Panic Attacks and Anxiety Disorders
- A patient with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is more likely to initially present for treatment in a medical, rather than mental health, setting; however, primary care physicians recognize symptoms of PTSD in these patients only approximately 50% of the time, and often do not make the diagnosis. Patients presenting to the emergency department for physical trauma are at risk, as are combat veterans and victims of rape or domestic violence. In addition, patients undergoing frightening, painful or life-threatening medical illnesses or procedures may develop PTSD. The provision of support and information about PTSD to patients in the emergency department may enable early recognition of the symptoms and may prevent the development of full-blown PTSD.
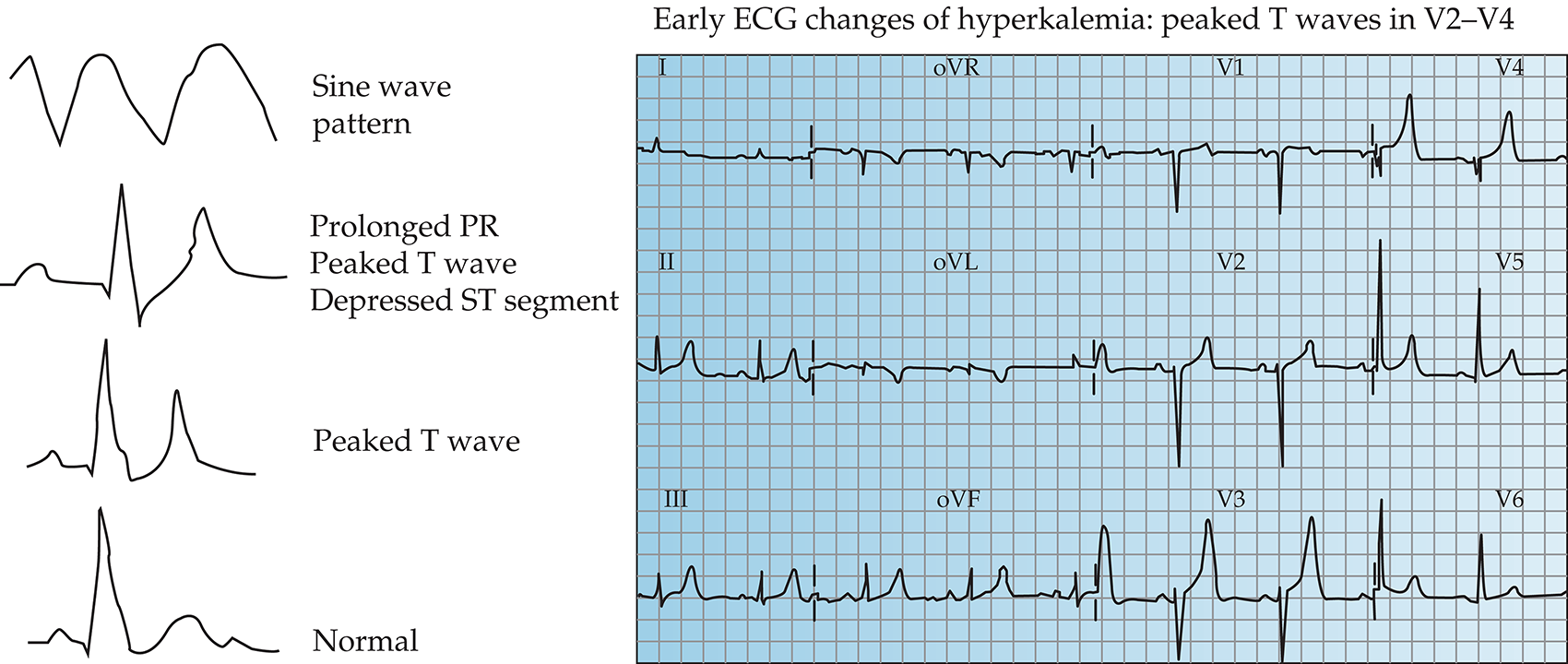
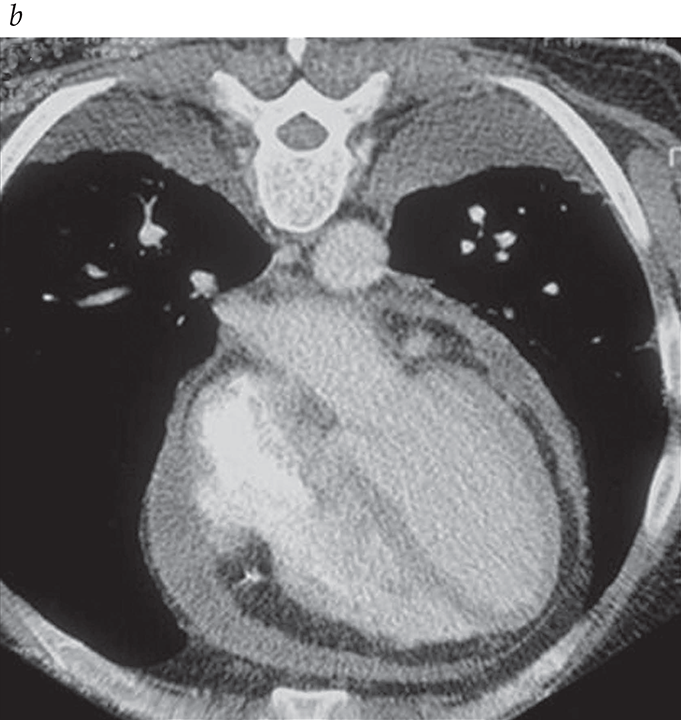
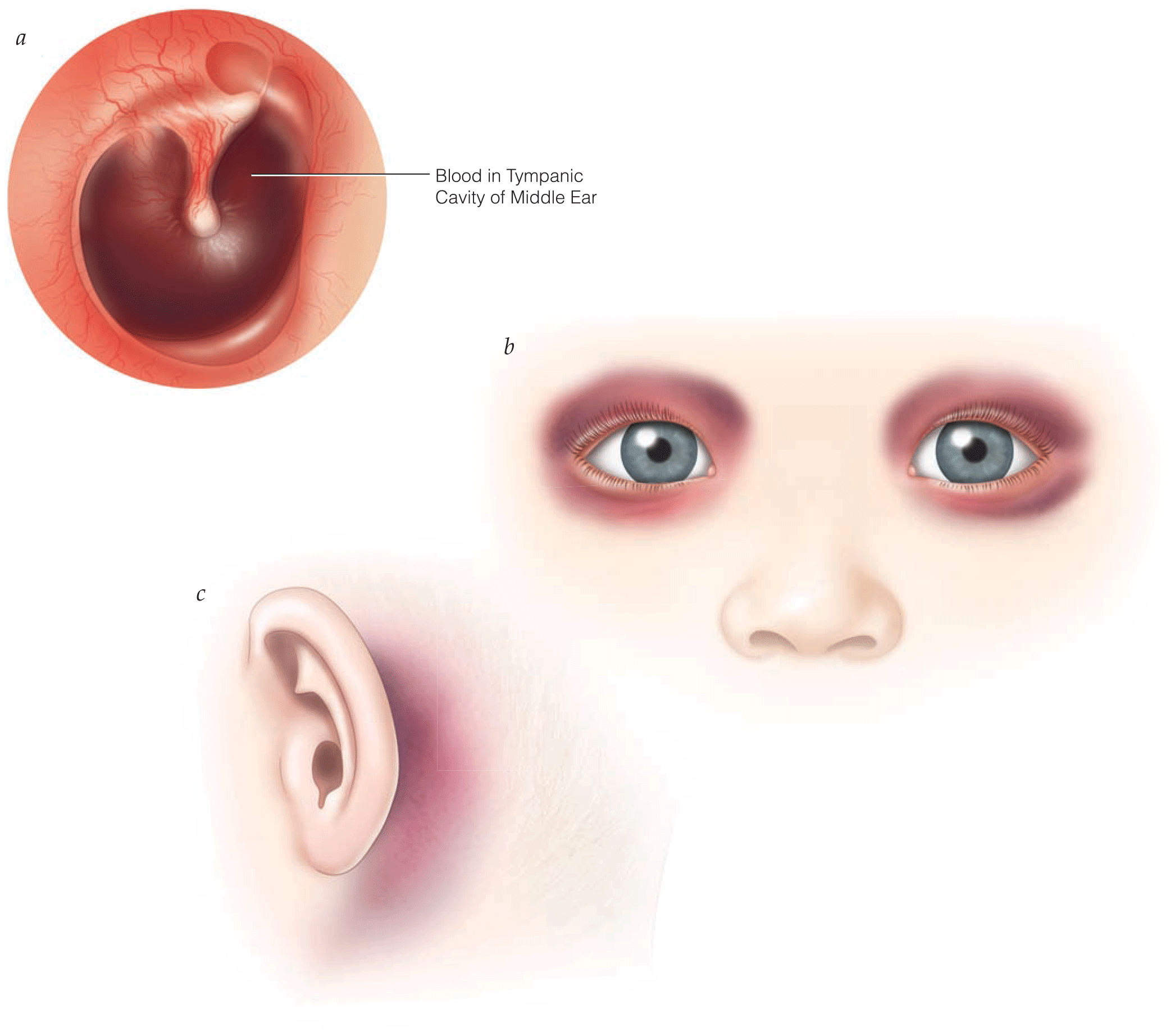
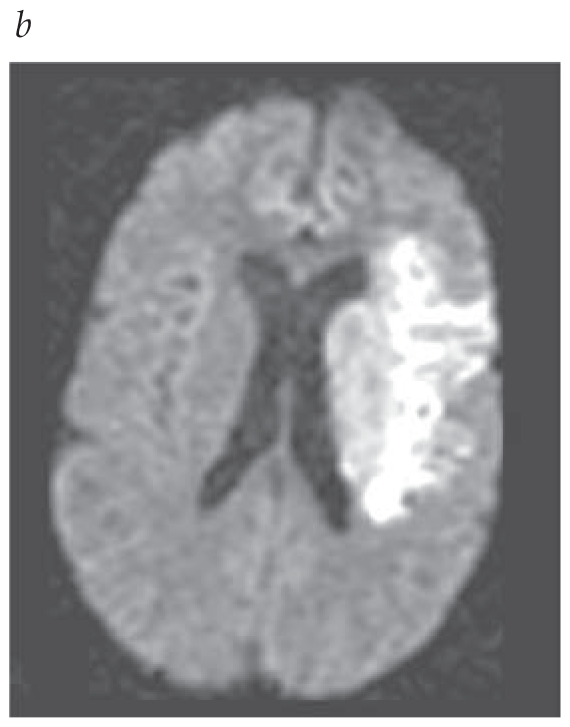



.png)







