- In the last decade, dozens of novel agents of abuse have emerged, many of them chemical variants of the naturally occurring cathinone found in the plant Catha edulis.
- Synthetic cathinones may be sold under the name of bath salts or plant food to subvert legal restrictions on their use. Their beta-ketone amphetamine structure results in their amphetamine-like sympathomimetic effects. However, synthetic cathinones also seem to modulate serotonin release, resulting in various psychoactive effects.
- Toxicity in patients using synthetic cathinones varies from euphoria and intoxication, to florid violent hallucinations, hyperthermia, rhabdomyolysis, seizures, and death. Unlike many other street drugs, synthetic cathinones are often known more commonly by their street name (e.g., bath salts), with the exact chemical composition changing over time in response to legal pressures.
Latest Updates

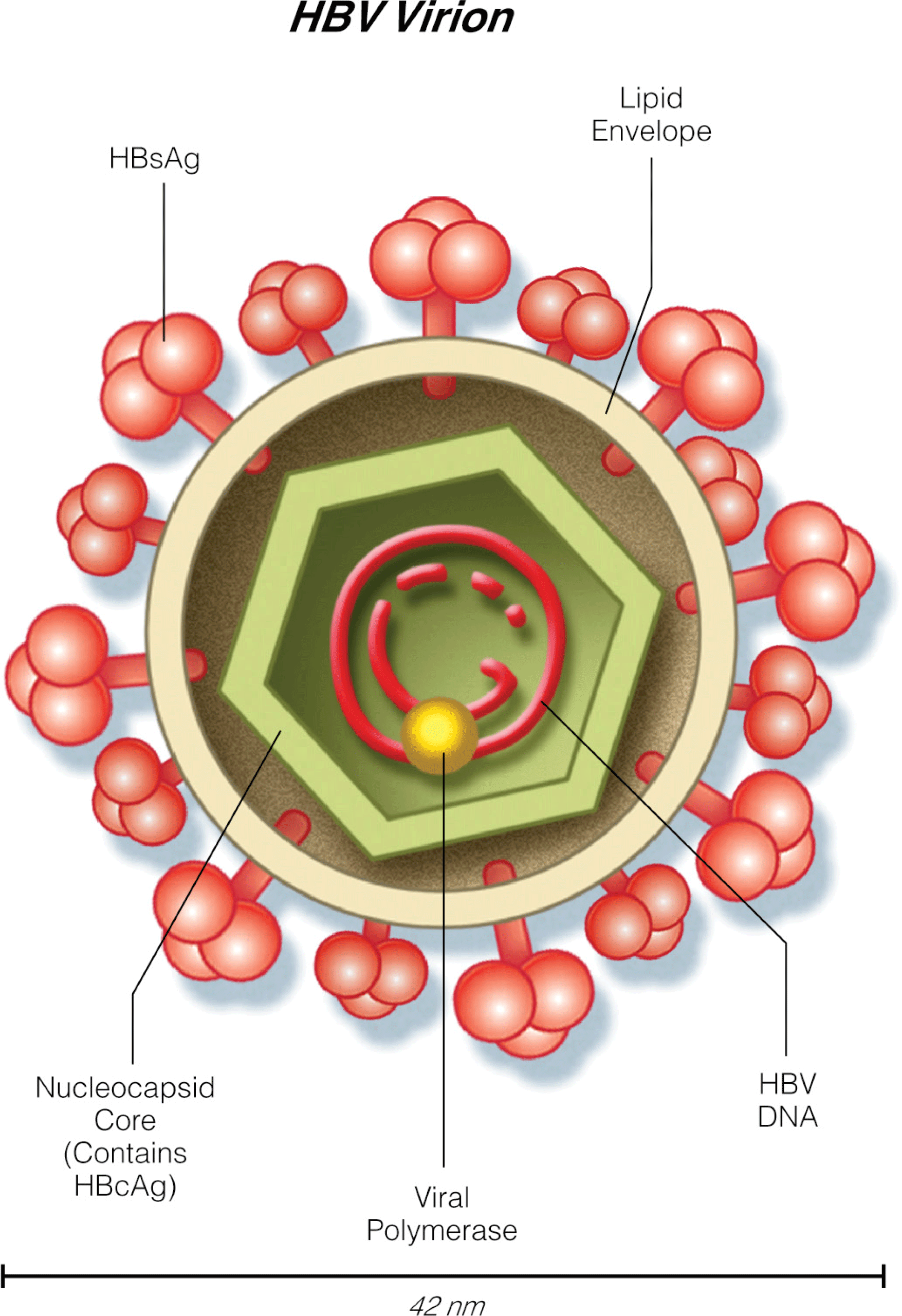
- Tenofovir alafenamide (AF) was FDA approved in November 2016 for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. It has enhanced plasma stability and more efficient delivery to the hepatocytes with a lower dose compared with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (DF). Tenofovir AF has similar efficacy to tenofovir DF but less nephrotoxicity (smaller increase in serum Cr and median changes in estimated GFR) and bone toxicity (smaller mean percentage decrease from baseline hip and spine bone mineral density).
- Major advances in basic research in hepatitis B are paving the way for the identification of new therapeutic targets with the goal of complete cure with physical elimination of cccDNA.
- Postmarketing studies have demonstrated a risk of HBV reactivation during treatment with hepatitis C direct antiviral agents, and it is recommended to monitor patients with HBV-HCV coinfection with serial lab tests and consider concomitant HBV treatment analogue for patients who meet the standard criteria for HBV treatment.
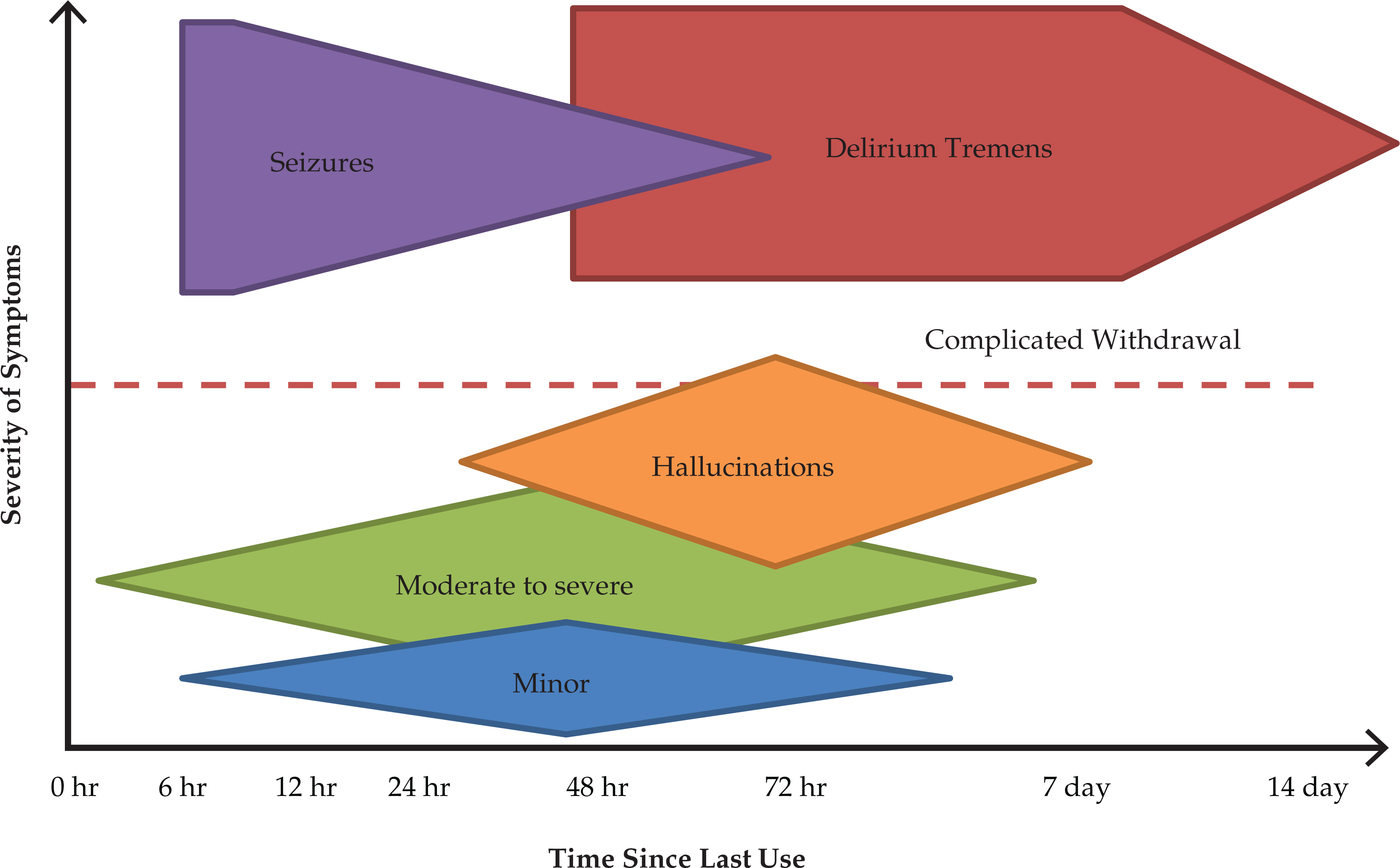
Alcohol and Drug Withdrawal Syndromes and Their Clinical Management
- Many published protocols for safely managing severe alcohol withdrawal (specifically delirium tremens) in the intensive care setting
- Increased outpatient treatment options for opioid withdrawal
- Increased focus on cannabis withdrawal syndrome (now included in the DSM-5), which will increase withdrawal and abstinence treatment research
- Updated with 2020 ASAM Practice Guidelines: Opioid Use Disorder

Alcohol and Drug Withdrawal Syndromes and Their Clinical Management
- Many published protocols for safely managing severe alcohol withdrawal (specifically delirium tremens) in the intensive care setting
- Increased outpatient treatment options for opioid withdrawal
- Increased focus on cannabis withdrawal syndrome (now included in the DSM-5), which will increase withdrawal and abstinence treatment research
- Updated with 2020 ASAM Practice Guidelines: Opioid Use Disorder

Alcohol and Drug Withdrawal Syndromes and Their Clinical Management
- Many published protocols for safely managing severe alcohol withdrawal (specifically delirium tremens) in the intensive care setting
- Increased outpatient treatment options for opioid withdrawal
- Increased focus on cannabis withdrawal syndrome (now included in the DSM-5), which will increase withdrawal and abstinence treatment research
- Updated with 2020 ASAM Practice Guidelines: Opioid Use Disorder

Alcohol and Drug Withdrawal Syndromes and Their Clinical Management
- Many published protocols for safely managing severe alcohol withdrawal (specifically delirium tremens) in the intensive care setting
- Increased outpatient treatment options for opioid withdrawal
- Increased focus on cannabis withdrawal syndrome (now included in the DSM-5), which will increase withdrawal and abstinence treatment research
- Updated with 2020 ASAM Practice Guidelines: Opioid Use Disorder
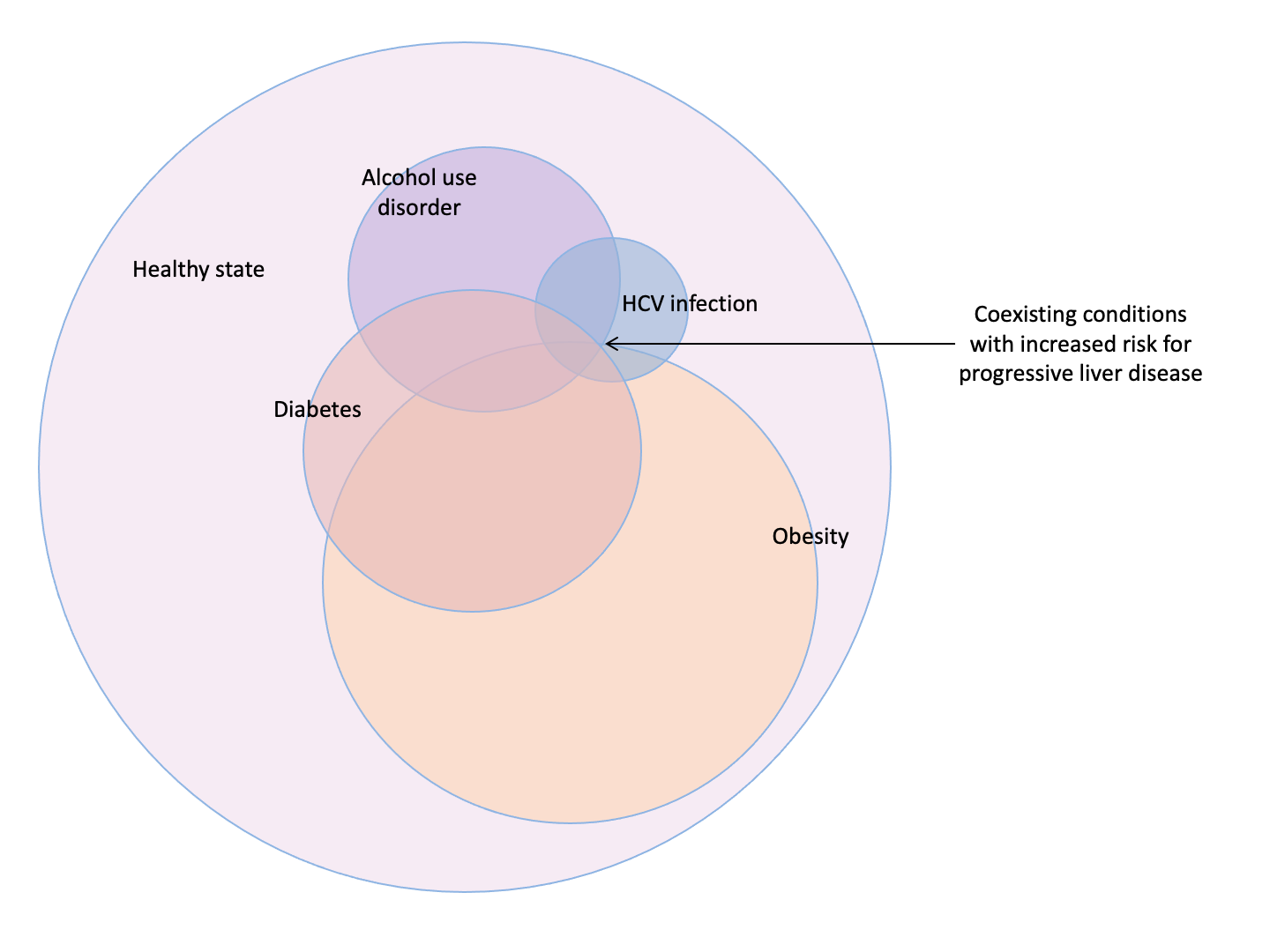
- The AUDIT-C questionnaire is a fast and reliable tool to screen patients for alcohol use disorder (AUD)
- In patients with AUD and liver disease, disulfiram or baclofen should be considered for preventing AUD relapse
- In patients with severe alcohol-associated hepatitis (AAH) identified by the Maddrey’s discriminant function (≥ 32), a trial of prednisolone is a reasonable therapeutic strategy
- Carefully selected cases of severe AAH identified by the Lille score as non-responders to pharmacotherapy (≥ 0.45) should be considered for early liver transplantation
- New post-liver transplant scores may predict harmful (HALT) and sustained (SALT) relapse of AUD and help patient selection for transplantation

- The AUDIT-C questionnaire is a fast and reliable tool to screen patients for alcohol use disorder (AUD)
- In patients with AUD and liver disease, disulfiram or baclofen should be considered for preventing AUD relapse
- In patients with severe alcohol-associated hepatitis (AAH) identified by the Maddrey’s discriminant function (≥ 32), a trial of prednisolone is a reasonable therapeutic strategy
- Carefully selected cases of severe AAH identified by the Lille score as non-responders to pharmacotherapy (≥ 0.45) should be considered for early liver transplantation
- New post-liver transplant scores may predict harmful (HALT) and sustained (SALT) relapse of AUD and help patient selection for transplantation


.png)







