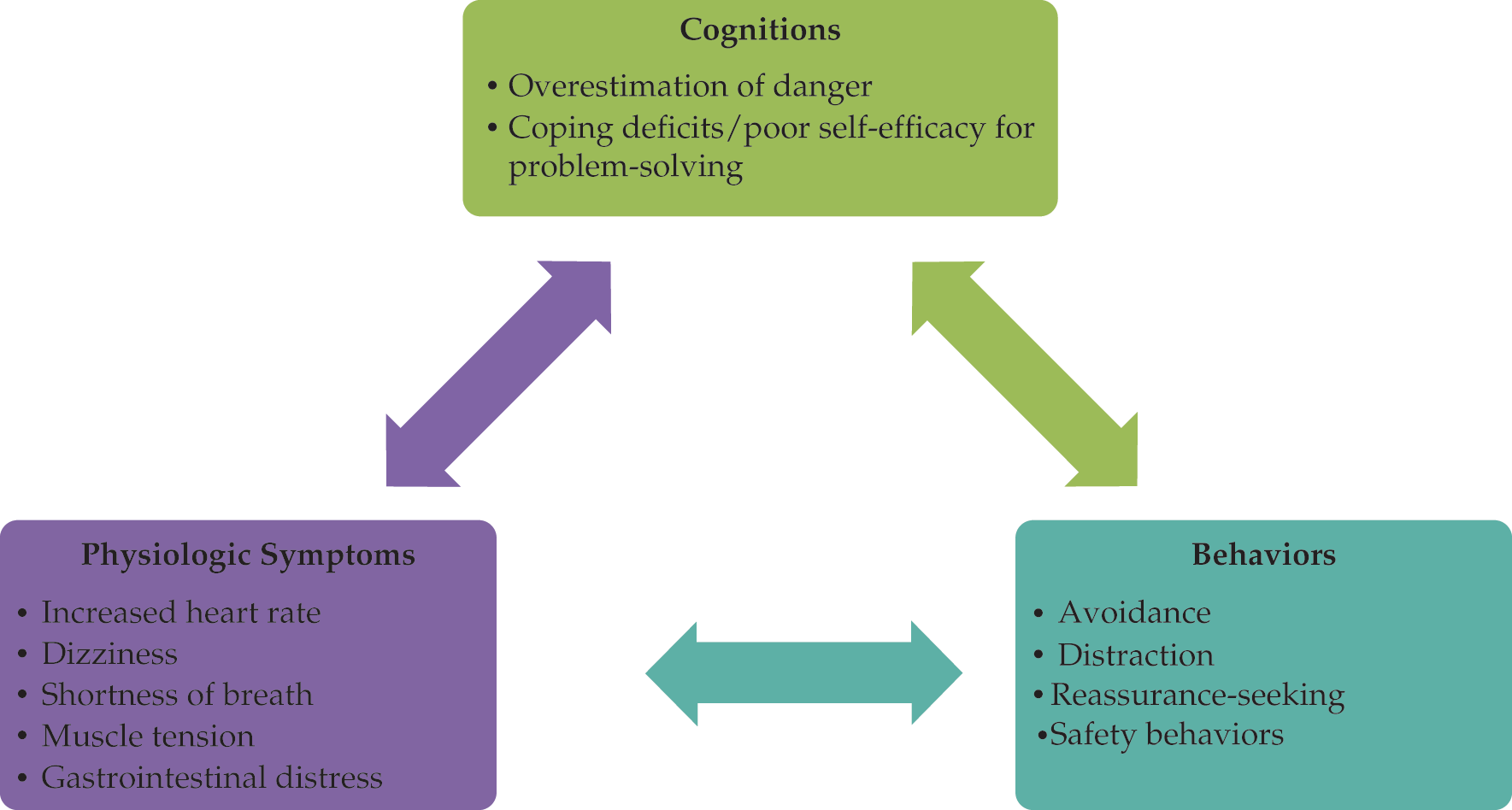
- Description of physiologic, cognitive, and behavioral components of anxiety and their relevance to diagnosis and treatment
- Review of cognitive-behavioral treatments and their efficacy for anxiety disorders in adults
- Review of pharmacologic treatments and their efficacy for anxiety disorders in adults


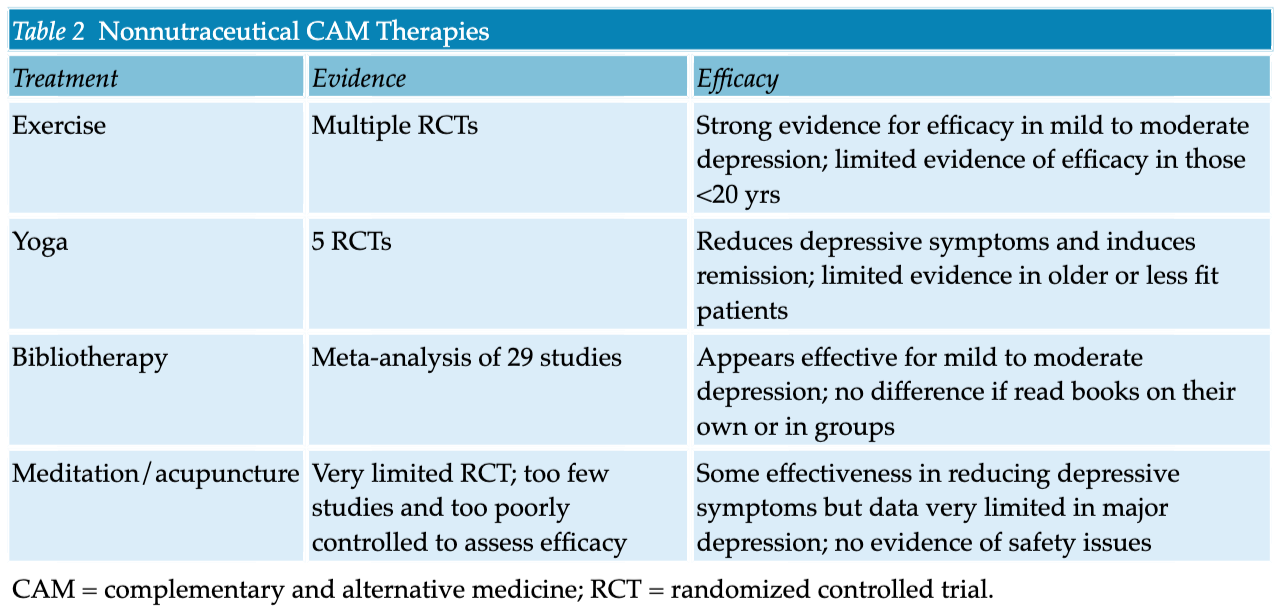
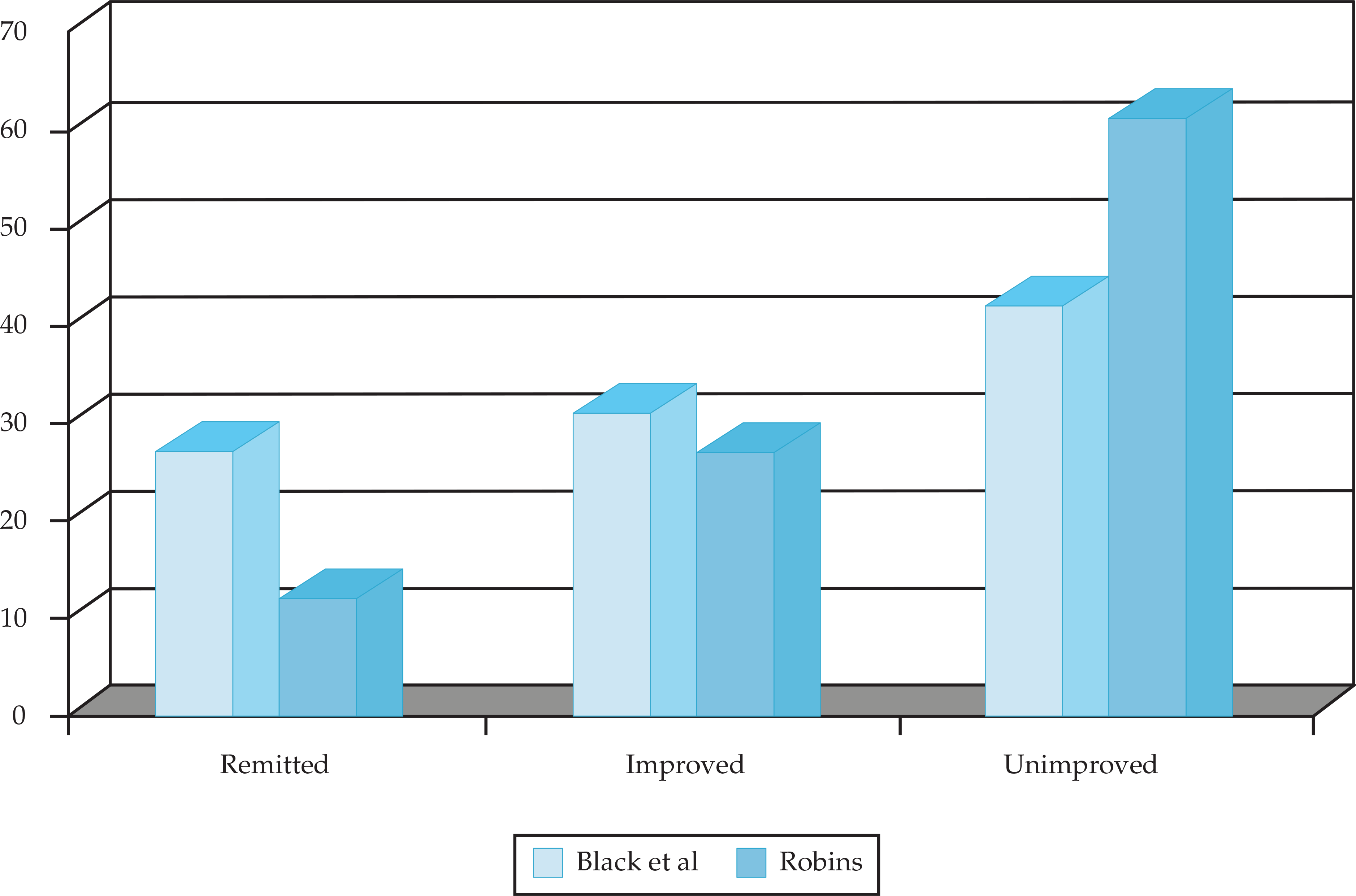
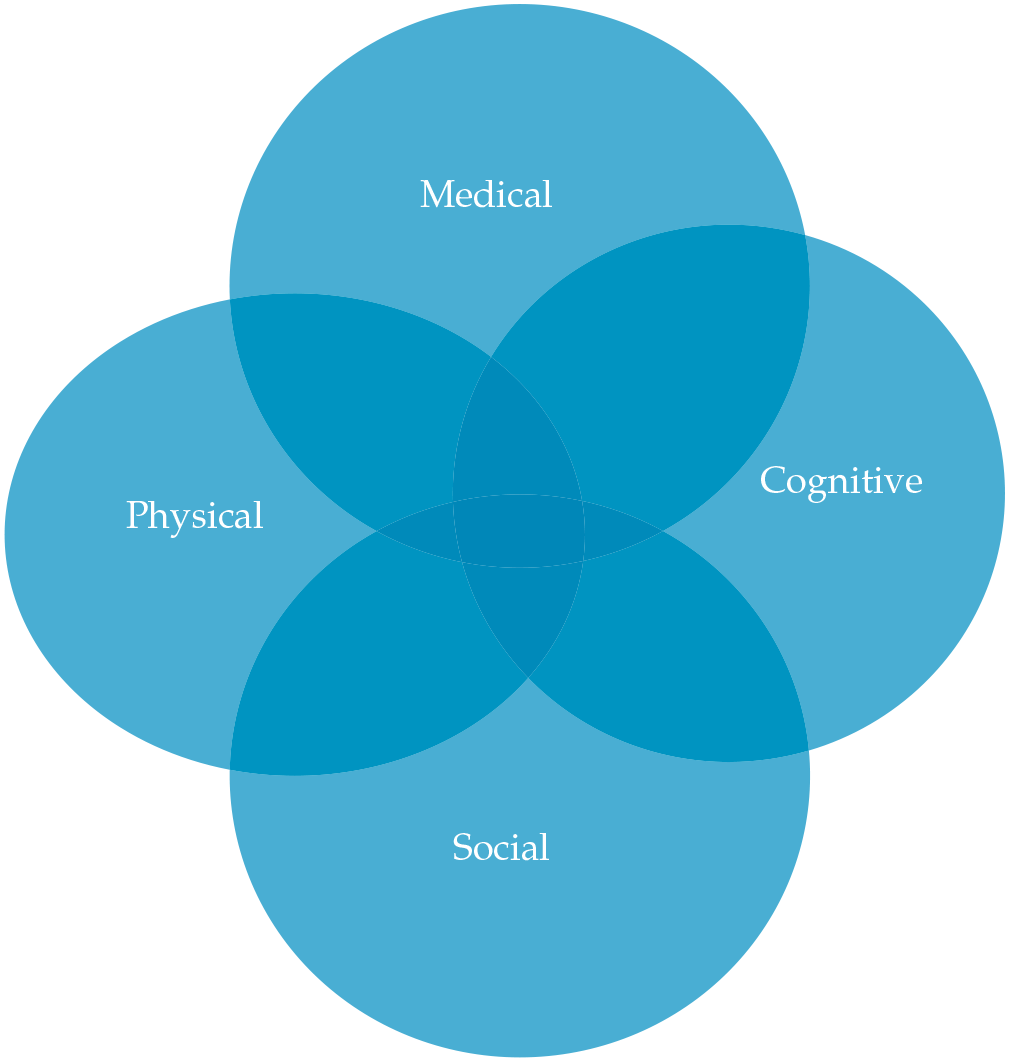


.png)






