- Update to pharmacologic options in multimodal analgesia
- Increasing use of epidural anesthesia
- Expansion of literature supporting regional nerve blocks and details on techniques
- Rise of opiate addiction crisis and information on best prescriber practices to minimize abuse
Latest Updates
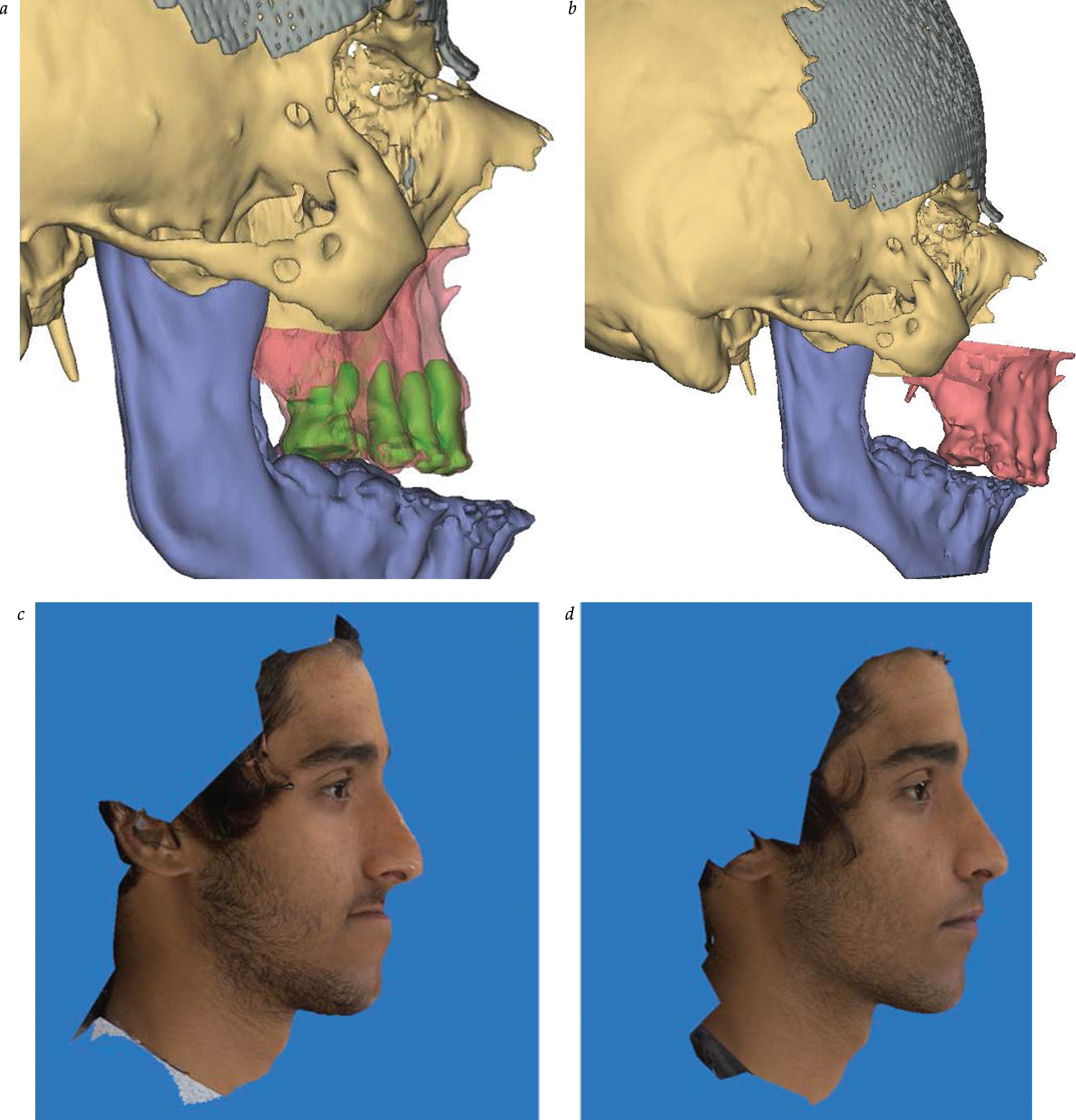
Distraction Osteogenesis in Plastic Surgery
- Distraction osteogenesis offers a unique opportunity to create new bone stock in areas of the craniofacial skeleton where bone is inadequate.
- The osteotomy site, vector, device selection, and timing are all important determinants of success in craniofacial distraction osteogenesis.
- Technological advances in both external and internal distraction devices allow for increased operative flexibility and creativity.
- 3D computer-aided design/manufacturing planning, increased device flexibility, and customized osteotomies allow for further tailoring of distraction osteogenesis to meet individual patient needs.

- Update to pharmacologic options in multimodal analgesia
- Increasing use of epidural anesthesia
- Expansion of literature supporting regional nerve blocks and details on techniques
- Rise of opiate addiction crisis and information on best prescriber practices to minimize abuse
- The International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD) was revised again in 2013 (ICHD-3 beta). The ICHD is organized hierarchically, with major headache groups denoted by an initial digit, headache types by a second digit, headache subtypes by a third digit, and, in some cases, headache subforms by a fourth digit. The level of detail needed depends on the context of the diagnosis; for clinical purposes, it is generally sufficient to code only to one or two digits, but more precise diagnoses are useful for research purposes.
Approach to the Patient with Glomerular Disease
- Serologic diagnosis of glomerular diseases (e.g., anti-GBM antibody, ANCA, anti-PLA2R antibody)
- Use of dysmorphic hematuria (by microscopy of urine sediment to detect glomerular disease
- Investigation of serum complement abnormalities as clues to underlying disease
- Improved analysis of renal biopsy material, leading to a more accurate diagnosis and/or prognosis
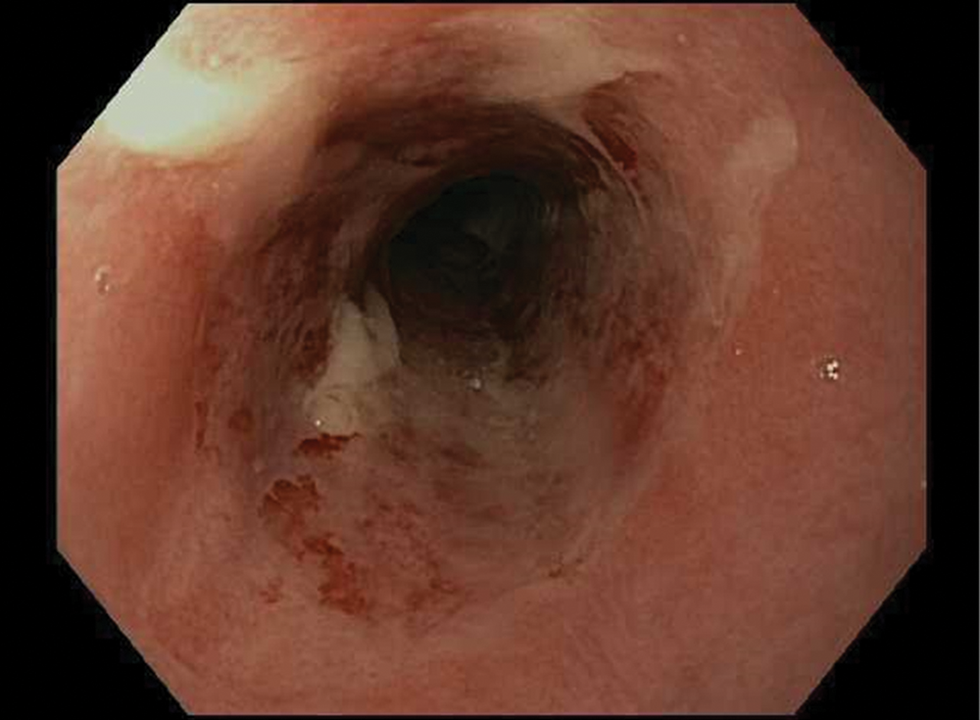
Infectious Diseases of the Esophagus
- Newer drugs such as isavuconazole offer alternatives for treatment of esophageal candidiasis.
- CMV esophagitis remains uncommon in immunocompetent hosts, and is a pathologic finding.
- HSV esophagitis often resolves spontaneously in immunocompetent hosts.
- The involvement of an infectious disease specialist is suggested in complicated cases.
- A new diagnosis of infectious esophagitis should trigger evaluation for HIV, malignancy, or other causes of immunosuppression.
Conservative Management of Male Stress Urinary Incontinence
- Review of clinical evaluation and diagnosis of male stress urinary incontinence with an emphasis on postprostatectomy incontinence
- Review of the pathophysiology and efficacy of pelvic floor physical therapy
- Review of injectable urethral bulking agents and the literature regarding their safety and efficacy
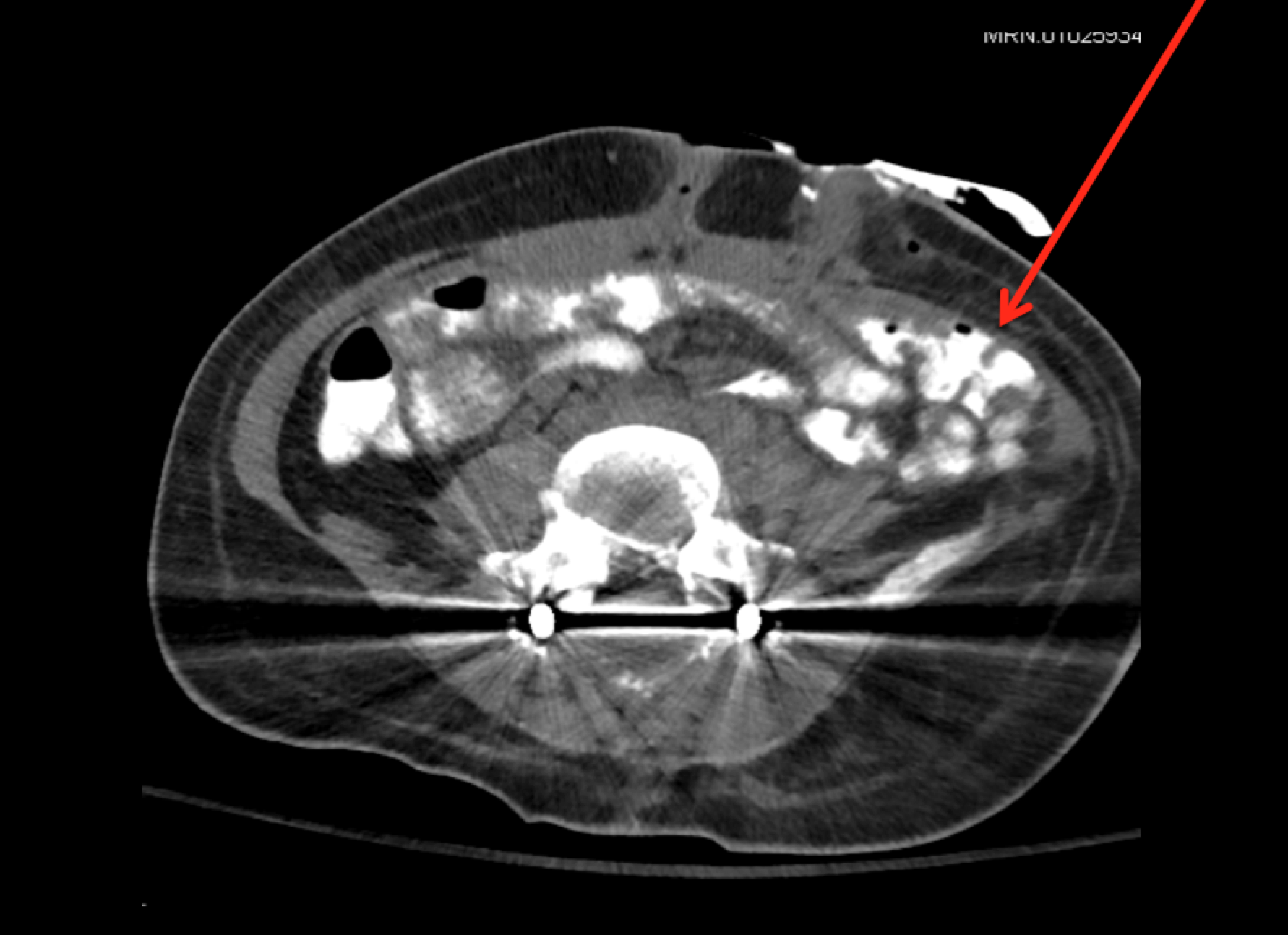
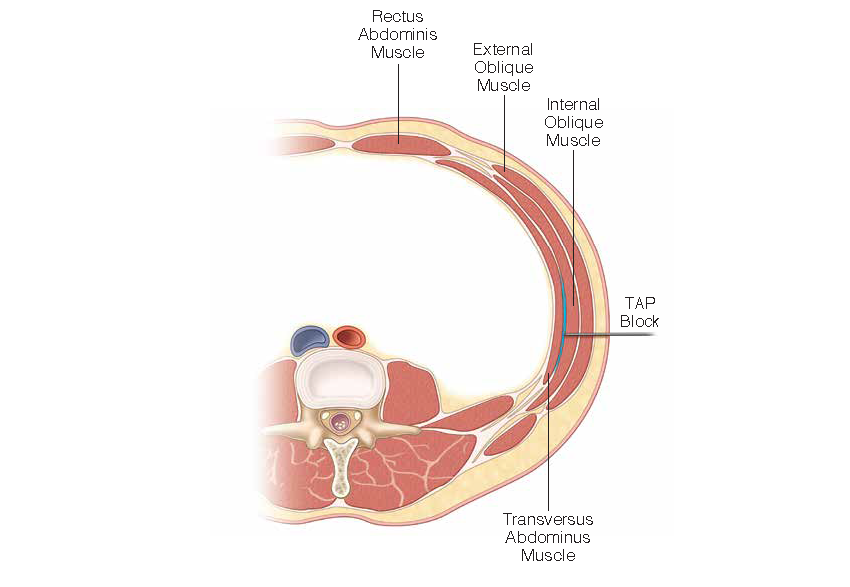
- Macroporous meshes with pore size greater than 1 mm avoid bridging scar formation and are thought to be the most biocompatible for hernia repair.
- Early gap formation of a newly repaired abdominal wall is a predictor of incisional hernia formation.
- Bridged abdominal wall closures with mesh have higher rates of hernia formation than direct-supported repairs and are therefore avoided when possible.
- Both anterior and posterior components release improved abdominal wall compliance and help to achieve direct-supported repairs with mesh in clinical situations when the abdominal wall could not otherwise be approximated.
- In complex abdominal wall situations, wounds should be closed with either primary skin closure or skin grafts as a first step in the reconstructive process.


.png)







