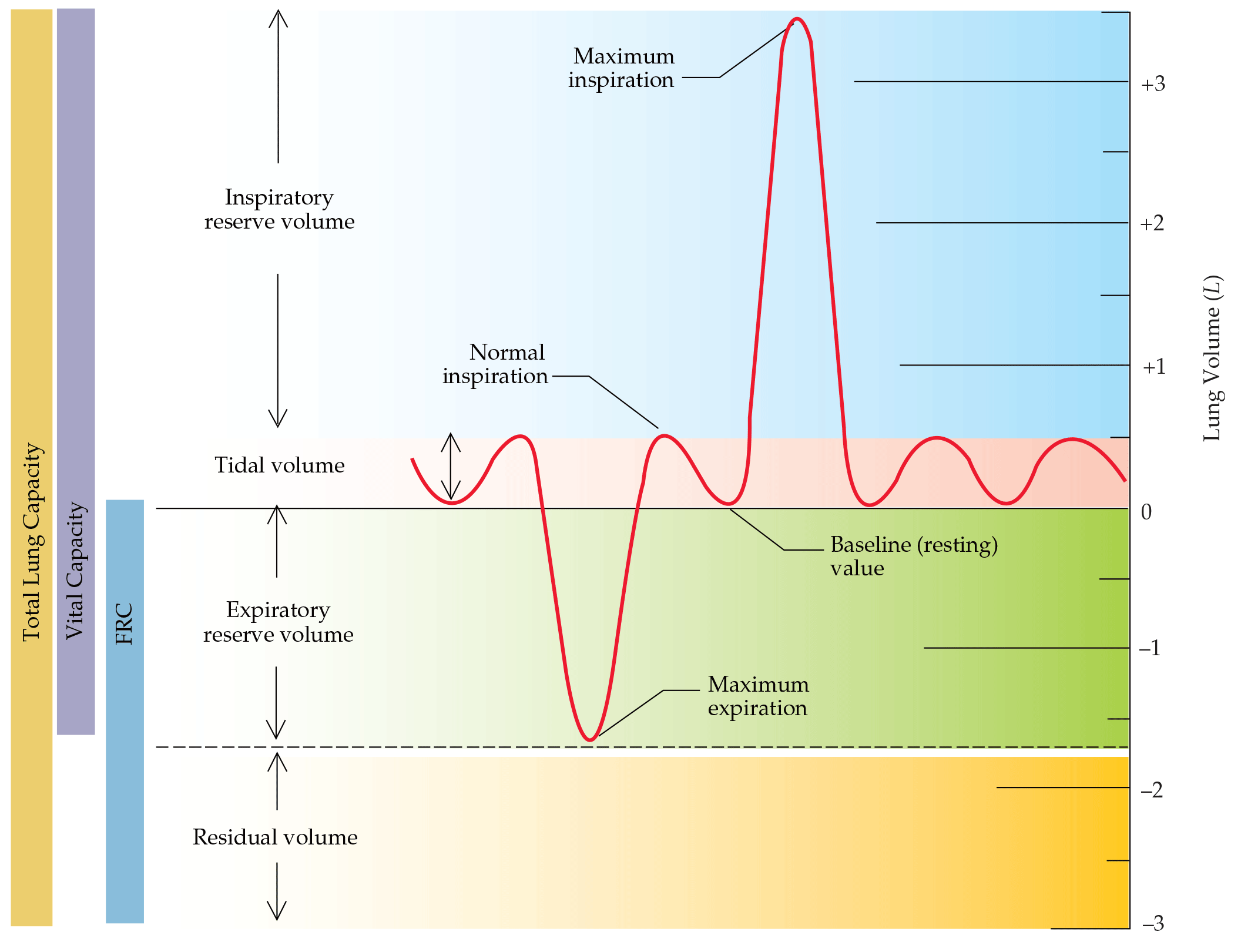
The Respiratory System: Physiologic Assessment and Real-world Application
- Reflectance Pulse Oximetry: The use of backscattered light rather than transmitted light can be helpful in low-signal settings.
- Improved Signal Processing for Pulse Oximetry: Proprietary algorithms and advances in signal processing have improved the precision of pulse oximetry.
- Calorimetric Detection: Colorimetric CO2 detection can be used to ensure nasoenteric placement rather than respiratory placement.
%20(3).jpg)


.png)







