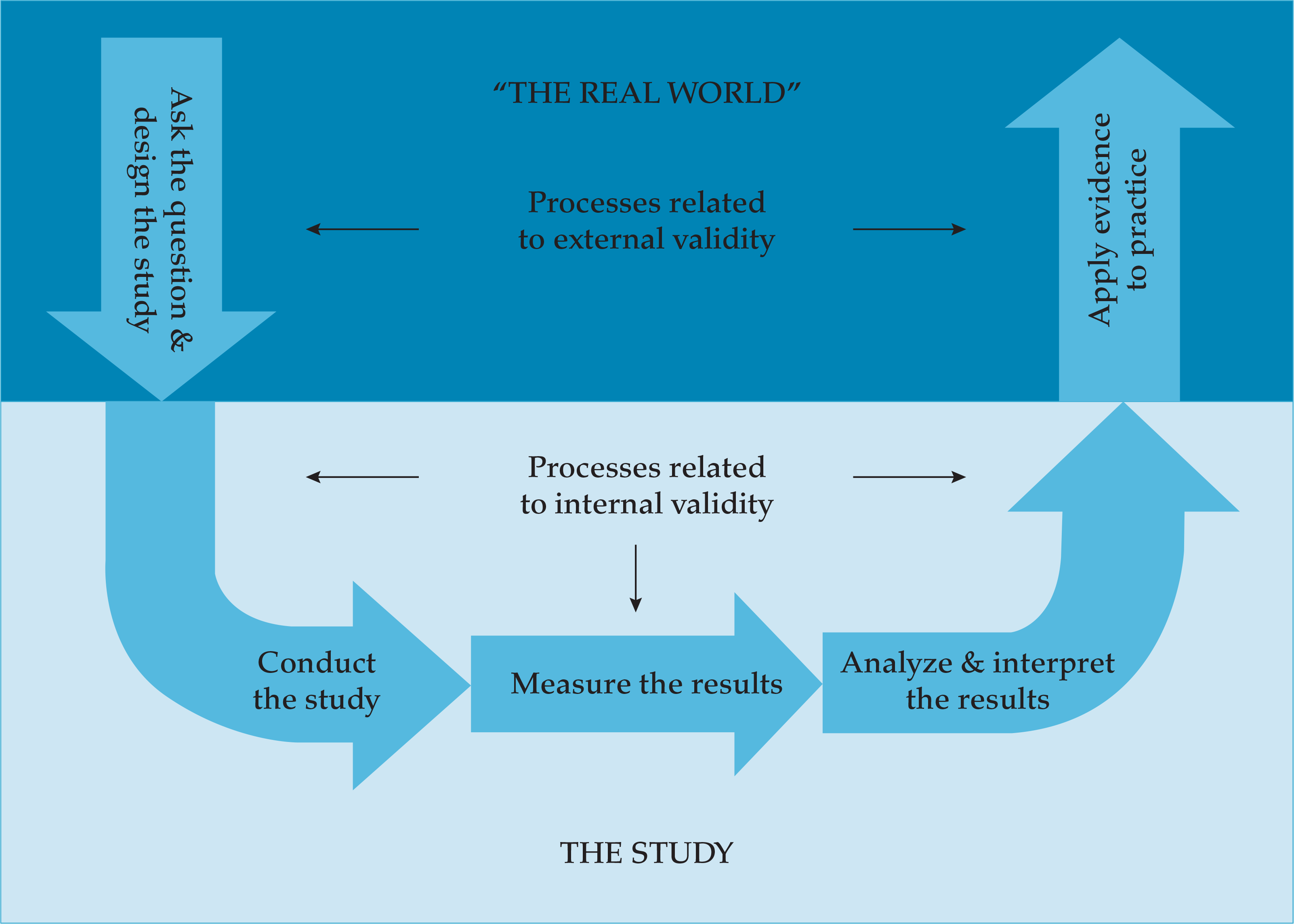
- Methods to appraise the strength of scientific evidence in surgery
- Overview of methods to evaluate the quality of research studies
- Methods to interpret and apply scientific evidence to clinical practice
- Different approaches in clinical and health services research
- Approaches to measuring the quality of care in surgery
Latest Updates

- Methods to appraise the strength of scientific evidence in surgery
- Overview of methods to evaluate the quality of research studies
- Methods to interpret and apply scientific evidence to clinical practice
- Different approaches in clinical and health services research
- Approaches to measuring the quality of care in surgery
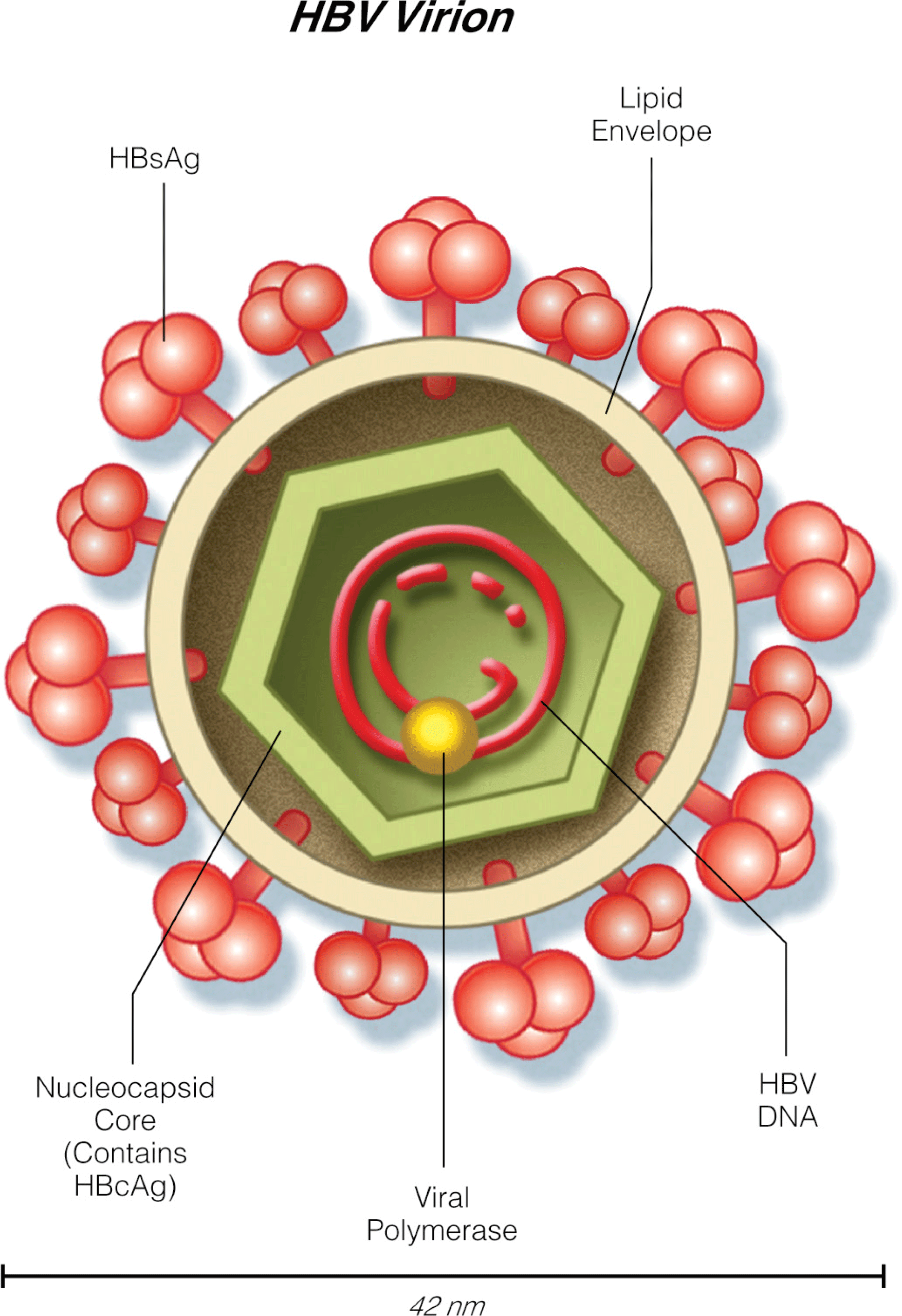
- Tenofovir alafenamide (AF) was FDA approved in November 2016 for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. It has enhanced plasma stability and more efficient delivery to the hepatocytes with a lower dose compared with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (DF). Tenofovir AF has similar efficacy to tenofovir DF but less nephrotoxicity (smaller increase in serum Cr and median changes in estimated GFR) and bone toxicity (smaller mean percentage decrease from baseline hip and spine bone mineral density).
- Major advances in basic research in hepatitis B are paving the way for the identification of new therapeutic targets with the goal of complete cure with physical elimination of cccDNA.
- Postmarketing studies have demonstrated a risk of HBV reactivation during treatment with hepatitis C direct antiviral agents, and it is recommended to monitor patients with HBV-HCV coinfection with serial lab tests and consider concomitant HBV treatment analogue for patients who meet the standard criteria for HBV treatment.
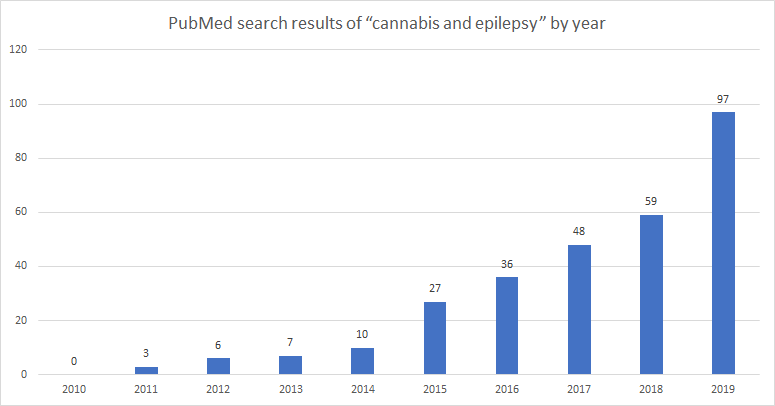
Cannabis for Seizure Disorders
- THC exerts anticonvulsive effects at low doses but may worsen seizure activity at higher doses
- CBD is the preferred agent of study for drug-resistant epilepsy, particularly in childhood epilepsy syndromes that do not respond to AEDs; CBD has shown great promise as an alternative modality in such cases, with a significant reduction in seizure frequency and severity in various models and studies
- Other phytocannabinoids sharing similarities with CBD, such as CBDV, are emerging as candidates to study epileptogenesis intervention
- Pathways implicated in cannabinoid treatment of seizure disorders do not involve CB1 or CB2 receptors; other endocannabinoid receptors predominate in the anticonvulsive mechanisms mediated by intracellular Ca2+ modulation and glutamatergic neurotransmission reduction

Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes
- In the setting of preterm premature rupture of membranes, pregnancy outcome is contingent upon the underlying cause, gestational age at diagnosis and delivery, and presence of complications (placental abruption, infection).
- Latency (time from rupture of membranes to delivery) depends on gestational age, severity of oligohydramnios, number of fetuses (shorter in twins), presence or absence of complications, fetal wellbeing, and use of broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Efforts to reseal ruptured membranes using a variety of tissue sealants has been attempted, but neither the safety nor efficacy of these sealants has yet been established.
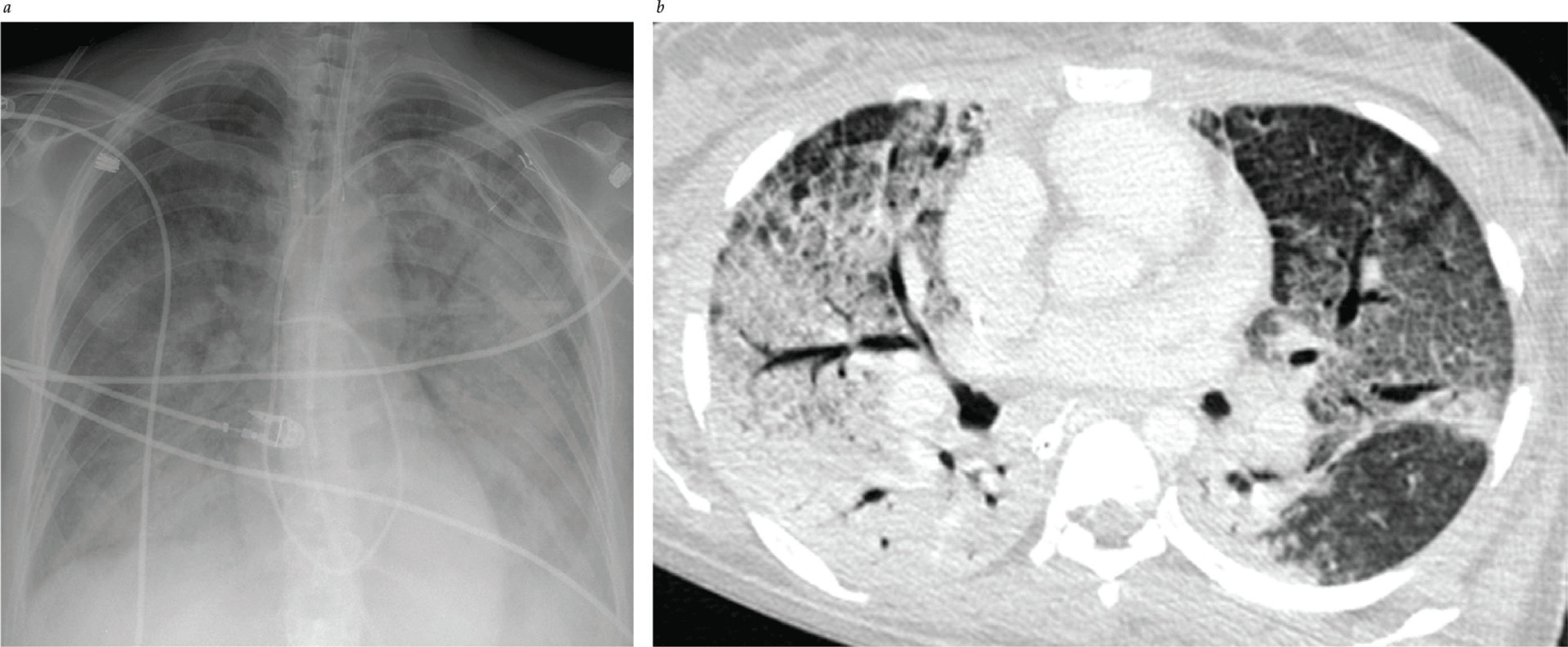
Pulmonary Edema II: Noncardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
- The Berlin definition (2011) is now used to define ARDS. Timing: new or worsening respiratory failure within 1 wk of known clinical insult. Chest imaging: bilateral opacities not fully explained by effusions, atelectasis, or nodules. Oxygenation parameters measured by PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 300, and PEEP or CPAP > 5.
- Recent epidemiologic studies reveal that outcomes for patients with ARDS are improving.
- Machine learning can be used to screen for ARDS using ventilator waveform data. It shows benefit in detecting moderate/severe ARDS without necessity of radiologic and ABG data.
Updated Review
Annette Esper, MD, Greg S Martin, MD, MSc, FACP, Gerald W. Staton Jr, MD, FACP
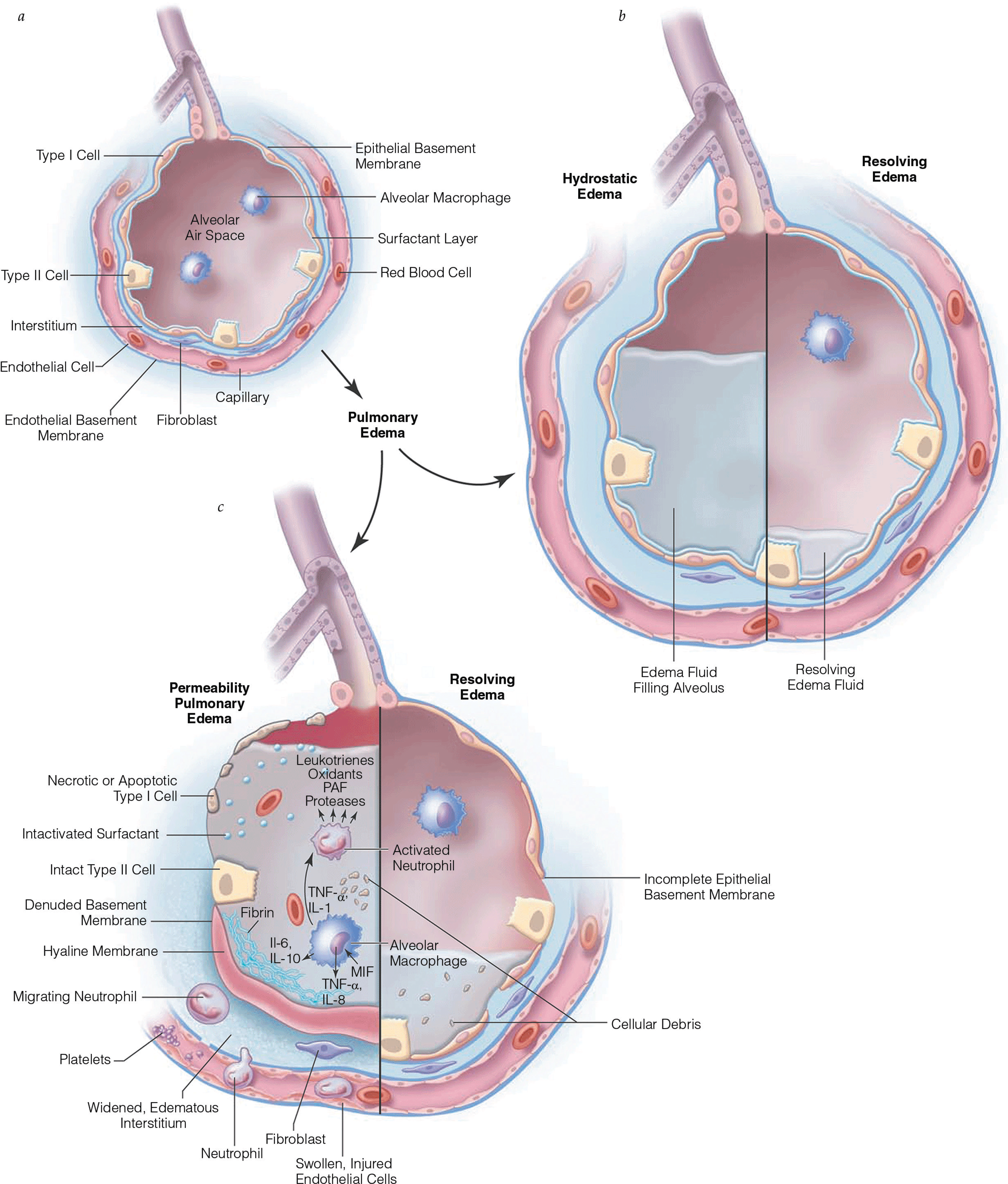
Pulmonary Edema I: Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
- Meta-analyses reveal that noninvasive positive pressure ventilation decreases mortality in patients with acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
- Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NPPV) is useful in treating hypoxemia and decreases the work of breathing and may improve mortality in acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
- Ancillary features that can be routinely visualized on an anteroposterior chest radiograph made with a portable x-ray machine may help differentiate cardiogenic from noncardiogenic pulmonary edema. A widened vascular pedicle and an increase in the cardiothoracic ratio suggest increased pulmonary capillary pressure; distinct air bronchograms are more common with noncardiogenic pulmonary edema.

Pulmonary Edema II: Noncardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
- The Berlin definition (2011) is now used to define ARDS. Timing: new or worsening respiratory failure within 1 wk of known clinical insult. Chest imaging: bilateral opacities not fully explained by effusions, atelectasis, or nodules. Oxygenation parameters measured by PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 300, and PEEP or CPAP > 5.
- Recent epidemiologic studies reveal that outcomes for patients with ARDS are improving.
- Machine learning can be used to screen for ARDS using ventilator waveform data. It shows benefit in detecting moderate/severe ARDS without necessity of radiologic and ABG data.
Updated Review
Annette Esper, MD, Greg S Martin, MD, MSc, FACP, Gerald W. Staton Jr, MD, FACP


.png)







