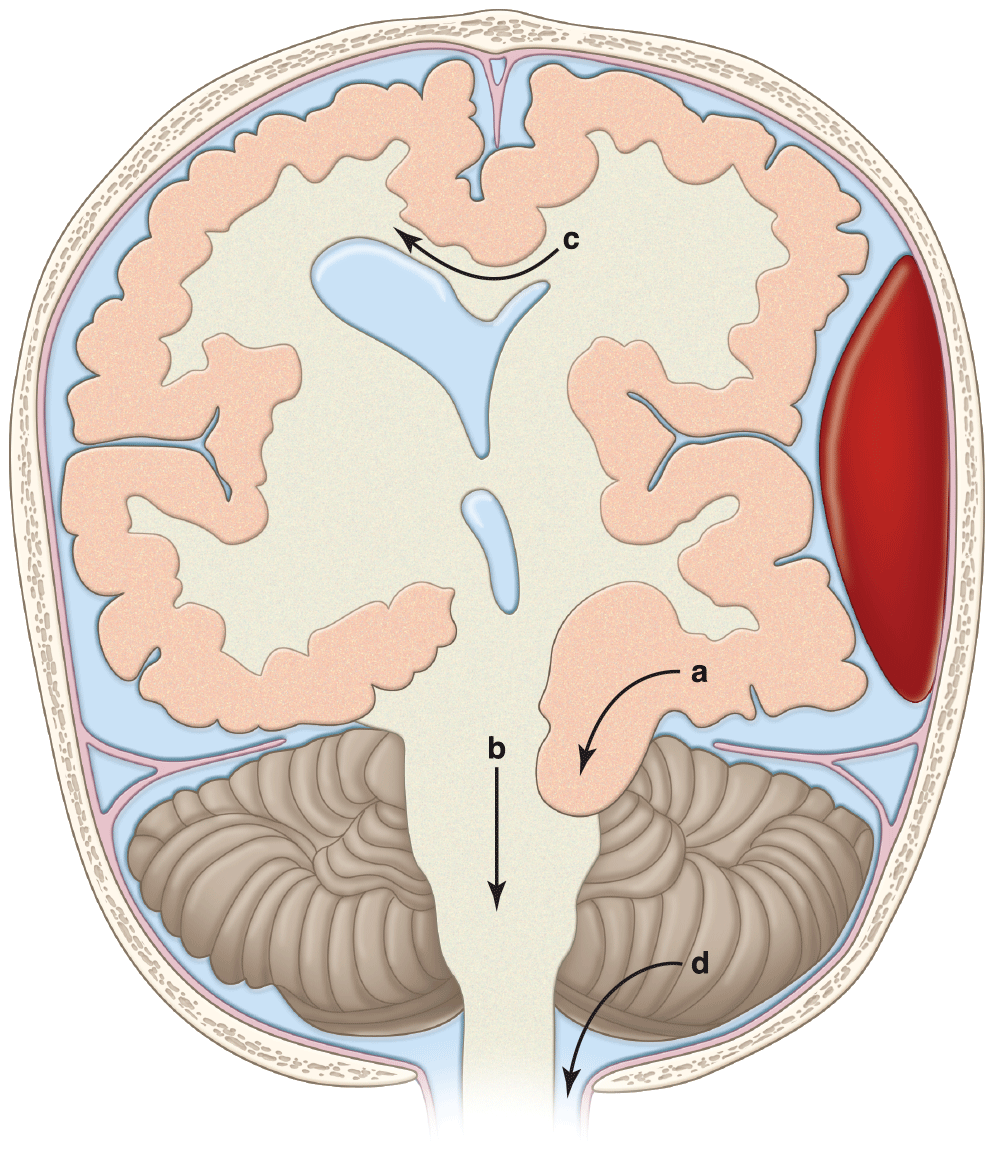
- Subdural hematoma and traumatic subarachnoid blood are the most common hemorrhagic computed tomographic (CT) findings in patients with head injury.
- In the patient with signs of brain herniation and borderline or shock vital signs, the ideal hyperosmotic agent is hypertonic saline.
- Although the incidence of traumatic findings on a cranial CT scan in patients with head injury, loss of consciousness, and a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 is about 6%, the need for neurosurgical intervention in this cohort is 0.4%.
- Guidelines for ordering CT scans in adults after head trauma are the Canadian CT head rule and the New Orleans criteria. The guideline for pediatric patients is the PECARN set of rules.
- Four-factor prothrombin complex concentrate can rapidly reverse the effects of warfarin in patients with intracranial hemorrhage.
- For the athlete with head injury, immediate removal from play and a graded increase in activity as long as the patient is asymptomatic are the basis of concussion management.
Latest Updates
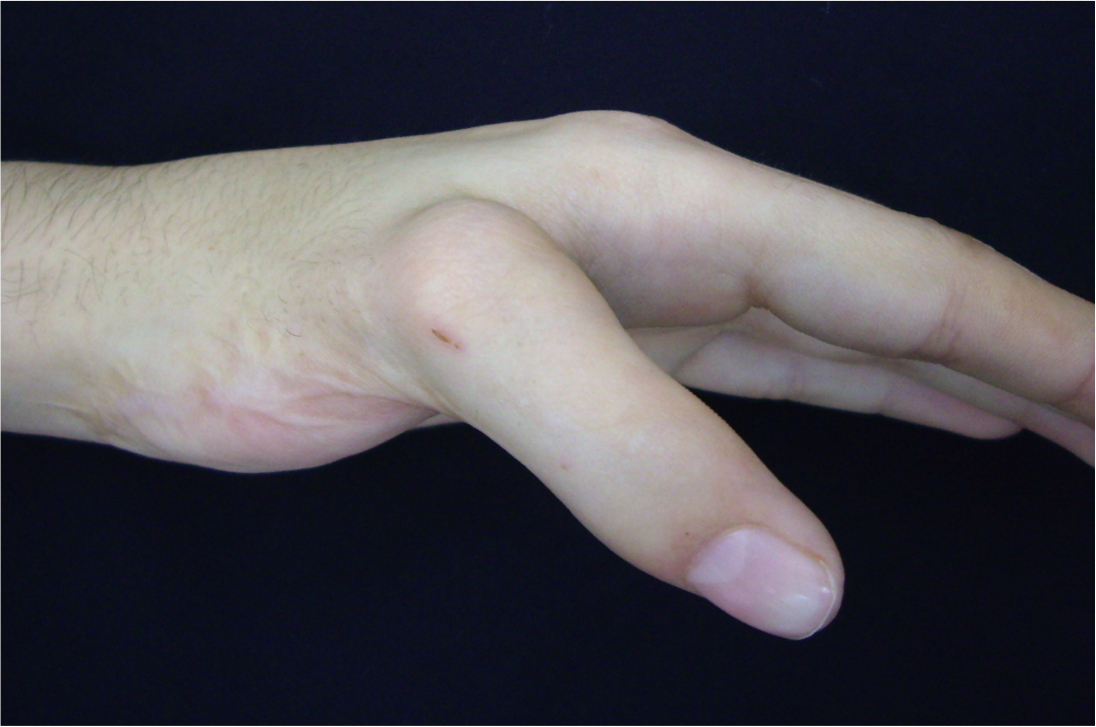
Common Congenital Hand Differences
- The child’s global health and genetic counseling should be addressed before focusing on the upper limb disorder.
- The main aim when treating these disorders is improving hand function; however, aesthetics must also be considered when planning surgery.
- Reoperation rates are high for even the most common congenital hand defects treated by experienced surgeons.
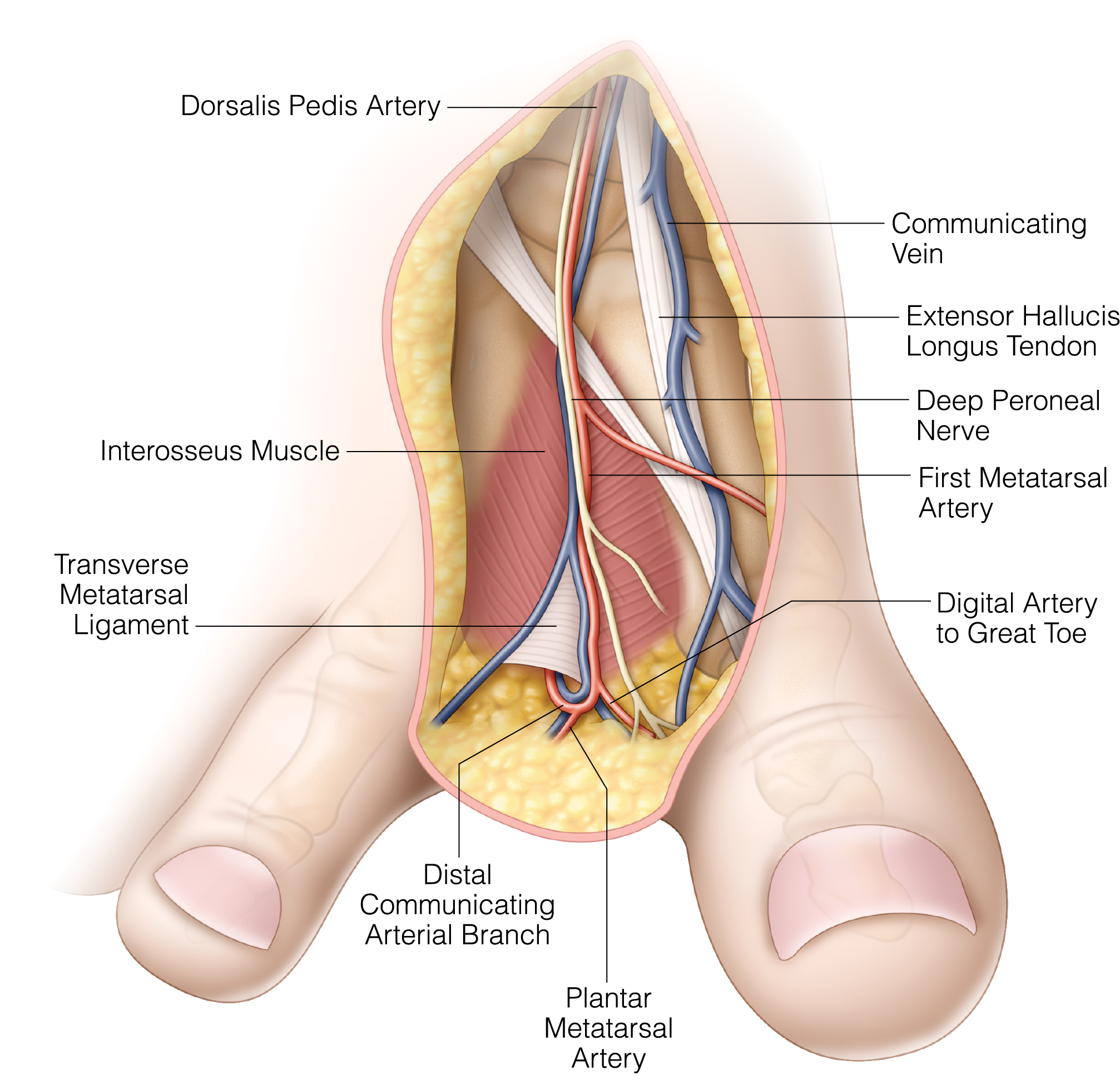
Reconstruction of the Thumb after Traumatic Tissue Loss
- Microsurgical toe transfer in children after traumatic amputation
- Single stage thumb reconstruction
- Cultural considerations in thumb reconstruction
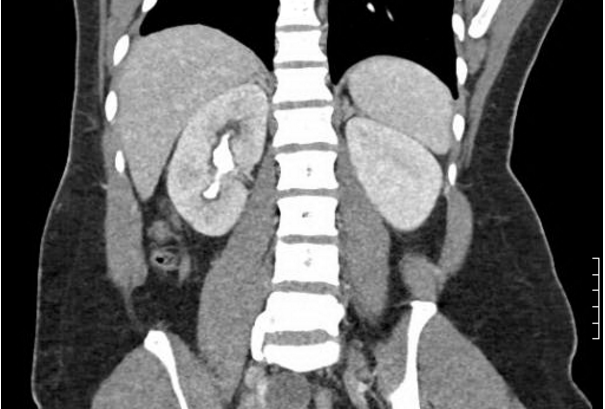
Pathophysiology and Treatment of Infection Stones
- Pathophysiology of infection stone formation
- Workup of patients suspected of having infection stones, including imaging
- Surgical management
- Medical Therapy
Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring in the Intensive Care Unit
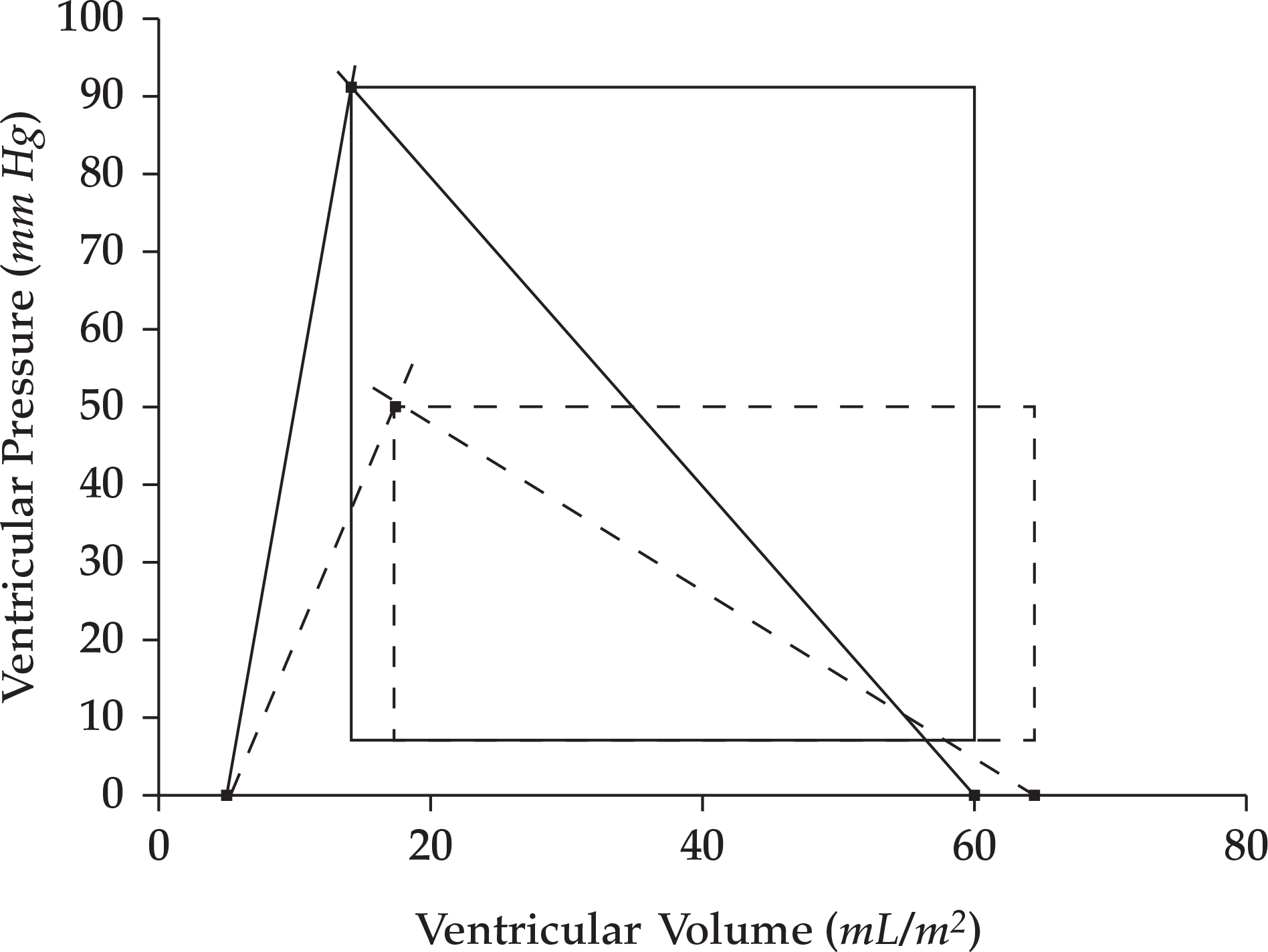
- Employment of invasive methods of hemodynamic monitoring allows the bedside estimation of global cardiovascular function and the independent determinants of cardiac function
- Global cardiac function and preload can be estimated with a peripheral arterial line.
- Assessment of adequacy of cardiac function during resuscitation from shock involves measurement of both blood flow and blood pressure.
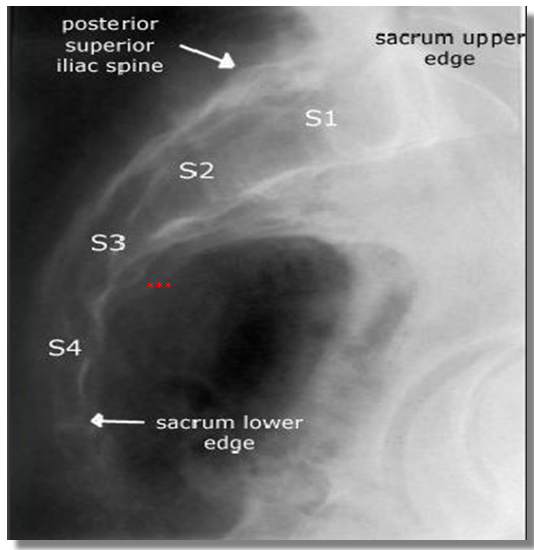
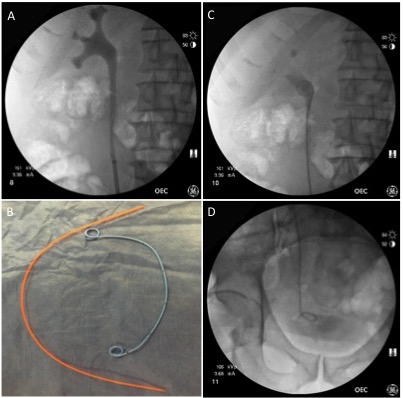
Neuromodulation for Overactive Bladder
- Use of neuromodulation in overactive bladder
- Expanding indications for sacral neuromodulation
- Future technologies in development
Medical Management of Neurogenic Bladder
• First -line therapy for neurogenic bladder with detrusor overactivity, poor compliance, or related incontinence areis antimuscarinic agents,; however, treatment failures need to be addressed quickly, with dose optimization and progression to botulinum toxin.
• Endless cycling of different oral medications that are ineffective is of little value to the patient because most are pharmacologically quite similar. The provider must move to a more effective therapy, such as botulinum toxin, in a timely fashion.
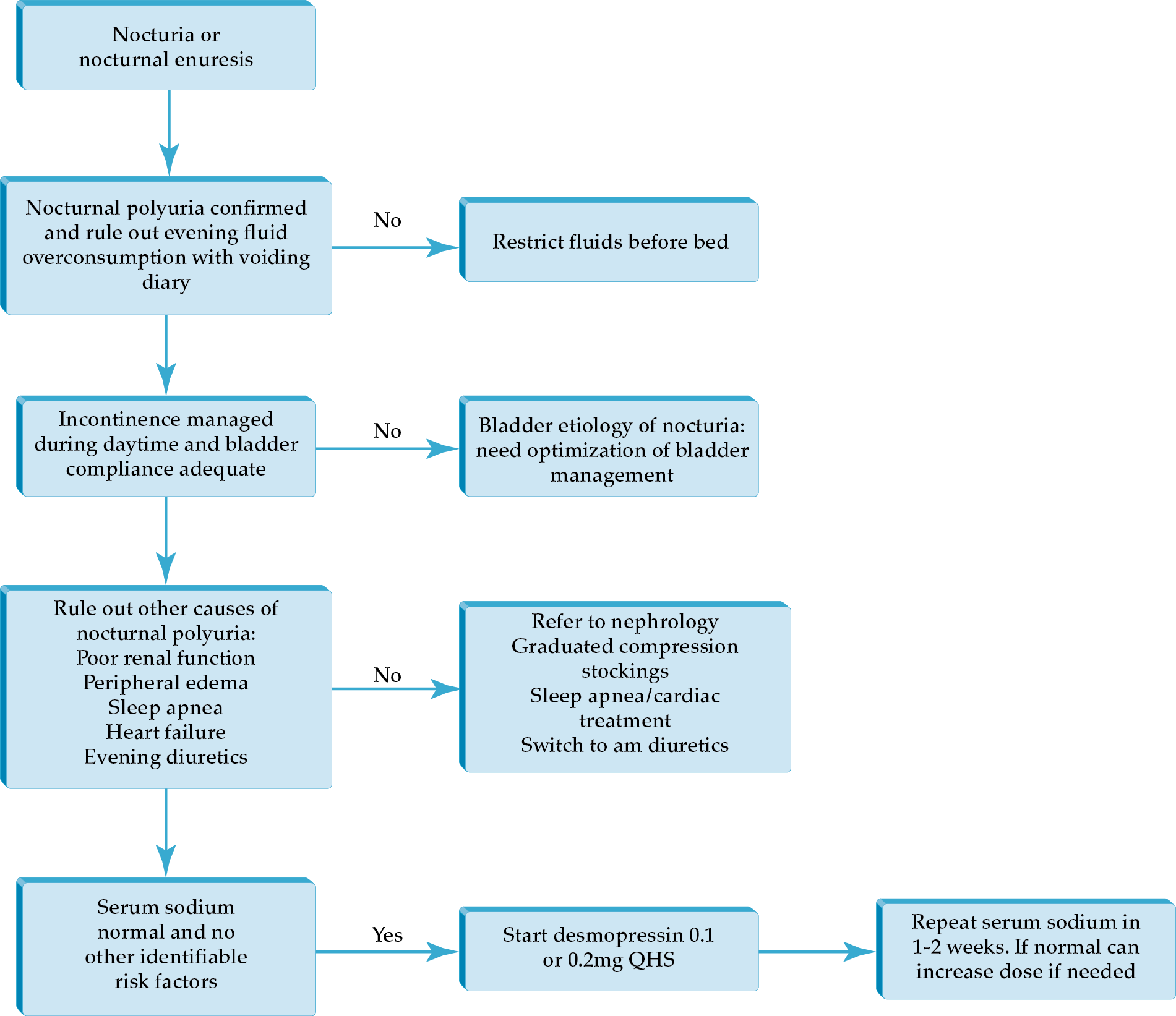
• Desmopressin is an often overlooked therapy for nocturnal polyuria, and if other reversible causes are treated and the patient is properly screened, this can be a very therapeutic intervention.


.png)







