Principles and Techniques of Abdominal Access and Physiology of Pneumoperitoneum
- Decreasing pain at access incisions
- Multi-modal pain management, TAPP block, opioid sparing analgesia.
- Heated, humidified CO2.
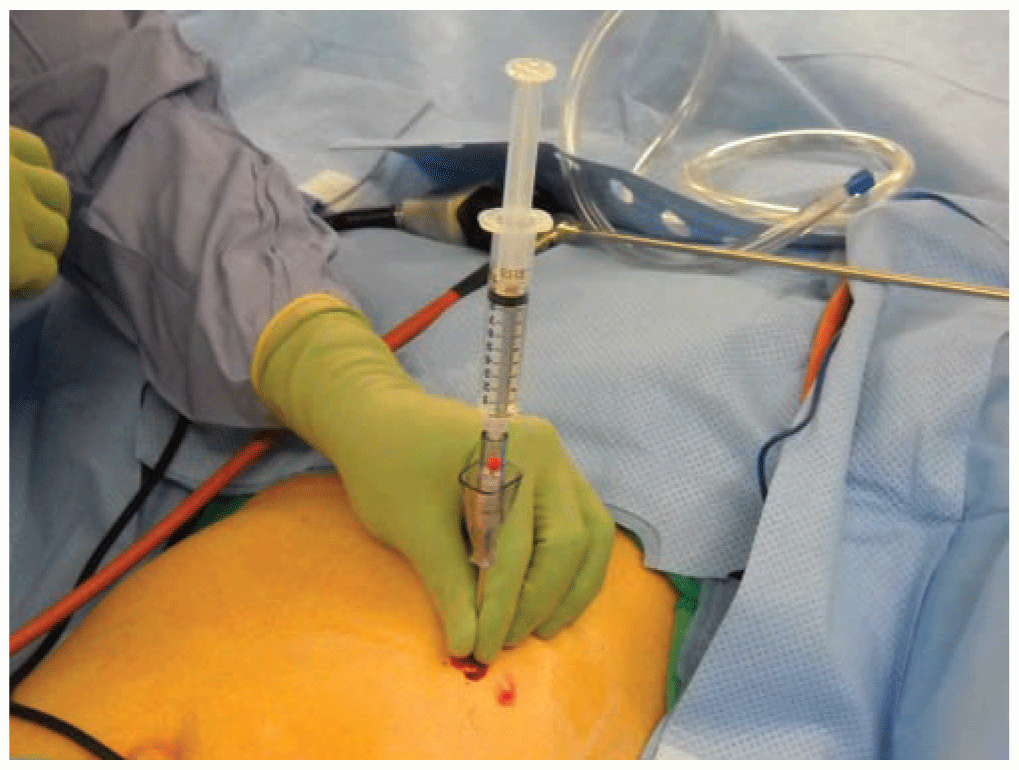
Principles and Techniques of Abdominal Access and Physiology of Pneumoperitoneum
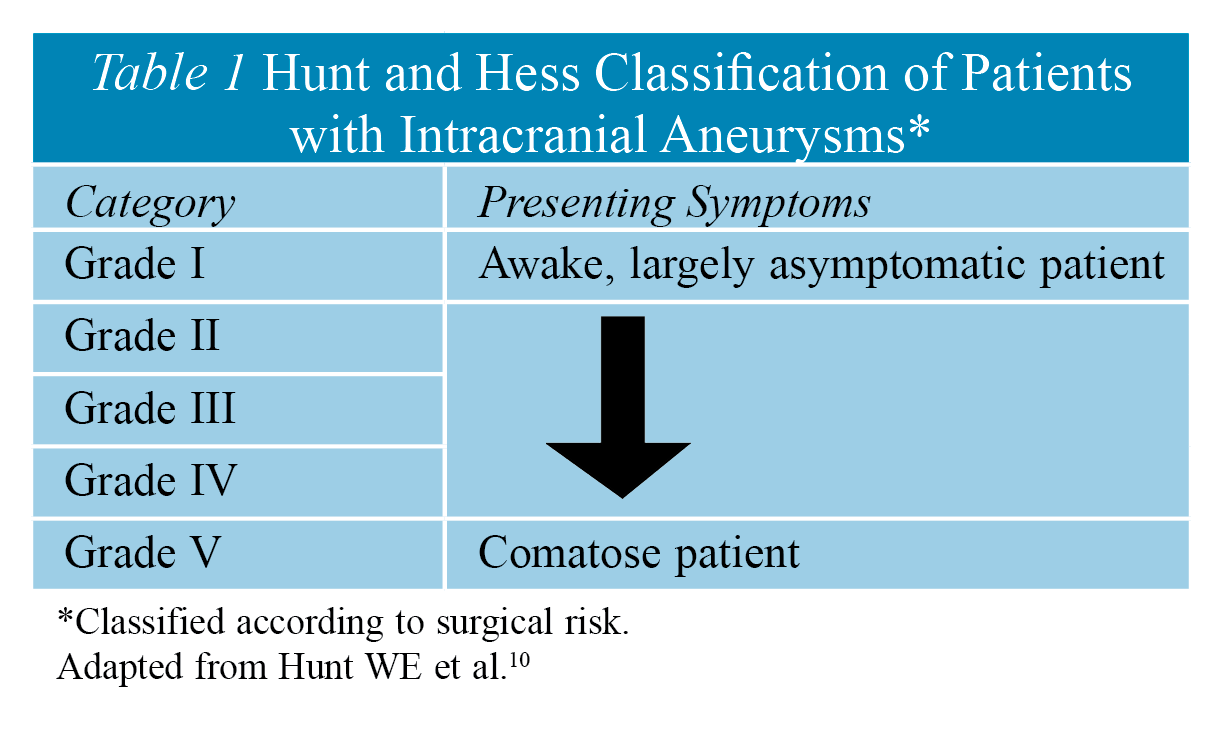
Anesthetic Management of Intracranial Aneurysms

Principles and Techniques of Abdominal Access and Physiology of Pneumoperitoneum
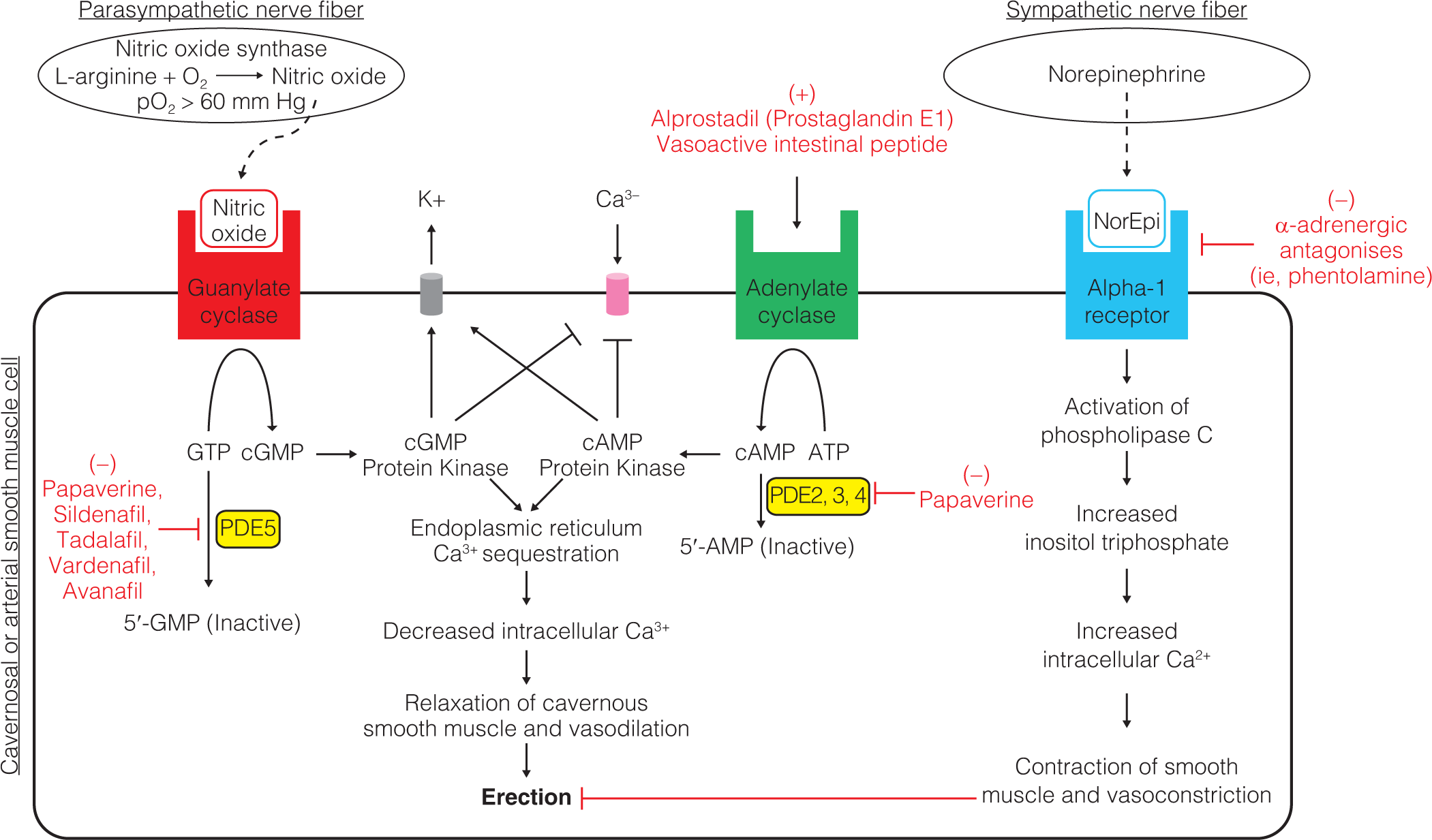
Medical Management of Erectile Dysfunction
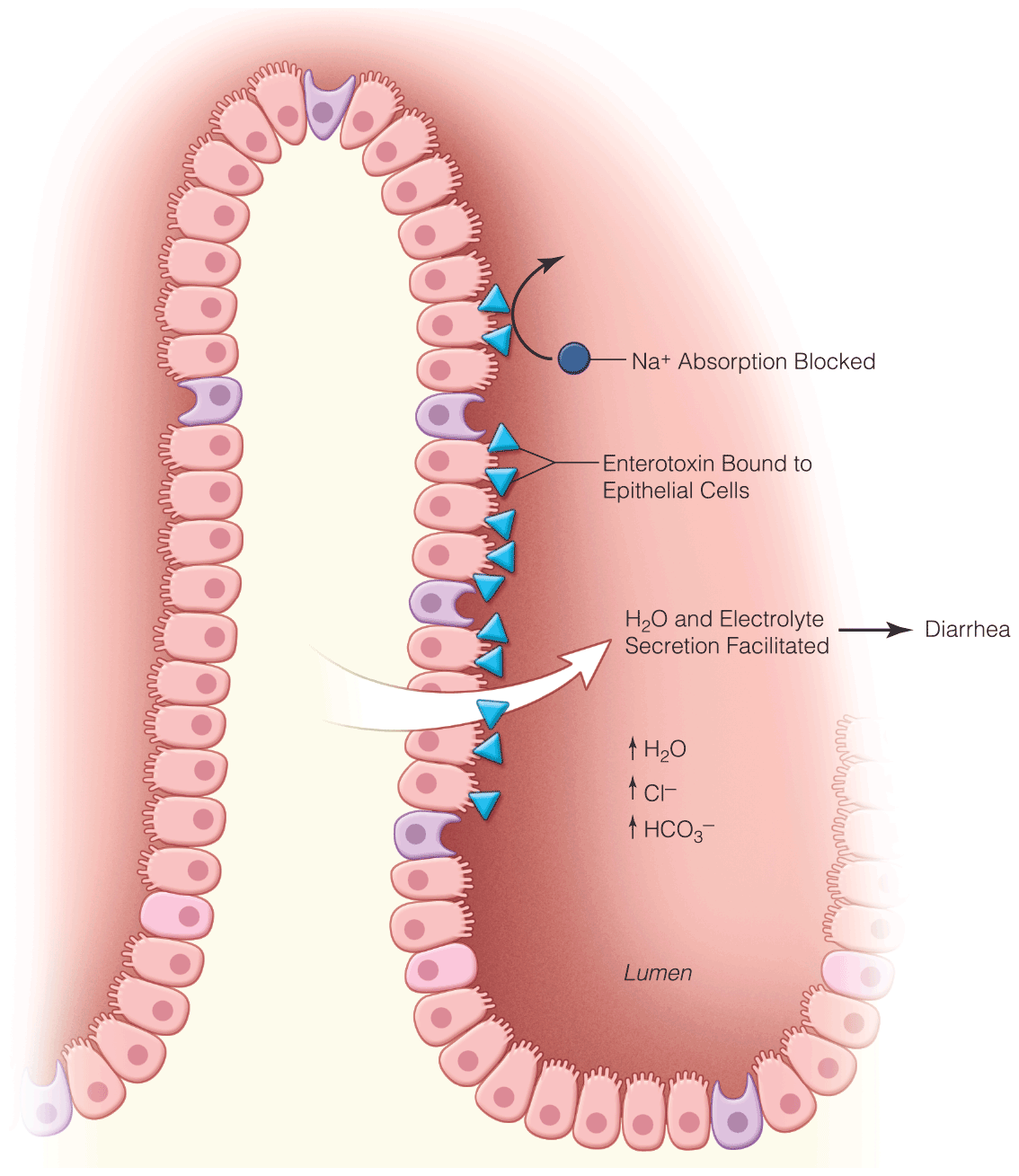
Pediatric Infectious Diarrhea and Dehydration

Pediatric Infectious Diarrhea and Dehydration
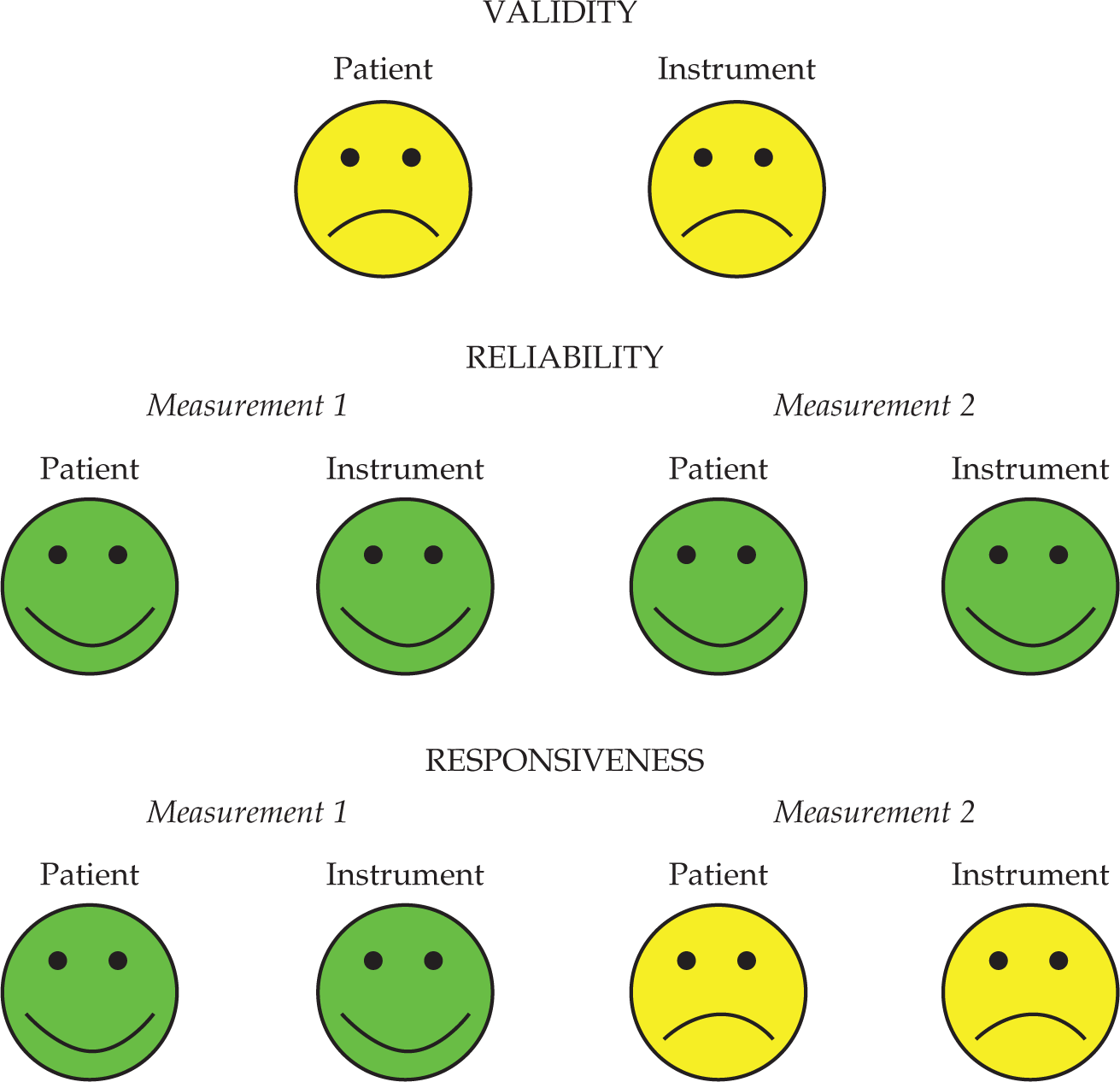
Quality of Life Following Management of Localized Prostate Cancer
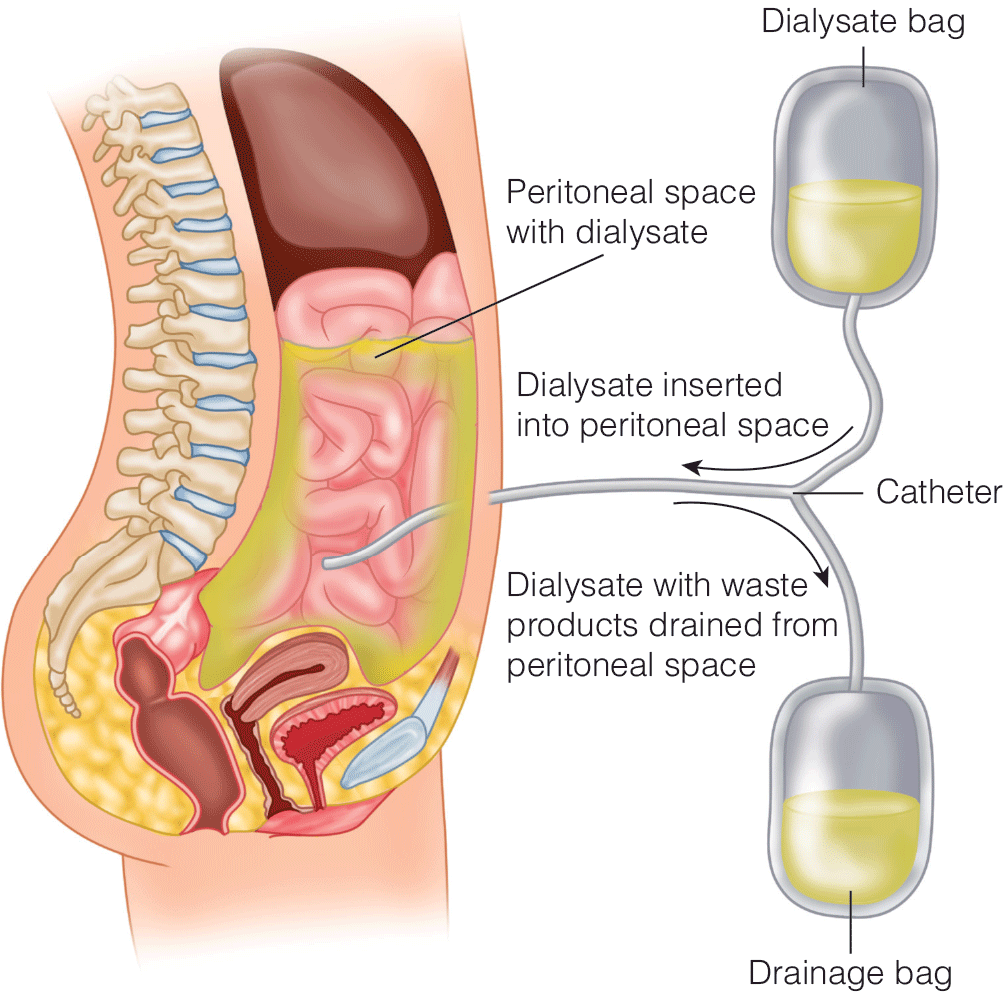
Transplantation for the General Surgeon: Care of the Transplant Patient