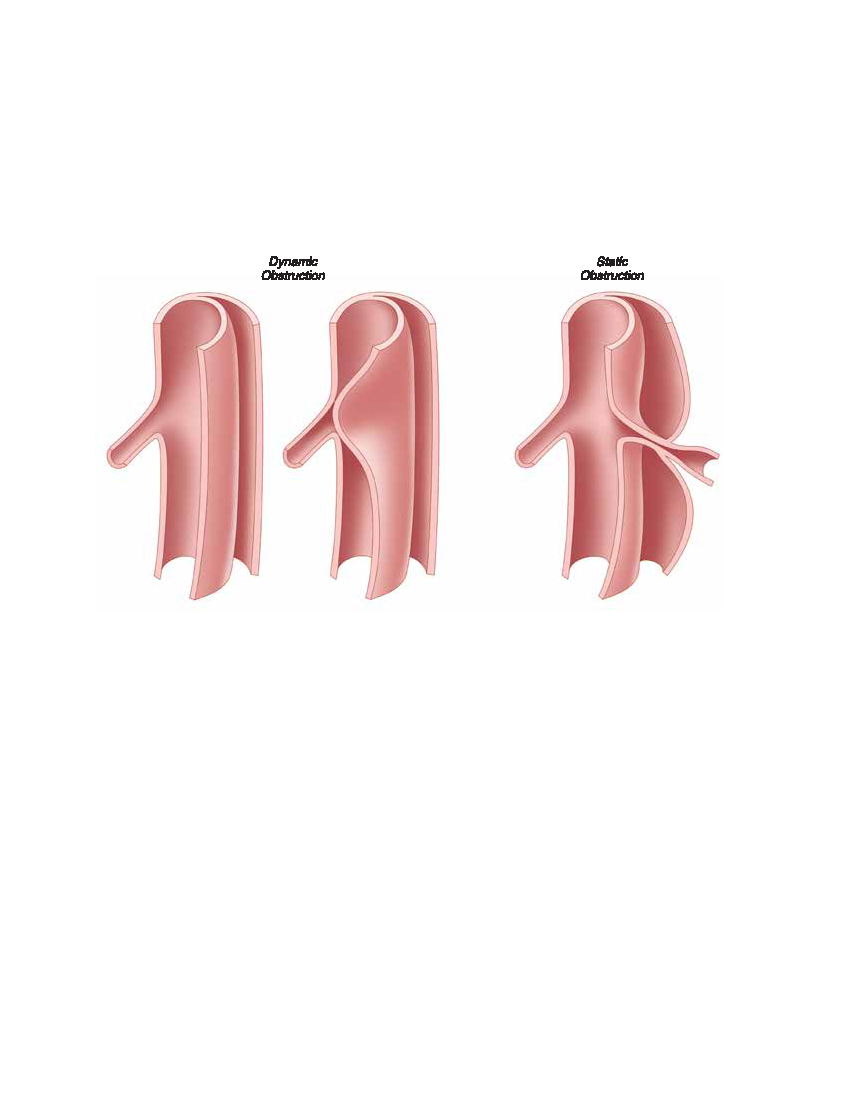
- Surgical treatment of uncomplicated type B aortic dissection
- Endovascular techniques for malperfusion syndrome
- Standard practice of intravascular ultrasonography
- Importance of false lumen thrombosis
- Maneuvers to decrease the risk of spinal cord ischemia in open aortic surgery
Latest Updates
Approach to the Geriatric Patient
- 2016 EAST practice management guideline on prevention of fall-related injuries in the elderly
- 2016 CTF on Preventive Health Care recommendations on screening for cognitive impairment in older adults
- 2016 USPSTF recommendation statement on screening for depression in adults
- 2015 AGS Beers criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults
- 2016 AAO preferred practice guideline on comprehensive adult medical eye evaluation
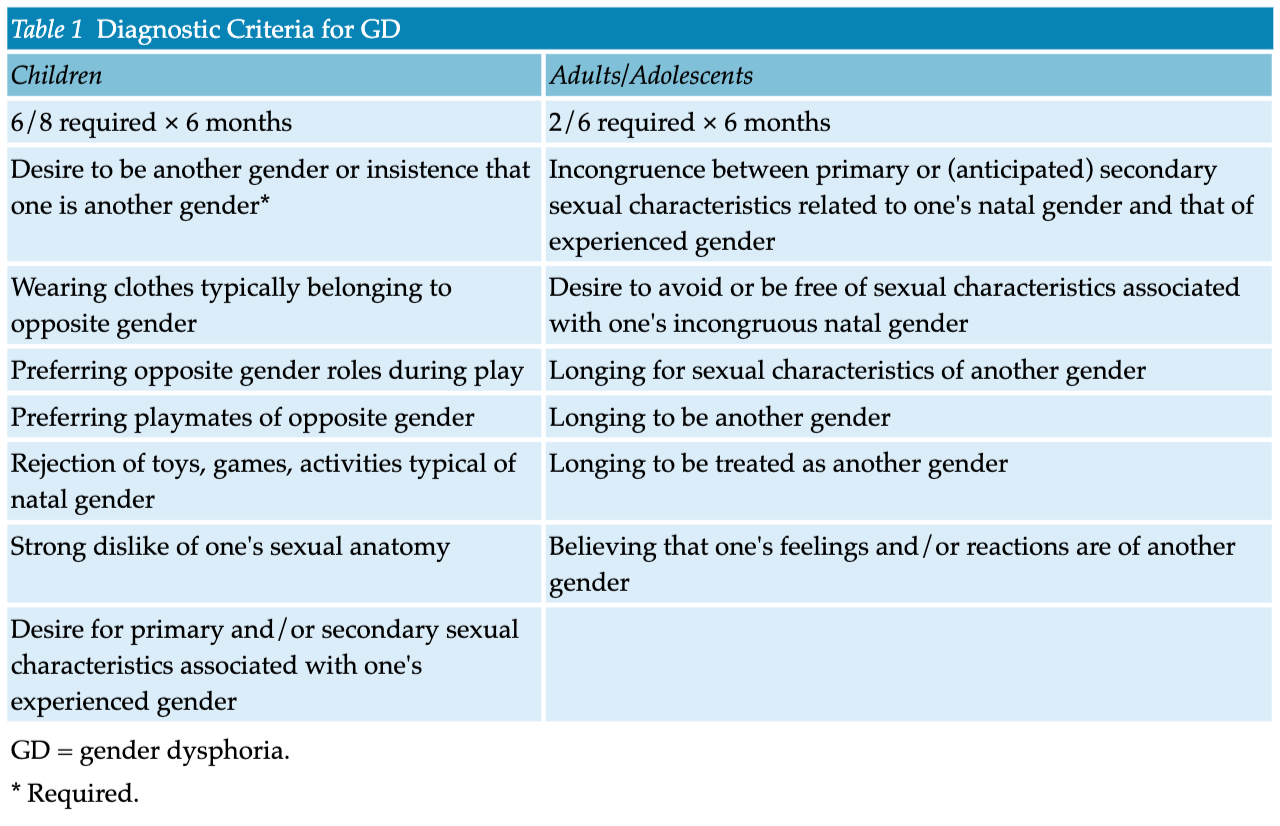
- For children to be diagnosed with GD, they must meet at least six of eight criteria (for at least 6 months), one of them being a desire to be another gender or insistence that one is another gender
- Patients who do not meet the full criteria for GD (eg, if symptoms last < 6 months) may be given a diagnosis of “other specified gender dysphoria” or “unspecified gender dysphoria”
- Although the etiology of GD is not well understood, various psychosocial and biological theories have been proposed. One theory suggests that in utero exposure to steroid hormones plays a role in the masculinization or feminization of certain brain regions, such as the hypothalamus
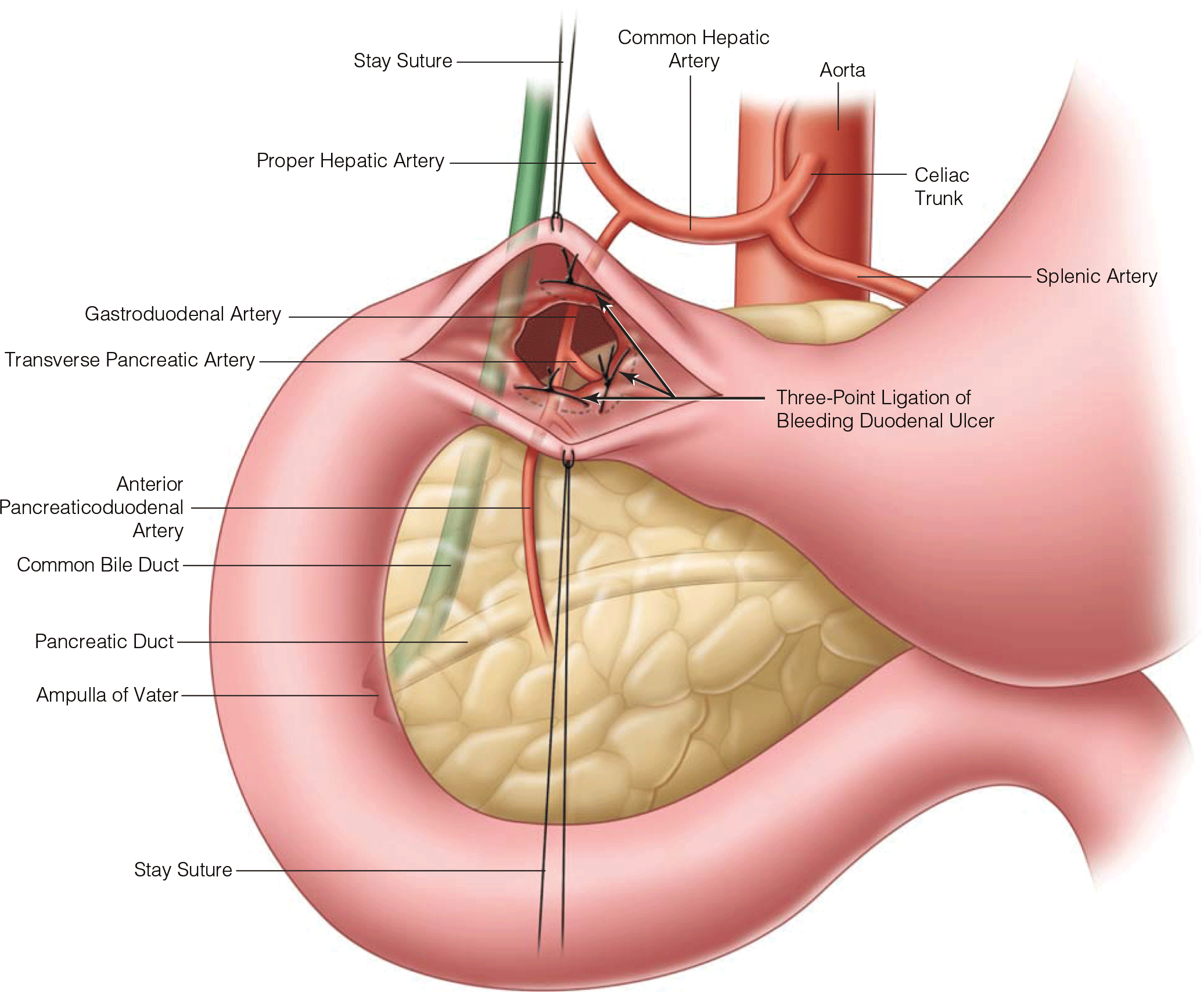
Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Several clinical prediction scores have been developed to risk-stratify patients presenting with upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) and can help guide the sequence of diagnostic tests and subsequent management. The two most commonly used are the Glasgow-Blatchford score and Rockall score. These scoring systems are designed to aid in the identification of patients who will require acute interventions and determine the risk of rebleeding and mortality.
- Endoscopic intervention is beneficial in high-risk patients with UGIB, reducing the rate of rebleeding, the need for surgical intervention, and mortality. Recent advances in the use of combination therapies and newer mechanical means of hemostasis have increased the success of endoscopic management.
- Contrast-enhanced, multiphase computed tomography (CT) techniques have improved dramatically over the last decade. CT serves as an excellent complementary test to endoscopic techniques in the management of the hemodynamically stable patient.
- Transcatheter angiographic embolization is an attractive alternative to surgical intervention in select patients. Advances in catheter-based delivery systems have increased the success rate of angiographic embolization, particularly in patients who have a failed second attempt at endoscopic hemostasis.

- For children to be diagnosed with GD, they must meet at least six of eight criteria (for at least 6 months), one of them being a desire to be another gender or insistence that one is another gender
- Patients who do not meet the full criteria for GD (eg, if symptoms last < 6 months) may be given a diagnosis of “other specified gender dysphoria” or “unspecified gender dysphoria”
- Although the etiology of GD is not well understood, various psychosocial and biological theories have been proposed. One theory suggests that in utero exposure to steroid hormones plays a role in the masculinization or feminization of certain brain regions, such as the hypothalamus

- Antecedents of dissociative amnesia range from massive psychological trauma to seemingly minor stressful life events.
- The memory impairment in dissociative amnesia is most frequently of a retrograde type and preponderantly circumscribed to the episodic-autobiographical memory domain.
- An abrupt loss of both memory for past experiences and personal identity is highly suggestive of the diagnosis of dissociative amnesia.
- Functional neuroimaging in dissociative amnesia often shows changes in brain areas involved in memory processing.
- Neuropsychological testing plays a key role in distinguishing between true and feigned amnesia.

- Antecedents of dissociative amnesia range from massive psychological trauma to seemingly minor stressful life events.
- The memory impairment in dissociative amnesia is most frequently of a retrograde type and preponderantly circumscribed to the episodic-autobiographical memory domain.
- An abrupt loss of both memory for past experiences and personal identity is highly suggestive of the diagnosis of dissociative amnesia.
- Functional neuroimaging in dissociative amnesia often shows changes in brain areas involved in memory processing.
- Neuropsychological testing plays a key role in distinguishing between true and feigned amnesia.
- Zika virus: Delayconception if potential exposure: 8 weeks: females or 3 months: males
- Subclinical hypothyroid: Treatment is associated with improved pregnancy outcomes when TSH levels are above 4 mIU/L.
- Tubal patency: Hysterosalpingo-contrast sonography was recently introduced as an additional screening method to assess tubal patency.


.png)







