- Over the past 10 years, our understanding of the pathogenesis of keloids and hypertrophic scars has improved markedly. As a result, these previously intractable scars are now regarded as being treatable.
- Keloids and hypertrophic scars are inflammatory disorders of the reticular dermis.
- Mechanical forces play an important role in the pathophysiology of keloids and hypertrophic scars.
- Hypertension is associated with the development of severe keloids and hypertrophic scars.
Latest Updates
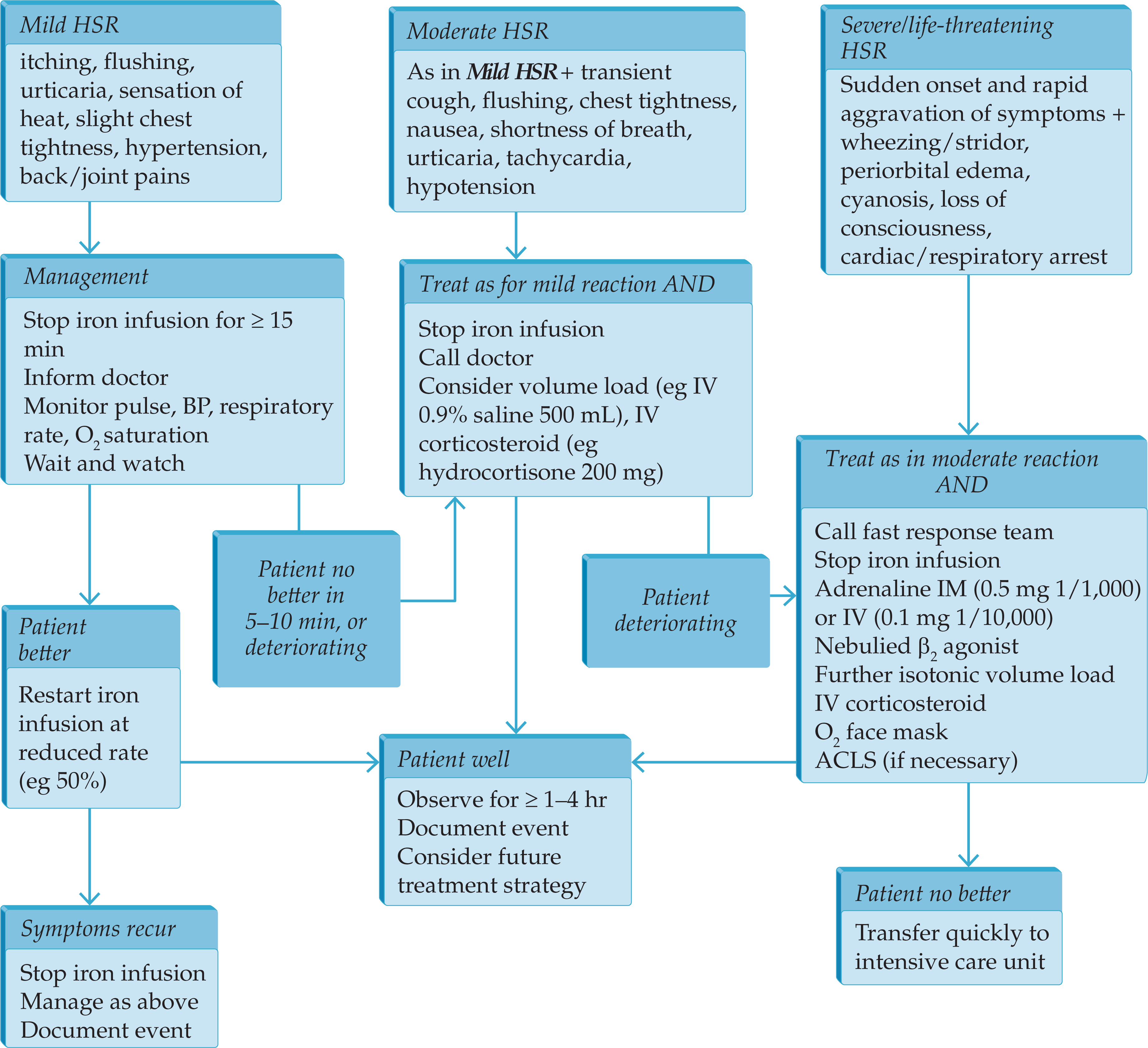
Hematologic Abnormalities in Chronic Kidney Disease
- Novel oral anticoagulants vs. vitamin K antagonists in CKD
- FDA-recommended dose adjustments for novel oral anticoagulants in CKD patients
- Recommendations for erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in CKD
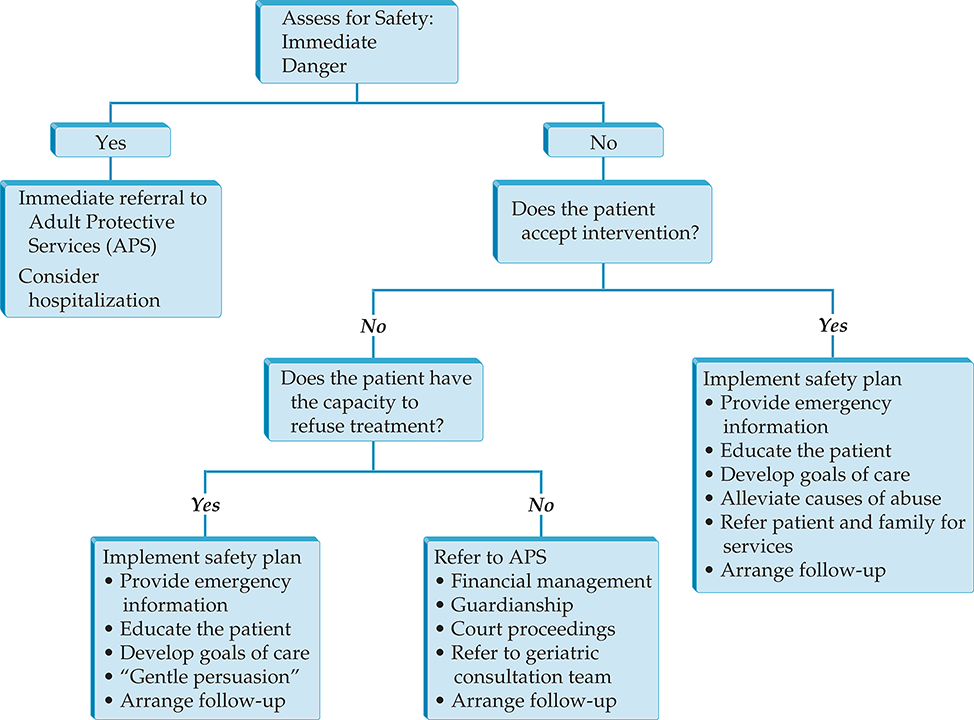
Elder mistreatment affects a considerable proportion of individuals older than 60 to 65 years of age and may include intentional abuse (physical, sexual, emotional, or financial) and neglect. As the proportion of the population that is older than 65 years of age increases, elder mistreatment will become an increasingly common issue. Only a minority of cases of elder abuse are reported; thus, an interview with the patient should be conducted in private if elder mistreatment is suspected. Patient risk factors for elder mistreatment include cognitive or behavioral impairment, poor physical health, and poor social supports.
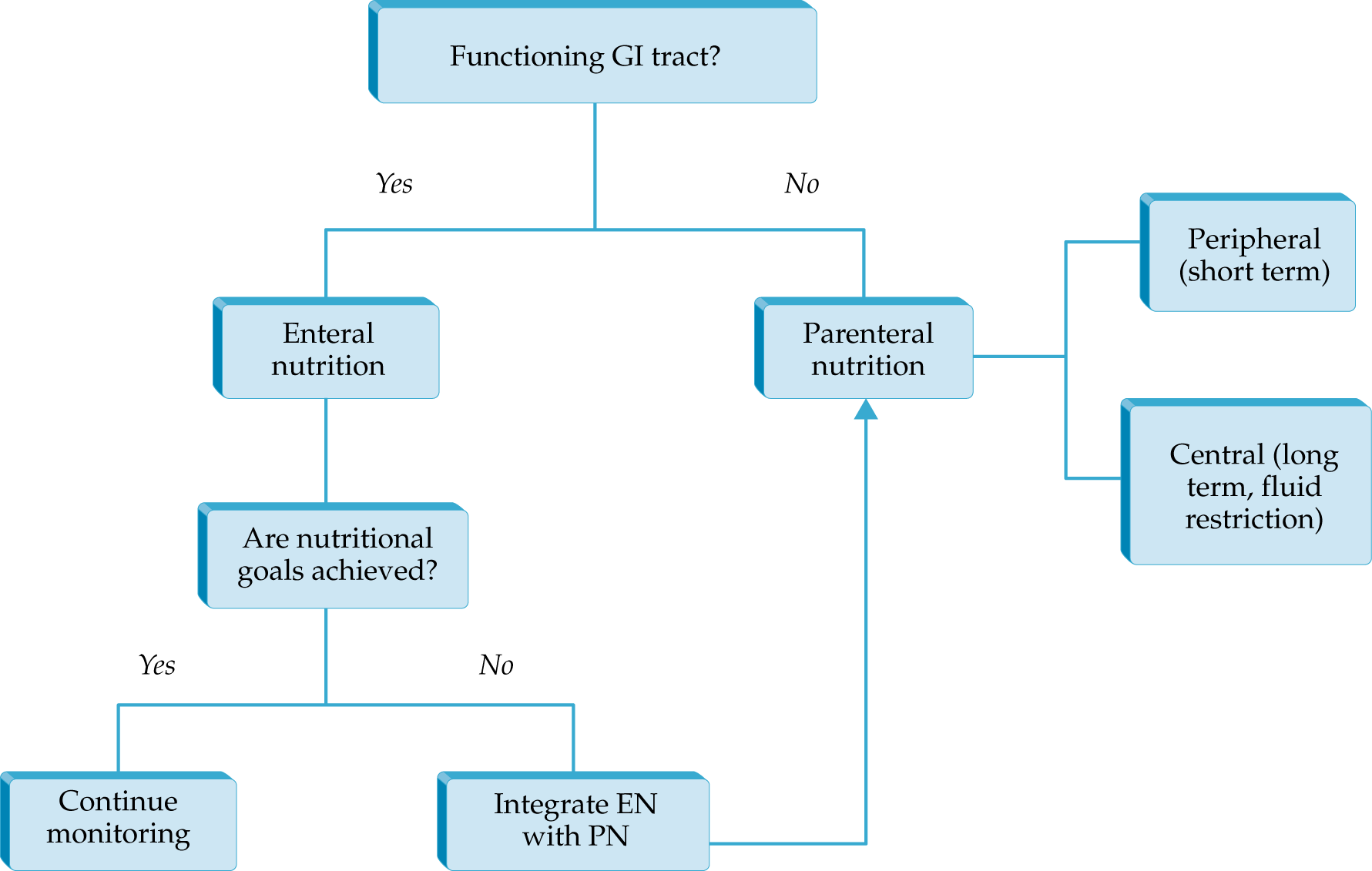
Nutritional Support in Acute Kidney Injury
- Data on critically ill patients consolidated the concept that nutritional support is associated with improvement of clinical outcome.
- Nutrient needs in patients with AKI can be difficult to estimate and should be directly measured.
- Nutritional support in the ICU should be targeted not only to mitigate the negative effects of the underlying disease on lean body mass but also to avoid further deterioration of the internal milieu.
- Targeting calcitonin gene related peptide can improve migraine pain
- Greater occipital nerve blocks may alleviate migraine acutely
- Clinical decision rules can be used to exclude subarachnoid hemorrhage
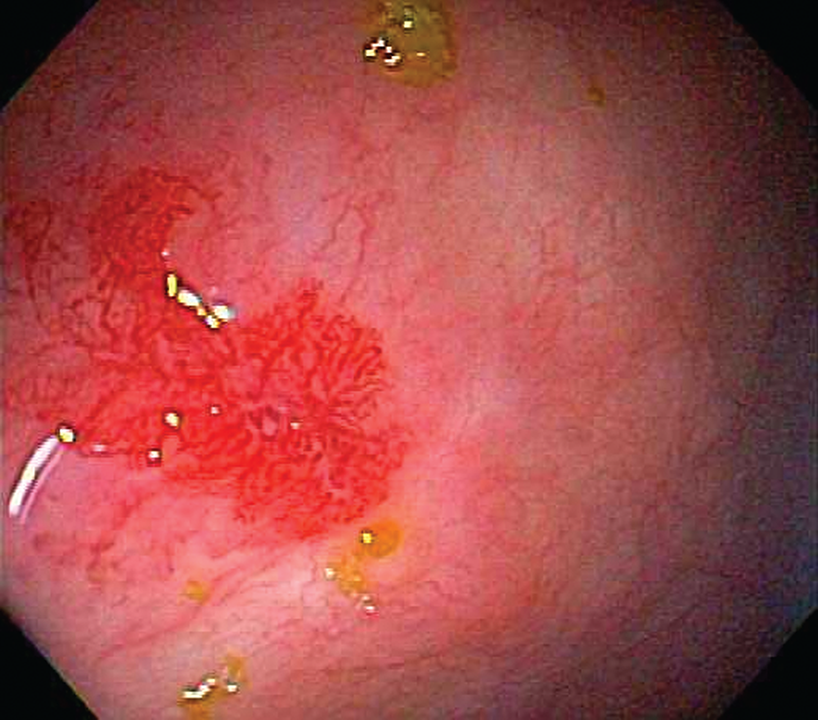
- Patients with gastrointestinal bleeding are critically ill. It is imperative to obtain early expert consultation and definitive care while resuscitation and stabilization begin; consults may include Gastroenterology, Surgery, and Interventional Radiology.
- Blood transfusions are indicated for patients with hemoglobin < 7 g/dL or < 9 g/dL if there is evidence of end-organ ischemia.
- Evidence-based clinical risk scores such as the Blatchford and Rockall scores can guide disposition decisions.
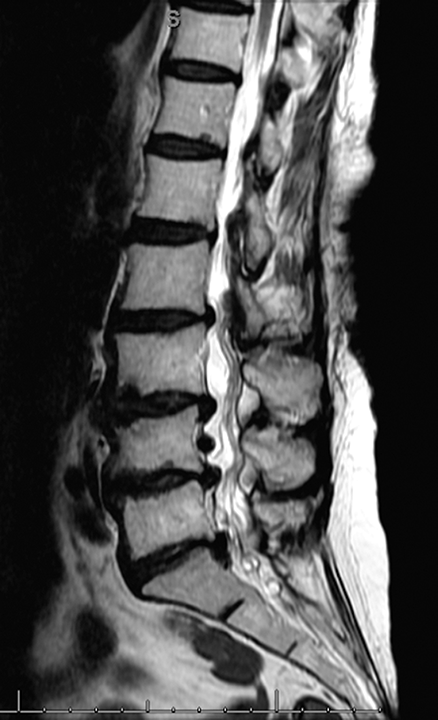
Back Pain and Common Musculoskeletal Problems
- 2018 AAFP Key Recommendations for Heel Pain
- 2017 AAFP Practice Guidelines – Low Back Pain: Noninvasive Management
- 2015 AAFP Key Recommendations for Corticosteroid Injections – Common Musculoskeletal Conditions

Treatment of Unhealthy Alcohol Use
- Treatment of unhealthy alcohol use, including mild-moderate AUD, can be initiated in primary care.
- The anticonvulsant, gabapentin, is a viable alternative to benzodiazepines for treating outpatient alcohol withdrawal in select patients.
- New evidence strongly supports the use of disulfiram for AUD when abstinence is the goal.
- Although not FDA approved, gabapentin and topiramate are effective options for treating AUD.


.png)







