- With advancements in non-invasive technologies like cell-free DNA, invasive prenatal testing is becoming less common.
- Chromosomal microarray analysis and genetic panel testing are increasingly employed prenatally to explore genetic causes for abnormalities.
- Care should be taken to consider complex ethical issues surrounding genetic testing during pregnancy.
Latest Updates
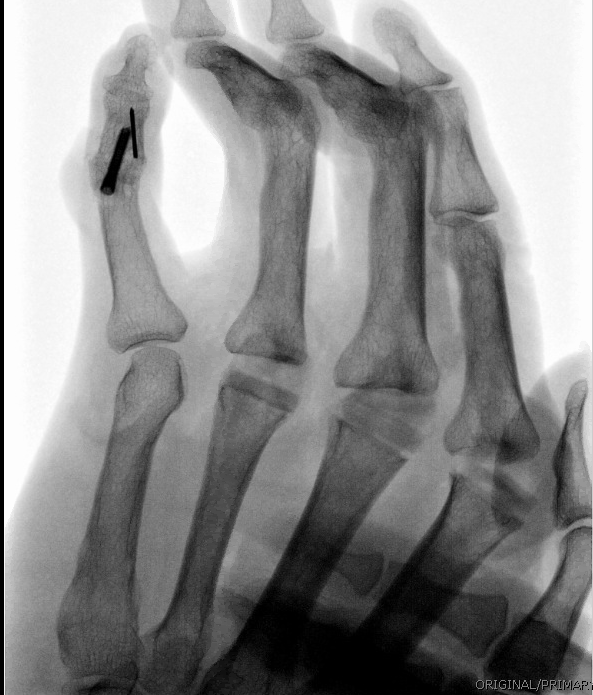
Osteoarthritis of the Interphalangeal and Metacarpophalagneal Joints of the Hand
- Headless screws are effective for distal interphalangeal joint fusion
- Thumb opponens or spica splinting effectively stabilize the metacarpophalangeal joint
- Outcomes are equivalent between silicone and metal/plastic arthroplasty
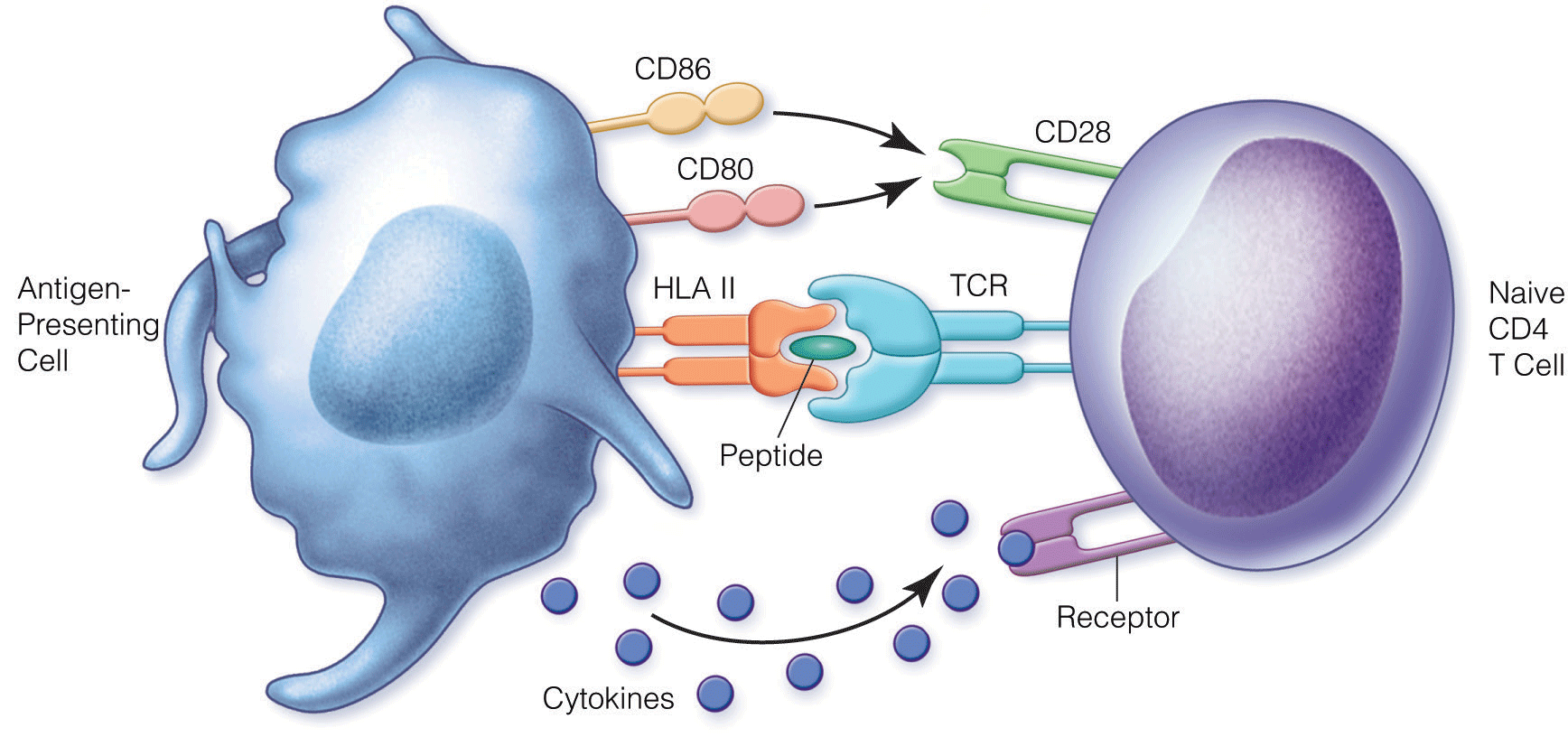
- Elucidation of HLA classes and their role in the complex (with mHAgs, etc) mechanisms of graft rejection have posited different approaches for immunosuppression to maintain graft survival in a recipient.
- Multiple agent approach for complex immunomodulation of recipient immune system, including agents cyclosporine, tacrolimus, belatacept, basiliximab, sirolimus, everolimus, MPA, and alemtuxumab.
- Detailed 2017 Renal Association guidelines delineate strategies, first-line and second-line choices for induction and maintenance immunosuppressive therapies in kidney transplant recipients. Furthermore, this guideline details the approach to management of rejection [see Table 13].

End of Life Care and Withdrawal of Life Support
- Enhanced understanding of differences in palliative care between surgical and medical intensive care units
- Improved specificity of bedside signs and indications for imminent death
- Review of studies in the surgical patient population suggesting palliative care consultation improves end-of-life outcomes without increasing mortality
- Preoperative detection of frailty with subsequent palliative care consultation may result in decreased perioperative mortality

End of Life Care and Withdrawal of Life Support
- Enhanced understanding of differences in palliative care between surgical and medical intensive care units
- Improved specificity of bedside signs and indications for imminent death
- Review of studies in the surgical patient population suggesting palliative care consultation improves end-of-life outcomes without increasing mortality
- Preoperative detection of frailty with subsequent palliative care consultation may result in decreased perioperative mortality
- Evolving CDC recommendations for containment and management of outbreaks that may be linked to bioterrorism. These should be referred to by physicians for the most up-to-date protocols.
- Tecovirimat is a novel agent that was FDA-approved in 2018 for the treatment of smallpox.
- Potential for ribavirin as an antiviral agent in the management of hemorrhagic fever viruses. The efficacy is not well delineated, and further investigation as to this modality is required.
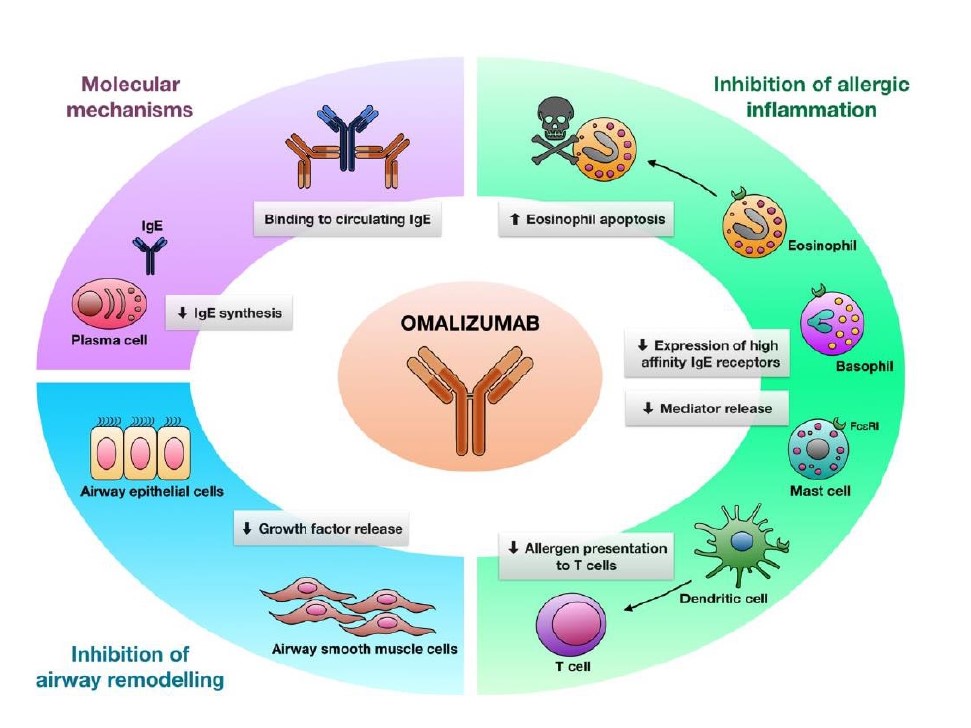
- Control of asthma symptoms may reduce the risk of obstetric complications
- Certain known comorbidities may contribute to more severe asthma exacerbation in pregnancy and should be evaluated.
- For most pregnant patients with asthma, general guidelines for asthma severity evaluation and treatment can be followed, as they would be for non-pregnant patients.
- Safety data on use of biologic agents such as humanized IgG1 monoclonal anti-immunoglobulin E antibody is increasing.
Coma, Cognitive Impairment, and Seizures
- When treating an unresponsive patient, targeted therapy is advised instead of routine use of the “coma cocktail” (empirical treatment with dextrose, naloxone, thiamine, and sometimes flumazenil).
- Avoidance of hypotension and maintenance of normoglycemia and normothermia are critical to the management of intracranial hypertension.
- Differing levels of awareness were noted among patients found to be in a minimally conscious state (MCS); subsequently, this condition was further subdivided into two categories, MCS plus (MCS+) and MCS minus (MCS-), based on the ability to follow commands versus just visual pursuit. Permanent vegetative state is no longer used.


.png)







