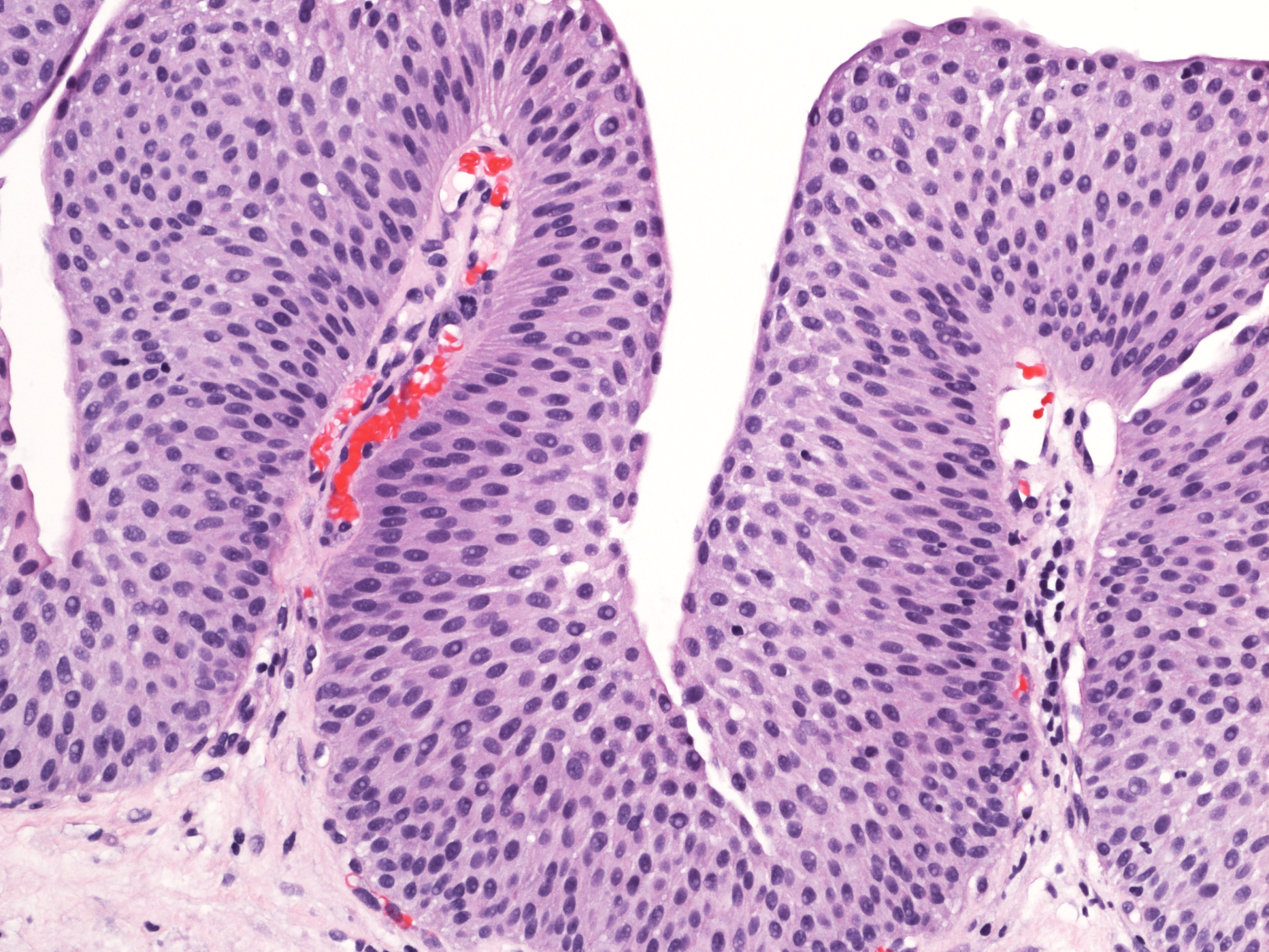
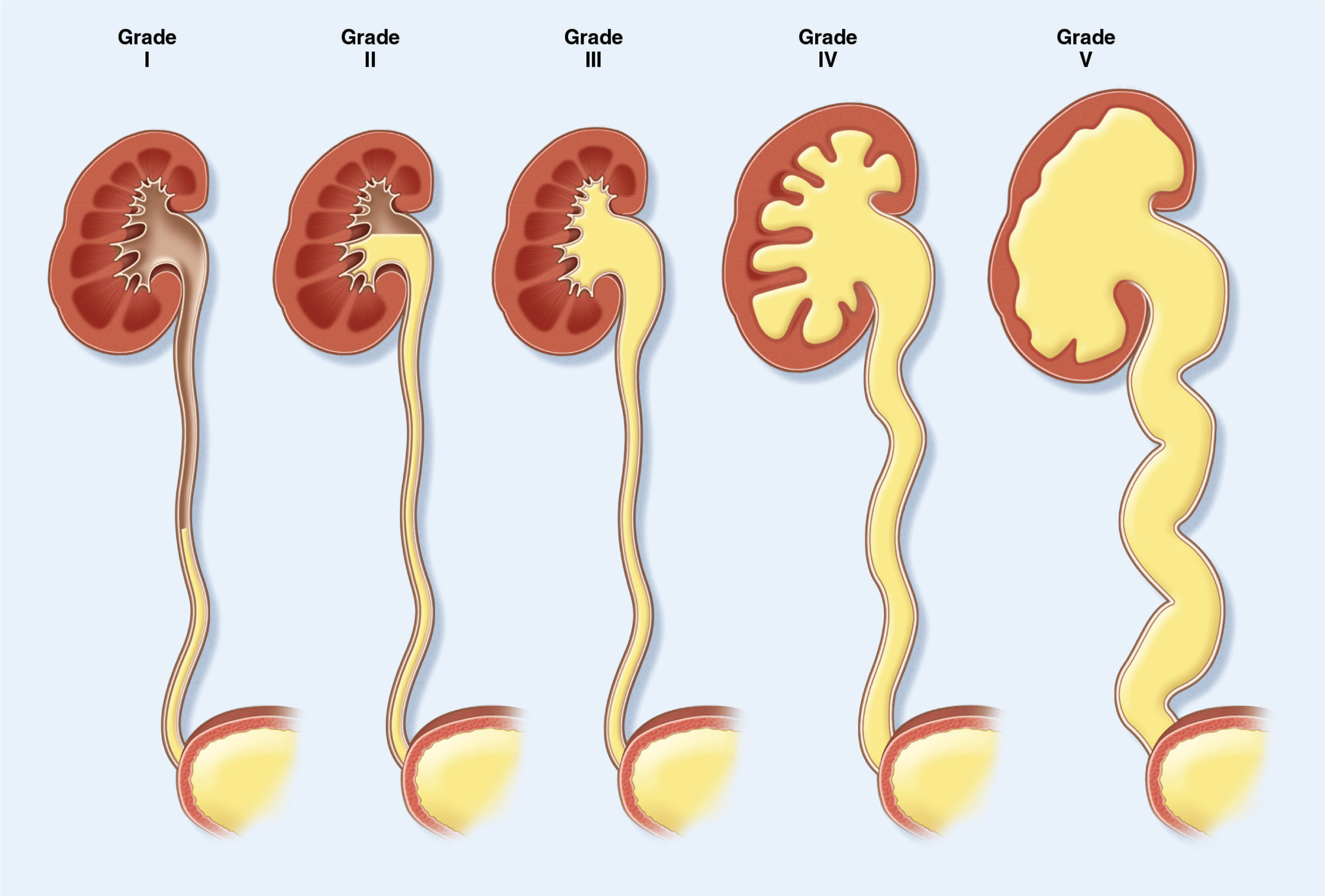
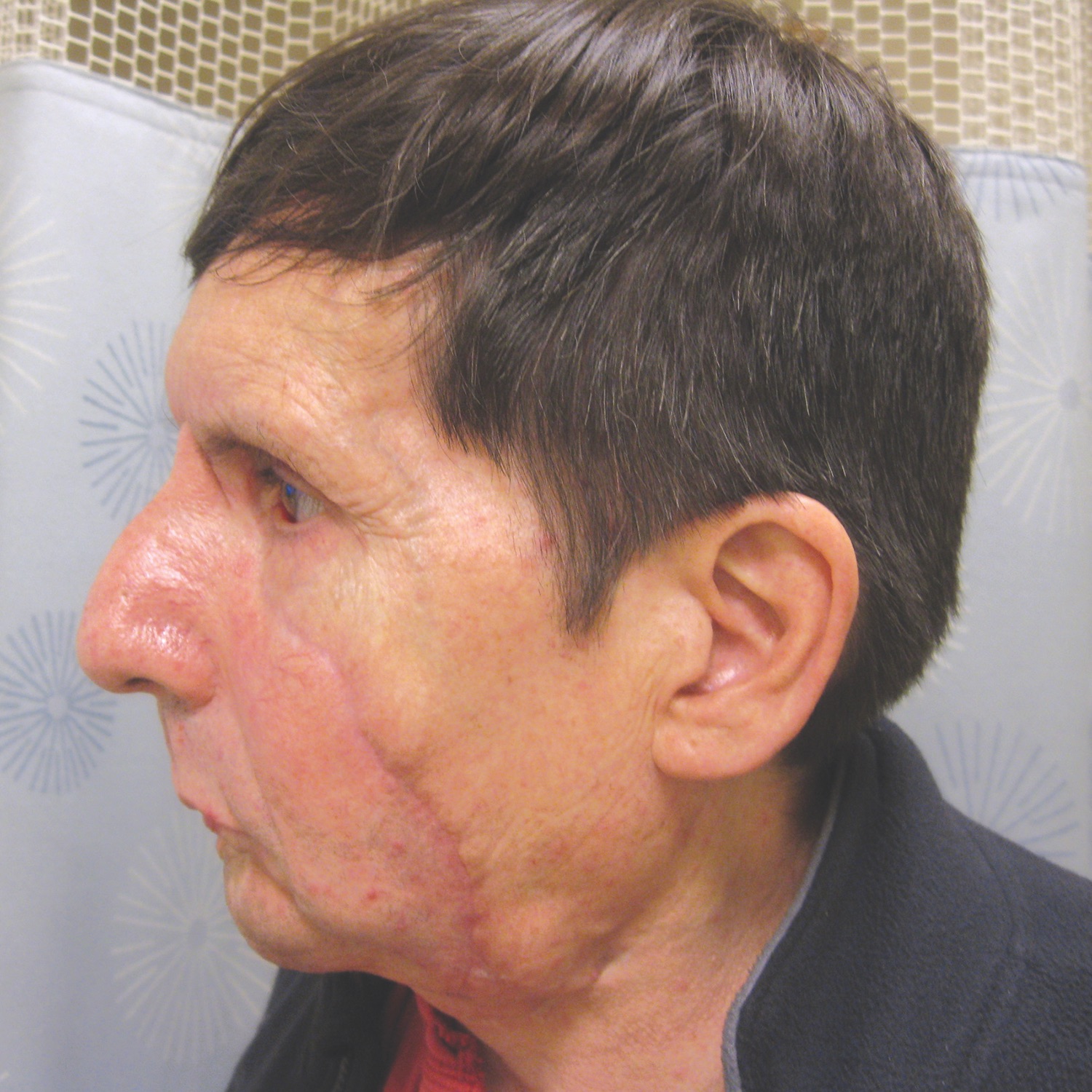
Urothelial Carcinoma: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Diagnosis
- Restrictions and bans on environmental, industrial and herbal medicine-related carcinogenic agents have largely eliminated these agents as drivers for urothelial cancers in industrialized countries; tobacco smoking remains the primary driver of bladder tumors in these countries.
- The diagnosis and management of urothelial carcinomas are rapidly evolving with urine- and blood-based biomarkers in development to diagnose and monitor patients with bladder tumors.
- Multimodality therapies including minimally invasive tumor resection and topical chemotherapy allow a majority of patients with bladder cancer to receive organ-sparing approaches.



.png)






