Repair of Femoral and Popliteal Artery Aneurysms
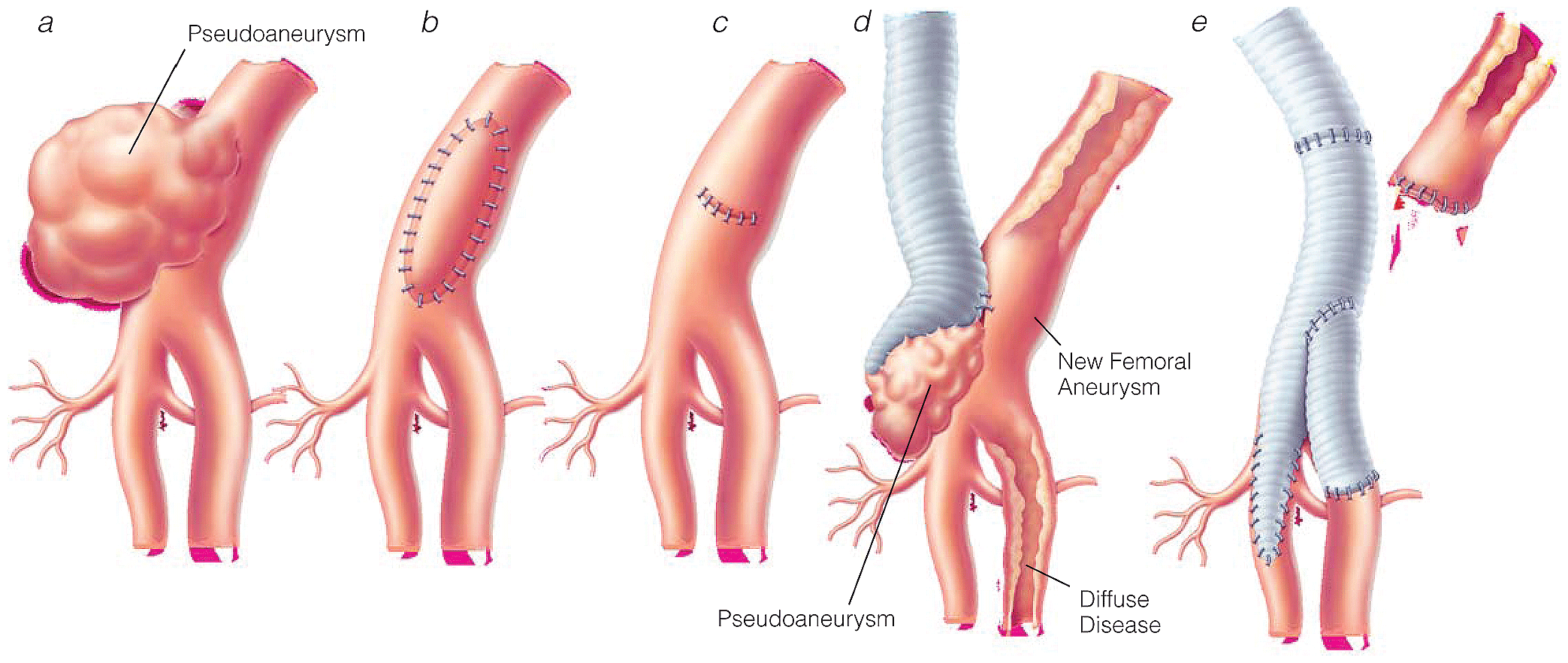
- Reported 5-year patency rate for saphenous vein and Dacron interposition grafts used for repair of isolated femoral artery aneurysms is 80 to 83%. Limitations on endovascular techniques are attributable to flexion and extension stresses at the femoral artery crossing the joint crease.
- Popliteal artery aneurysm repair is often preferred with autogenous vein, but synthetic grafts may be required if autogenous vein is unavailable/inadequate. An innovative option is popliteal reconstruction using superficial femoral artery autograft and replacing superficial femoral artery segment with synthetic interposition when suitable autogenous vein is absent.
- Intraoperative completion angiography is recommended to allow detection and correction of technical problems with reconstruction before closure in cases of popliteal artery aneurysm repair.


.png)







