- Advances are being made in the realm of treatment, including new short acting Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor medications, such as Neupogen (Filgrastim), Zarxio (Filgrastim-sndz), Fulphila (Pegfilgrastim-jmdb), and Leukine (Sargramostim) which have been FDA approved for treatment of severe neutropenia.
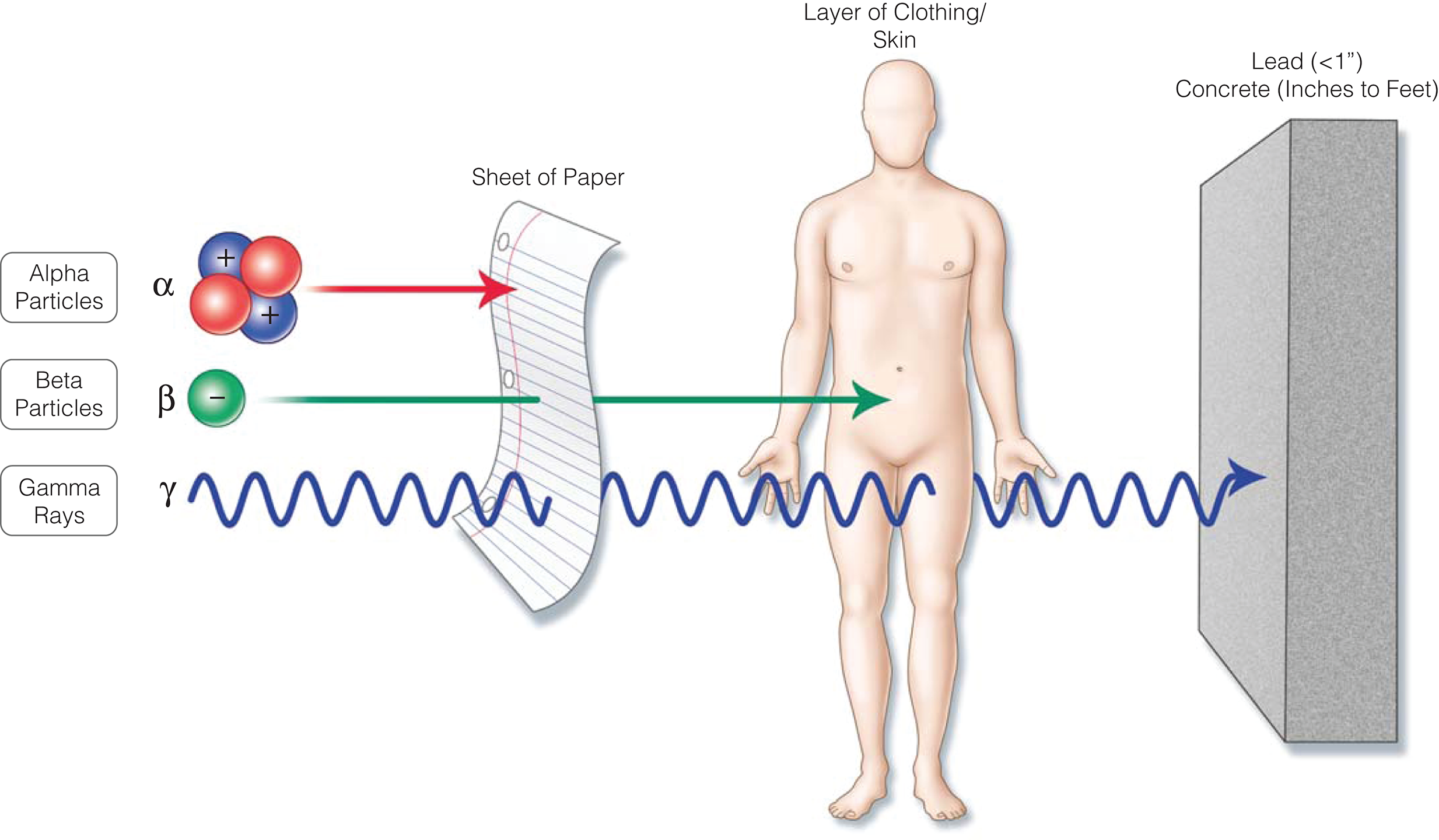
- Previously accepted policies due to "radiation phobia" by those in the scientific community were based on a linear-no threshold scale for radiation dose and the link to cancers such as leukemia. These scales continue to be discredited as being magnitudes lower than the observed rates of incidence. In current literature, scientists are challenging the idea that the dose threshold for exposure is as low as we accept right now (~ 100 mSV) and in fact are demonstrating that the increased risk for cancer development amongst individuals exposed to similar doses does not exist until a much higher radiation dose. Scientists will continue to follow this and establish an acceptable recommendations because of the ubiquitous nature of radiation exposure in our medical and industrial lives.
- Patients developing hematopoietic syndrome, or even simply anemia, after significant exposure to radiation requiring blood transfusion are at increased risk of developing Graft-versus-Host disease. Current guidelines state that, when possible, cellular transfusion products (i.e, whole blood, pRBCs) should be irradiated with at least 25 Gy prior to administration. The samples should also undergo leukocyte reduction as well. In situations of mass casualty incidents, guideline therapy may be adjusted based on the supply of blood available against the anticipated need for blood on mass scale.
Latest Updates
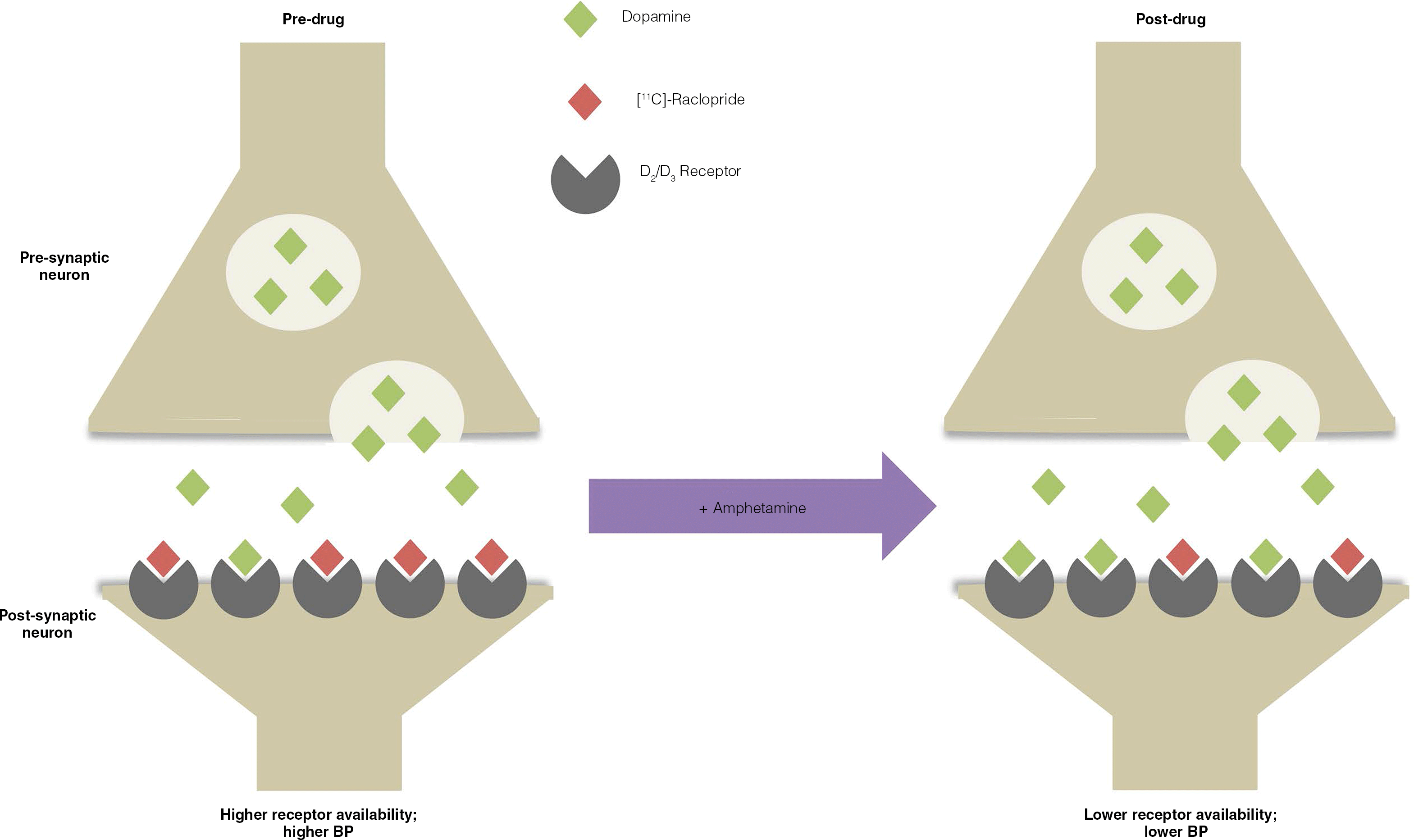
- Epidemiology of and heritable risk factors for developing addictive disorders
- Dysregulated brain networks and neurochemical systems in several substance and nonsubstance addictions
- Treatment options for substance and nonsubstance addictions
- Updated with 2020 ASAM Practice Guidelines: Opioid Use Disorders
- Nonpharmacologic measures that have the potential to improve outcomes in osteoarthritis include patient education, physical and occupational therapy assessment and interventions, exercise, weight loss, and dietary measures.
- Therapies with potential to prevent or retard the progression of articular cartilage breakdown have received a great deal of attention in recent years, including tetracyclines, protease inhibitors, antiresorptive agents (i.e., bisphosphonates, calcitonin), glycosaminoglycan compounds, growth factors, and cytokine inhibitors.
- In patients with badly damaged knees and hips, total joint replacement is an effective option. Almost all patients experience significant pain relief, and some have improved range of motion. Joint loosening and infection are potential late complications in prosthetic joints but are uncommon.
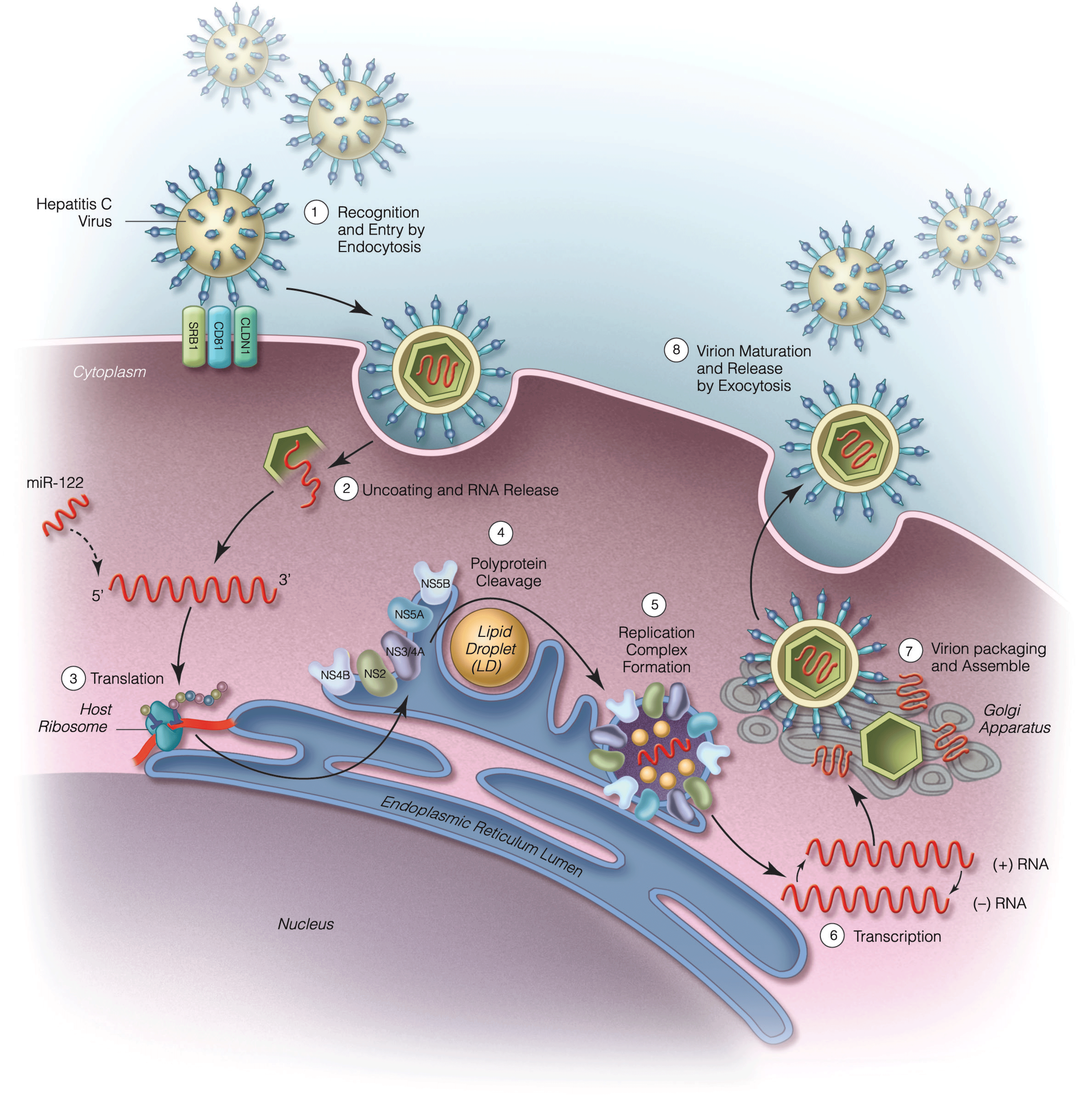
Viral Hepatitis C: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Transmission, And Natural History
- Changing incidence and prevalence of HCV
- Increasing burden of HCV-related liver disease

- Nonpharmacologic measures that have the potential to improve outcomes in osteoarthritis include patient education, physical and occupational therapy assessment and interventions, exercise, weight loss, and dietary measures.
- Therapies with potential to prevent or retard the progression of articular cartilage breakdown have received a great deal of attention in recent years, including tetracyclines, protease inhibitors, antiresorptive agents (i.e., bisphosphonates, calcitonin), glycosaminoglycan compounds, growth factors, and cytokine inhibitors.
- In patients with badly damaged knees and hips, total joint replacement is an effective option. Almost all patients experience significant pain relief, and some have improved range of motion. Joint loosening and infection are potential late complications in prosthetic joints but are uncommon.
- 2019 ACR/AF Practice Guidelines: Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Knee, and Hip

- Nonpharmacologic measures that have the potential to improve outcomes in osteoarthritis include patient education, physical and occupational therapy assessment and interventions, exercise, weight loss, and dietary measures.
- Therapies with potential to prevent or retard the progression of articular cartilage breakdown have received a great deal of attention in recent years, including tetracyclines, protease inhibitors, antiresorptive agents (i.e., bisphosphonates, calcitonin), glycosaminoglycan compounds, growth factors, and cytokine inhibitors.
- In patients with badly damaged knees and hips, total joint replacement is an effective option. Almost all patients experience significant pain relief, and some have improved range of motion. Joint loosening and infection are potential late complications in prosthetic joints but are uncommon.
- 2019 ACR/AF Practice Guidelines: Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Knee, and Hip
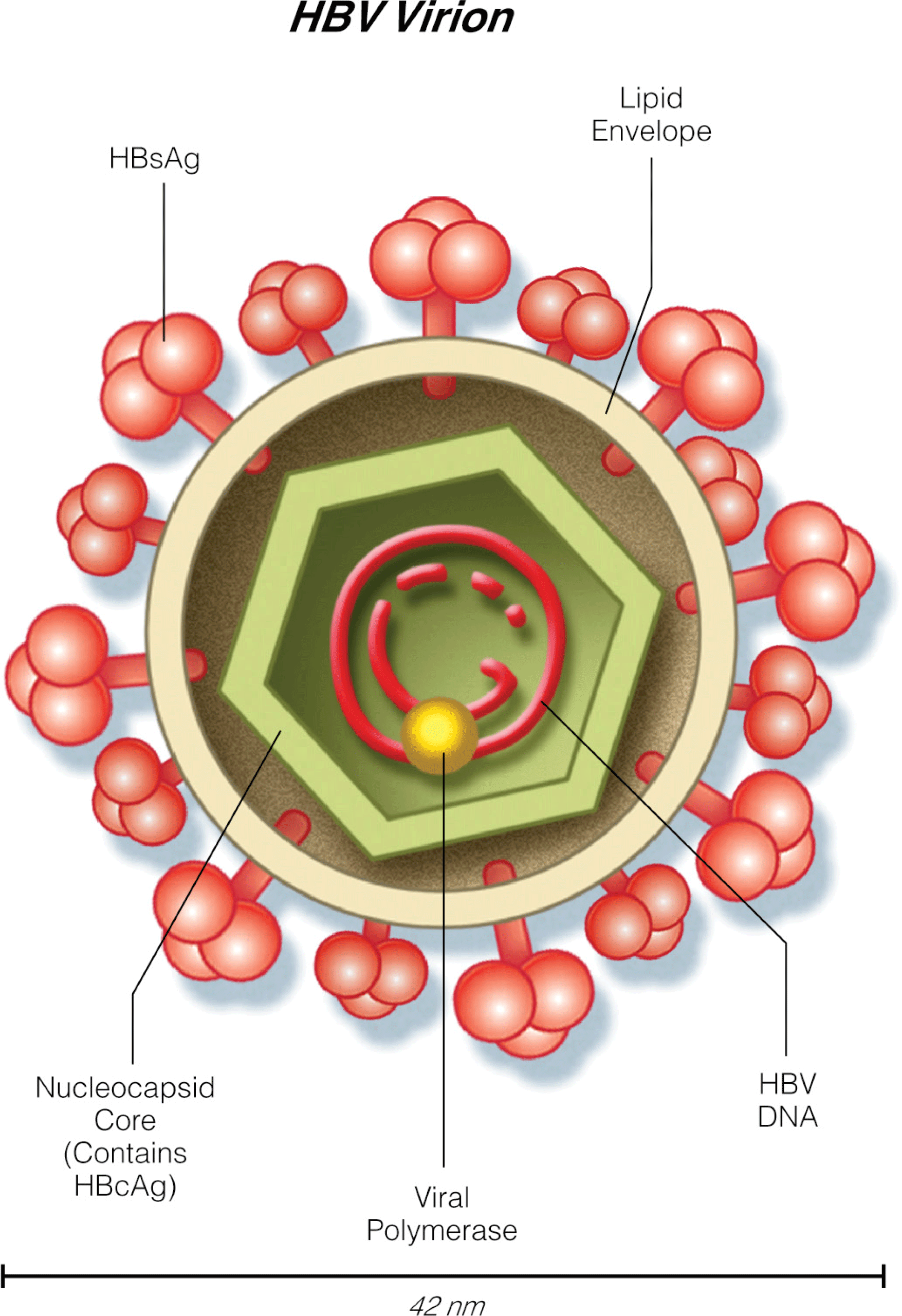
- Tenofovir alafenamide (AF) was FDA approved in November 2016 for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. It has enhanced plasma stability and more efficient delivery to the hepatocytes with a lower dose compared with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (DF). Tenofovir AF has similar efficacy to tenofovir DF but less nephrotoxicity (smaller increase in serum Cr and median changes in estimated GFR) and bone toxicity (smaller mean percentage decrease from baseline hip and spine bone mineral density).
- Major advances in basic research in hepatitis B are paving the way for the identification of new therapeutic targets with the goal of complete cure with physical elimination of cccDNA.
- Postmarketing studies have demonstrated a risk of HBV reactivation during treatment with hepatitis C direct antiviral agents, and it is recommended to monitor patients with HBV-HCV coinfection with serial lab tests and consider concomitant HBV treatment analogue for patients who meet the standard criteria for HBV treatment.
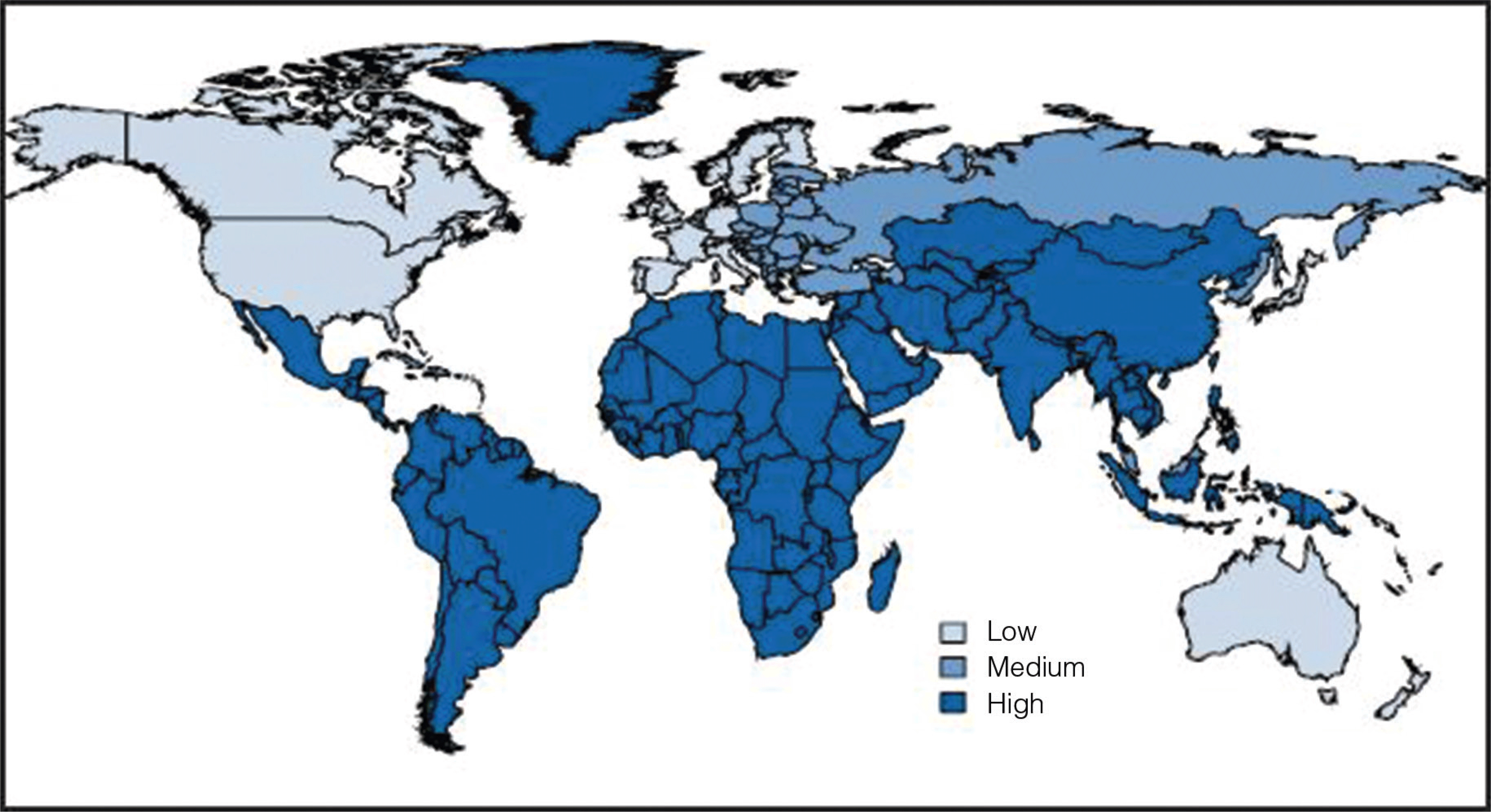
- Several safe and effective vaccines exist to prevent hepatitis A infections.
- Significant morbidity continues to occur in the United States among international travelers, injection drug users, and persons with underlying liver disease.
- In developing countries, the epidemiologic transition has increased the prevalence of clinically severe hepatitis A infections.


.png)







