Latest Updates

Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is an advanced form of life support that has undergone explosive growth in its use over the past decade.
- Advancement in the design of the circuit oxygenator has been the major technological improvement in ECMO. This has allowed for longer durations of support without damaging the red blood cells.
- The indications for ECMO continue to expand with active growth in ECMO as a bridge to heart and lung transplantation and left ventricular assist device placement for refractory heart failure and as a rescue modality during cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- Continued research is needed to standardize ECMO practices and protocols to improve survival.
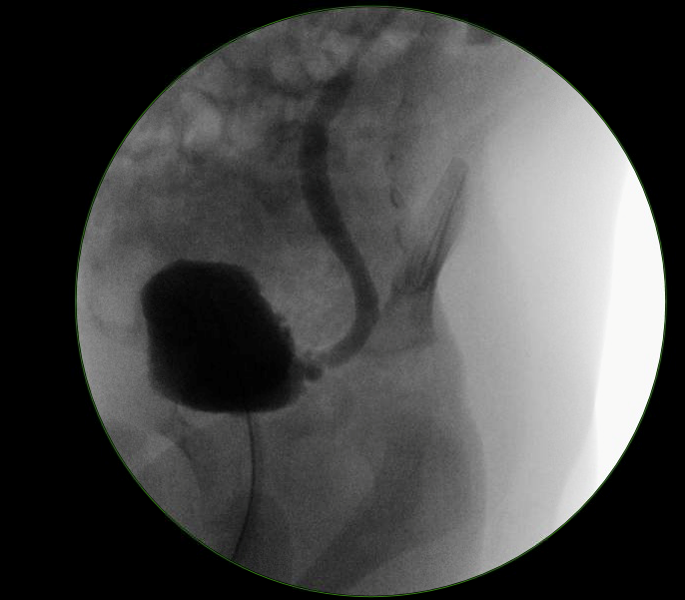
Endoscopic Correction of Vesicoureteral Reflux
- The appropriate endpoint of endoscopic correction of vesicoureteral reflux is elimination of hydrodistension and at least 1 mL bulking substance per ureter
- The double hydrodistension implantation technique is the most effective method of endoscopic injection
- The timing of vesicoureteral reflux is the most important factor in predicting spontaneous reflux resolution
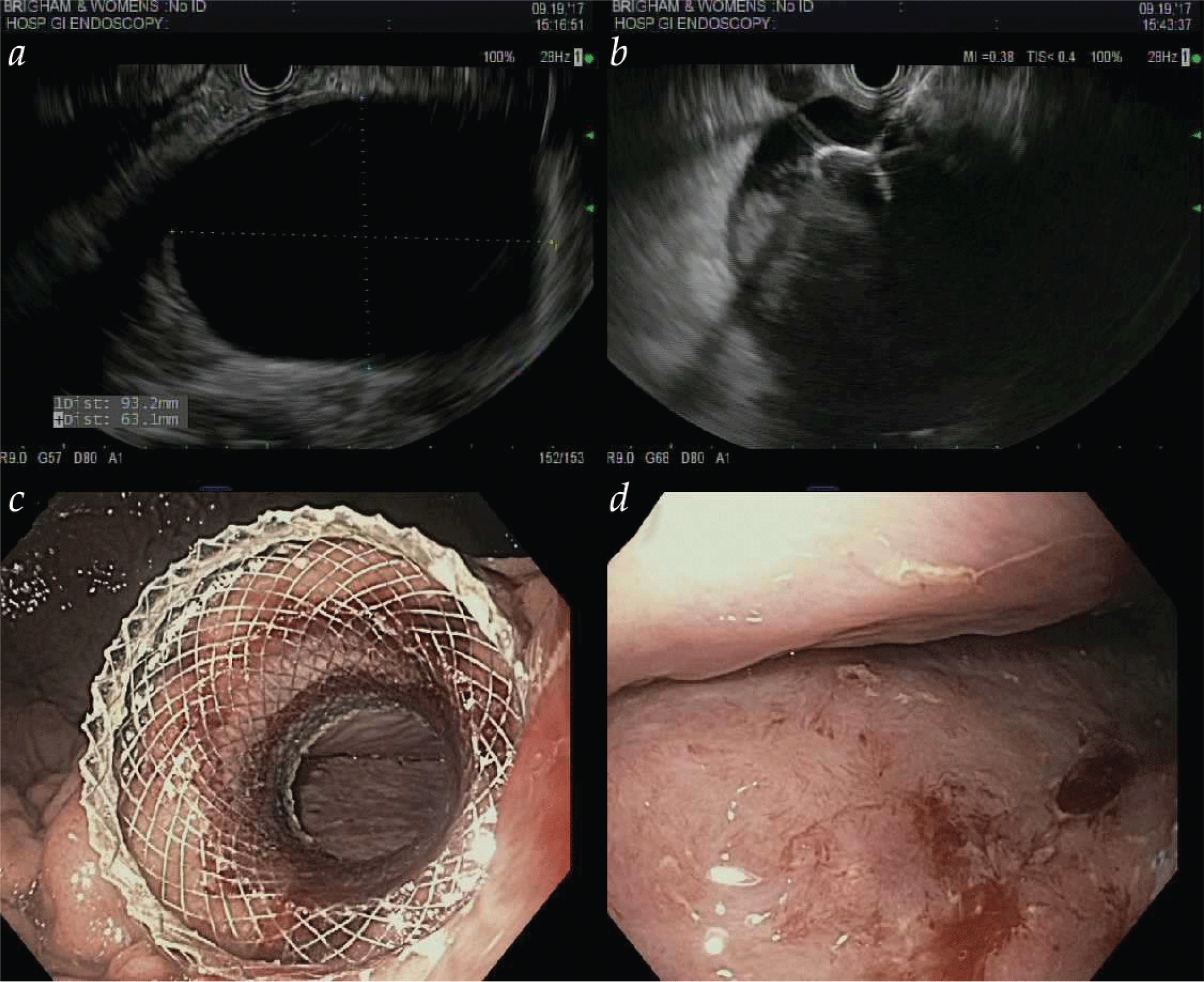
- Endoscopic techniques such as endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection allow for resection of superficial mucosal neoplasms throughout the gastrointestinal tract.
- Multimodality endoscopic eradication therapy involves combining endoscopic mucosal resection and radiofrequency ablation to achieve complete eradication of Barrett esophagus.
- Peroral endoscopic myotomy has been developed as a minimally invasive endoscopic alternative to Heller myotomy in the treatment of achalasia.
- Novel endoscopic techniques allow for drainage of pseudocysts and walled-off pancreatic necrosis and create connections between luminal gastrointestinal structures.
- Novel endoscopic techniques exist in both primary management of patients with obesity and management of complications of bariatric surgery.

- Endoscopic techniques such as endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection allow for resection of superficial mucosal neoplasms throughout the gastrointestinal tract.
- Multimodality endoscopic eradication therapy involves combining endoscopic mucosal resection and radiofrequency ablation to achieve complete eradication of Barrett esophagus.
- Peroral endoscopic myotomy has been developed as a minimally invasive endoscopic alternative to Heller myotomy in the treatment of achalasia.
- Novel endoscopic techniques allow for drainage of pseudocysts and walled-off pancreatic necrosis and create connections between luminal gastrointestinal structures.
- Novel endoscopic techniques exist in both primary management of patients with obesity and management of complications of bariatric surgery.
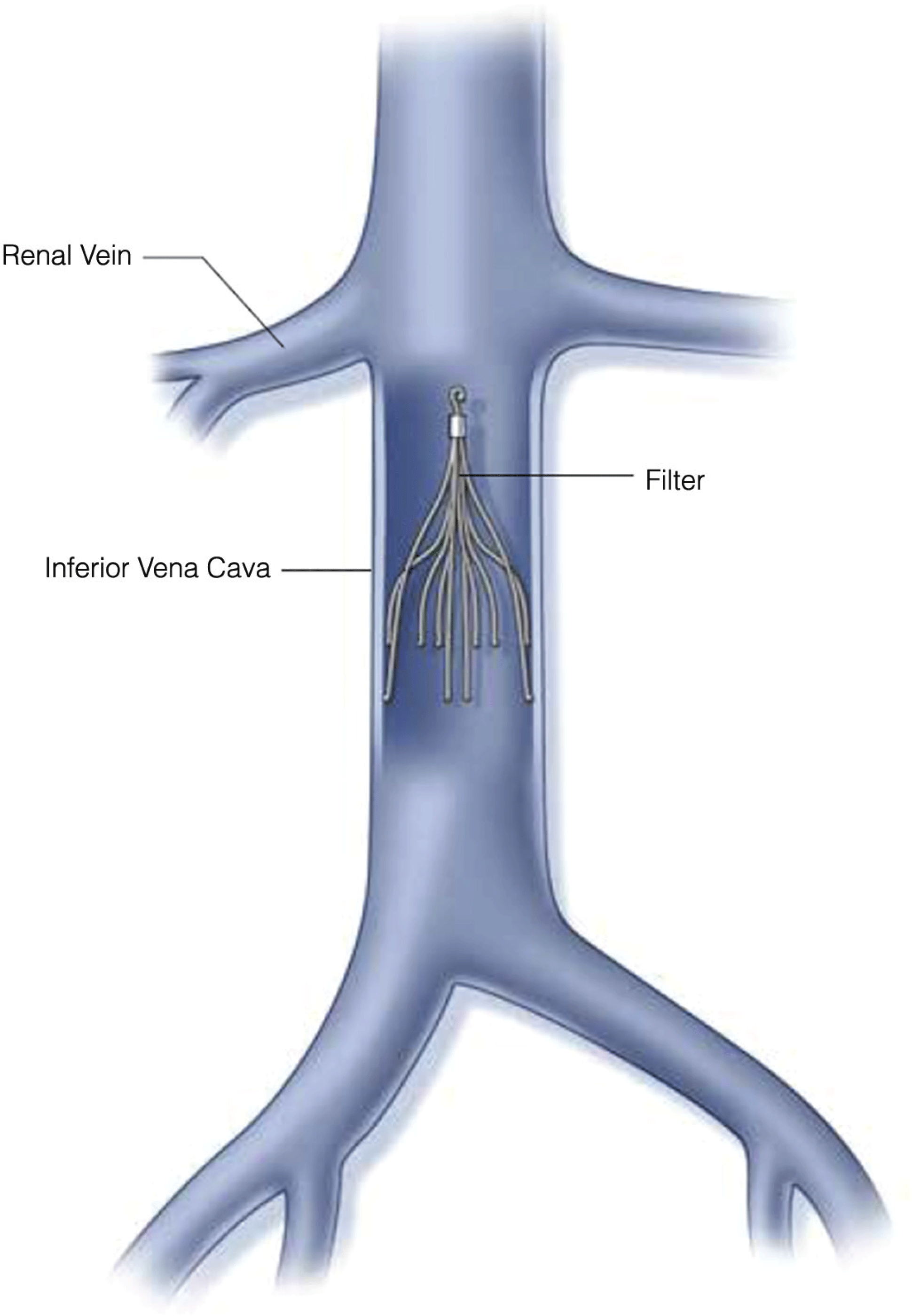
Medical Management Of Pulmonary Embolism
- Description of current guidelines for the management of high-risk (“massive”), medium-risk (“submassive”), and low-risk pulmonary embolism
- Detailed discussion of anticoagulants available in the United States including the newer direct oral anticoagulants
- Review of indications for catheter-based interventions and inferior vena cava filter placement
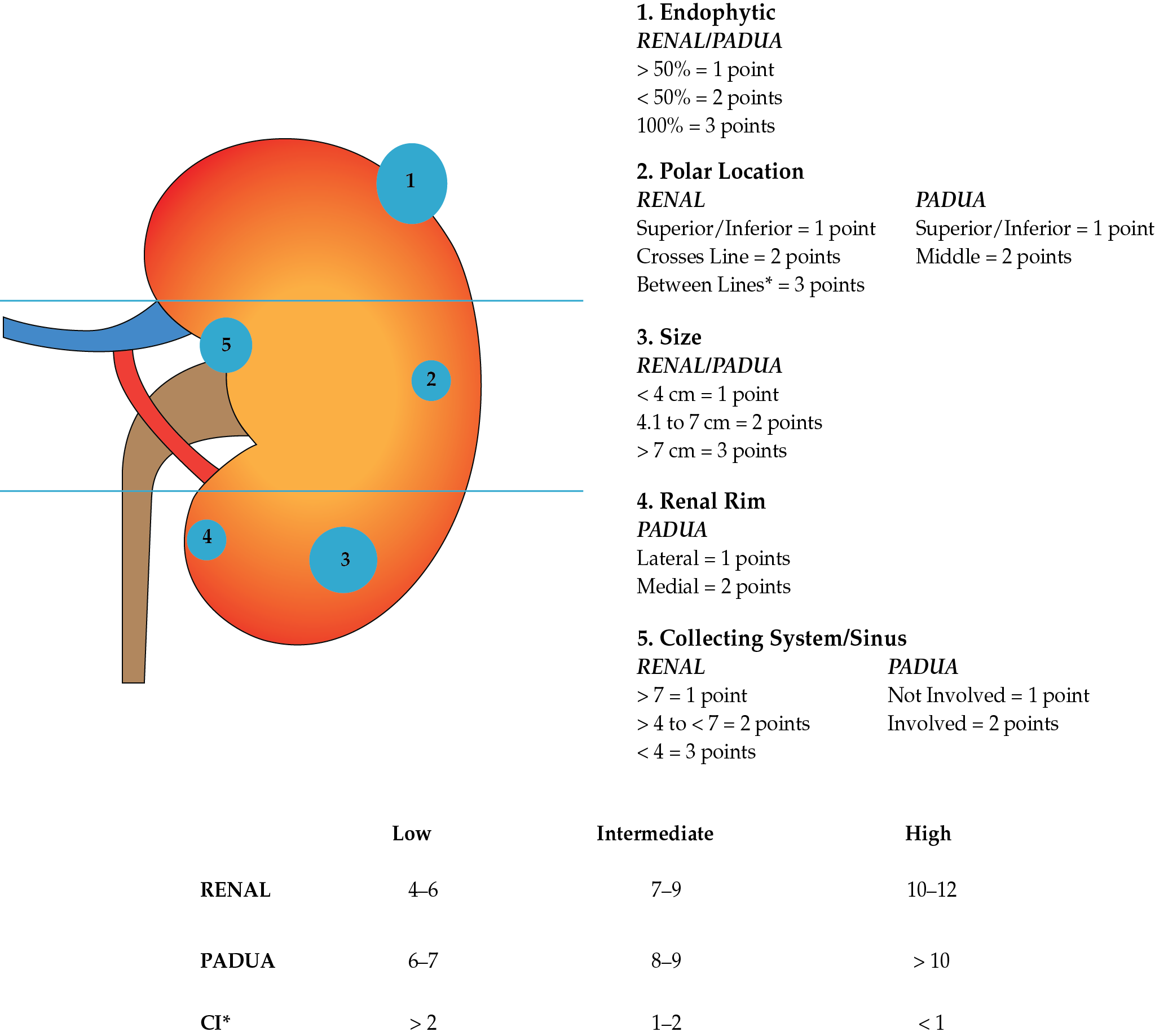
Management of Small Renal Masses
- An improved understanding of the natural history of SRMs underscores their overall slow growth rate and low propensity to metastasize.
- Up to 30% of SRMs are benign, highlighting a role for upfront renal tumor biopsy to stratify those patients requiring therapy. Contemporary experience has demonstrated the safety in performing renal tumor biopsy and the excellent diagnostic rates (> 90%) that can be achieved at centers of excellence.
- There is an increasing role for active surveillance for SRMs, with appropriately selected patients achieving excellent clinical outcomes.
- Partial nephrectomy remains the gold standard treatment for SRMs requiring intervention when technically feasible.
- The management of SRMs is evolving towards a personalized medicine approach with integration of clinical nomograms and genomics to better predict which patients require treatment and when.
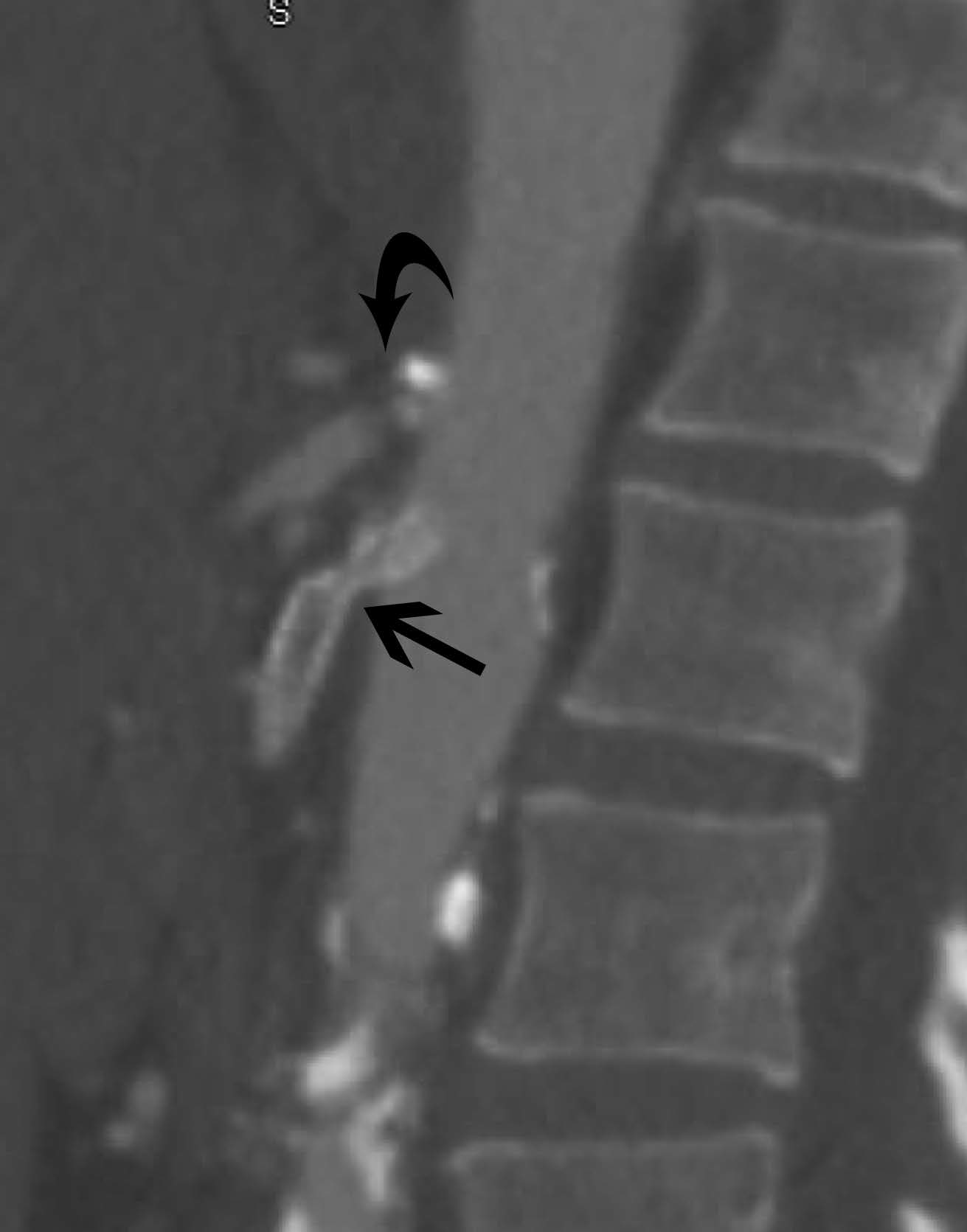
Endovascular Techniques in Mesenteric Ischemia
- Endovascular therapy (EVT) has become the first-line treatment of choice for revascularization in chronic mesenteric ischemia. It offers better short-term morbidity over open repair but does have a decreased long-term primary patency, requiring higher rates of reintervention. Reintervention is associated with low mortality and excellent symptom improvement. Secondary patency is similar between open repair and EVT.
- EVT has become the first-line treatment of choice for acute mesenteric ischemia in some centers with skilled interventionalists. This has reduced the need for laparotomy in patients presenting without peritoneal signs and suspicion of bowel necrosis. A high index of suspicion should remain in these patients, and hesitation should not be made for laparotomy should the patient decline clinically.
- Retrograde open superior mesenteric stenting during laparotomy has provided an alternative to surgical bypass in the critically ill patient with AMI. This technique allows inspection and resection of the nonviable bowel.
- Currently accepted surveillance duplex ultrasonography (DUS) criteria for native mesenteric arteries have a poor correlation with in-stent restenosis after mesenteric angioplasty and stenting. Given the high rate of recurrence, lack of accepted DUS criteria can make clinical decision making difficult regarding reintervention. New velocity criteria have been proposed but require validation in individual laboratories.



.png)






