Neurobiology of Psychotic Disorders
- Polygeneic risk stratification scores in development, with associated multi-biomarker assays in assessment of psychosis risk.
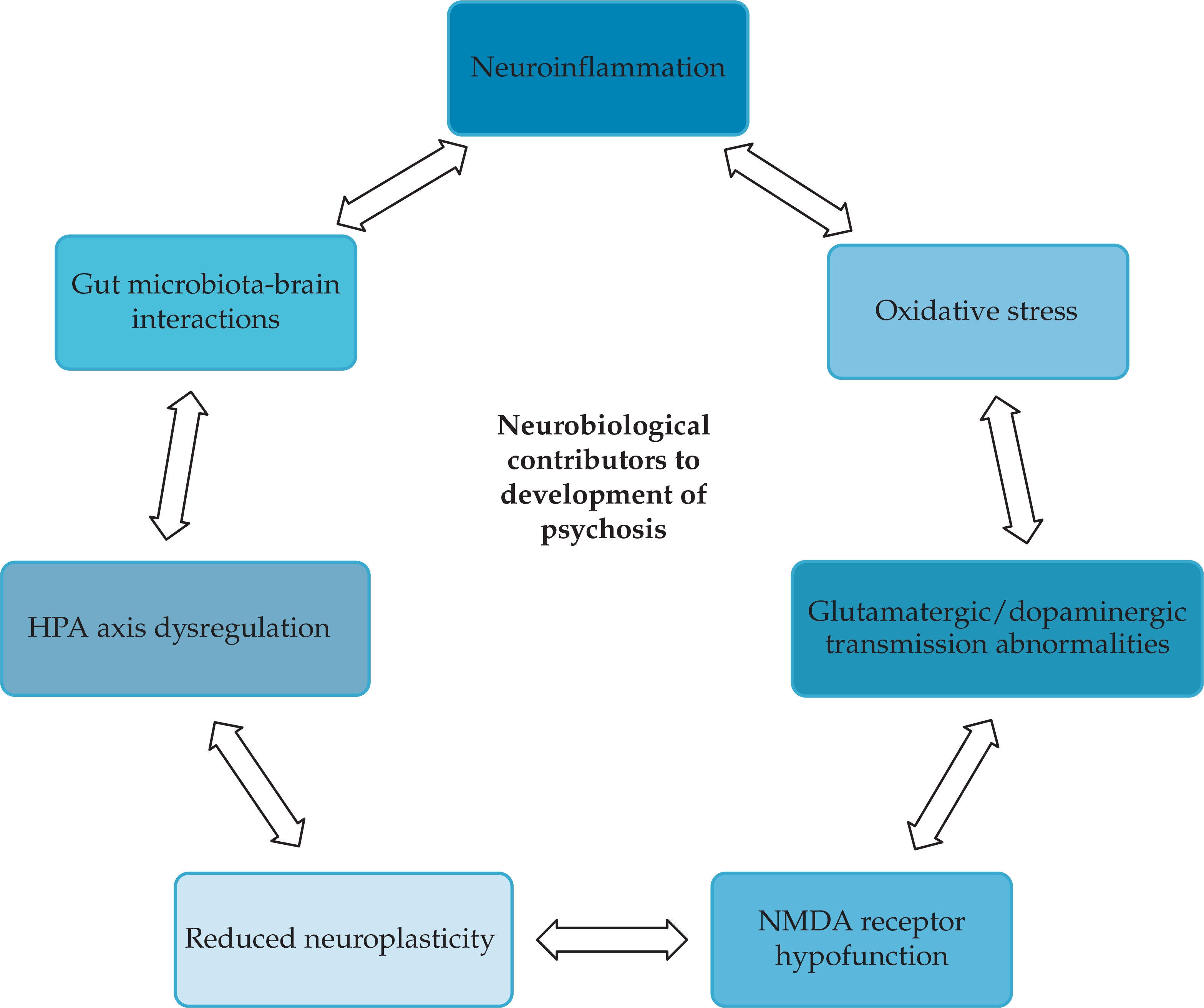
- Microbiome and potential link to psychosis and its interventions. It has been shown that gut microbiota may have an influential role on the course of psychosis and risk.
- Mindfulness therapies and their potential indication in psychosis treatment. Cognitive therapies show promising benefits in management of psychotic symptoms and course, and are outlined as an important aspect in therapy as per the 2020 APA practice guidelines.


.png)







