The Risk Of Surgery In Patients With Liver Disease 2
- Presents extensive evidence-based appreciation of the risks of operating on patients with some non-cirrhotic liver disease, particularly various forms of acute hepatitis —especially alcoholic—acute liver failure, steatosis, and steatohepatitis, and rare entities such as Wilson disease.
- Substantiates the relative safety of minimally invasive surgery in patients with mild or moderately advanced cirrhosis, compared to open surgery, for many operations.
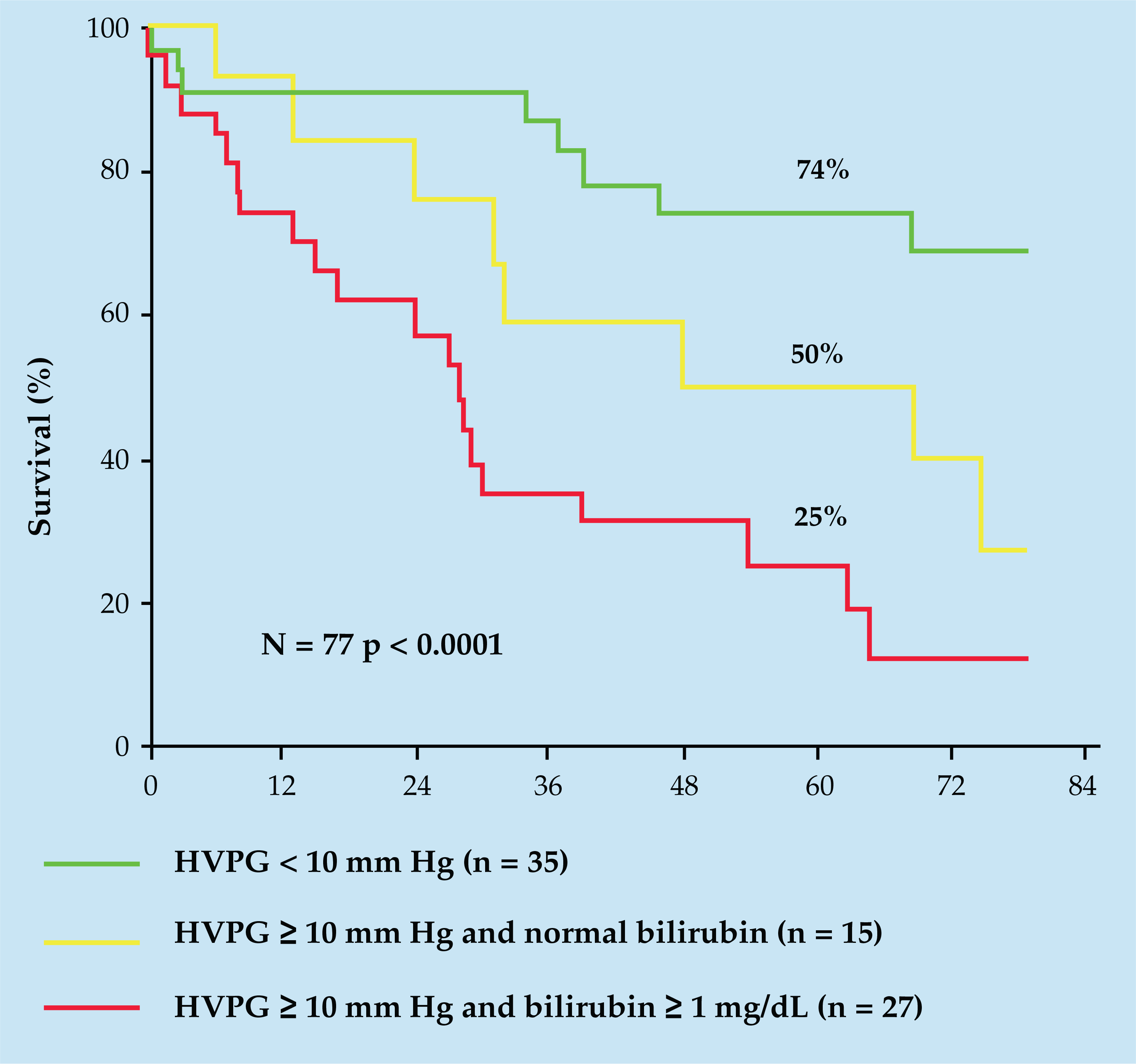
- Amasses numerous clinical results that link the outcomes of a wide spectrum of surgical operations in patients with cirrhosis to indices of severity of liver injury, especially the Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) score and class, and/or the model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score.
- Describes a decision tree devised to guide clinicians in determining whether or not to proceed to surgery in any given patient with acute or chronic liver disease, depending on the severity of the liver disease.


.png)







