Pediatrics: Cystic Fibrosis in Childhood and Adolescence
- As patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) are living longer, gastrointestinal issues are becoming more evident.
- The CFTR genotype determines the CFTR phenotype.
- One episode of distal intestinal obstruction syndrome (DIOS) increases the risk of a future episode.
- In differentiating DIOS from constipation in CF, it is important to use an abdominal x-ray.
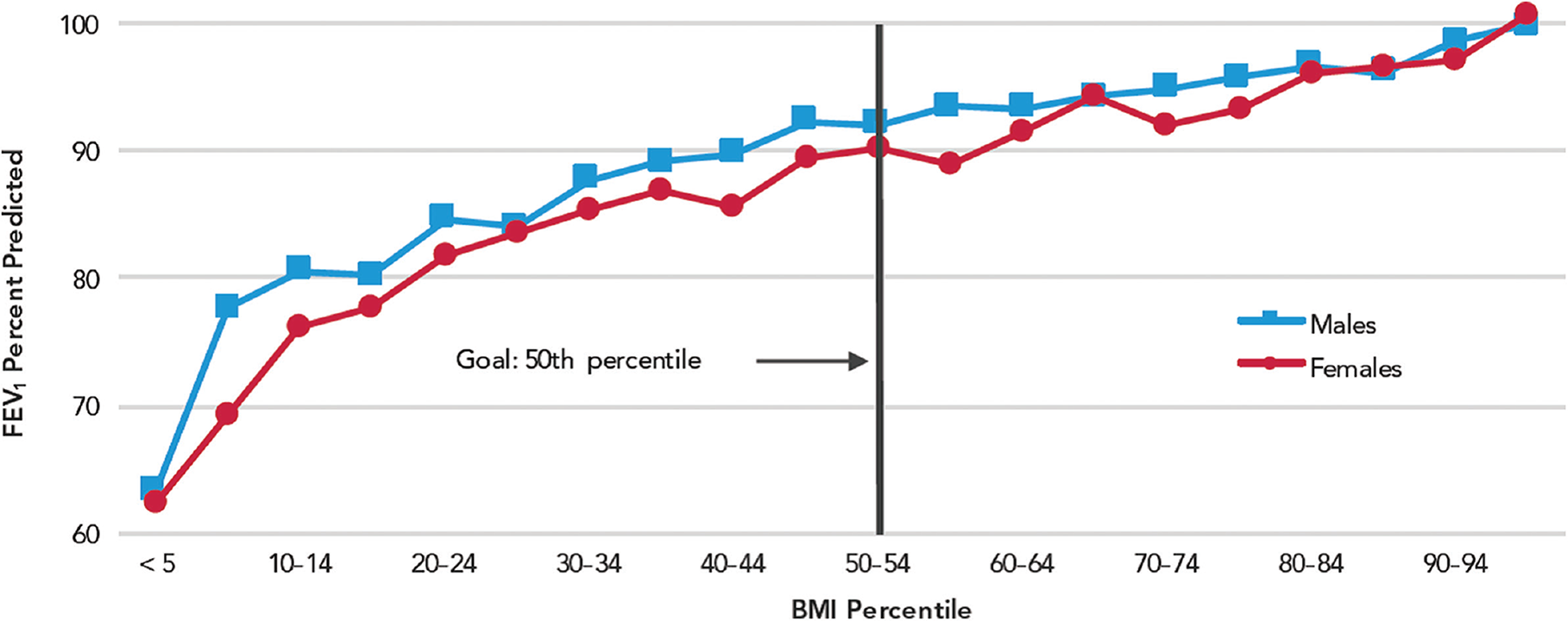
- CFTR potentiator and corrector medications may be helpful for nutritional outcomes in CF patients.


.png)







