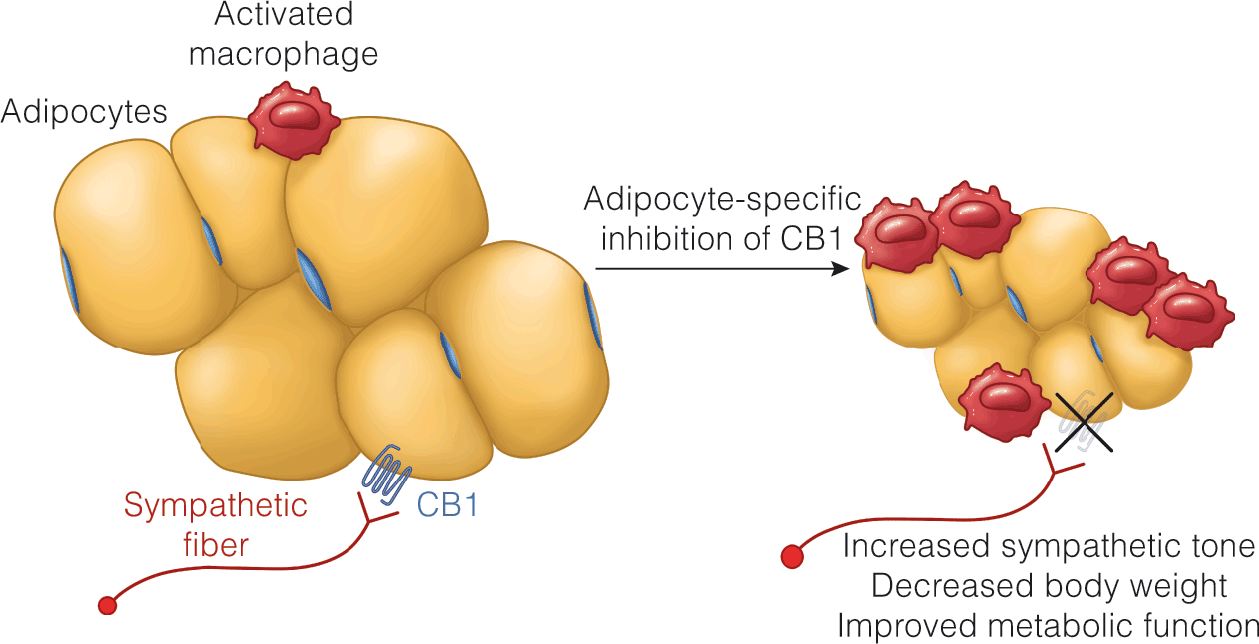
- Cannabis induces differential effects on energy homeostasis in the context of acute vs. chronic use; acute use stimulates energy intake
- Chronic use dampens endogenous eCB tone, decreasing energy storage
- Epidemiologic data demonstrate that chronic cannabis users tend to have lower BMIs with lower prevalence of obesity compared to nonusers
- Full CB1 antagonists (rimonabant) induce weight loss in obese patients, but are associated with psychiatric adverse effects
- Partial agonist/antagonist agents, such as THCV, may solve blockade of eCB tone responsible for increased energy intake, while avoiding adverse effects
Latest Updates
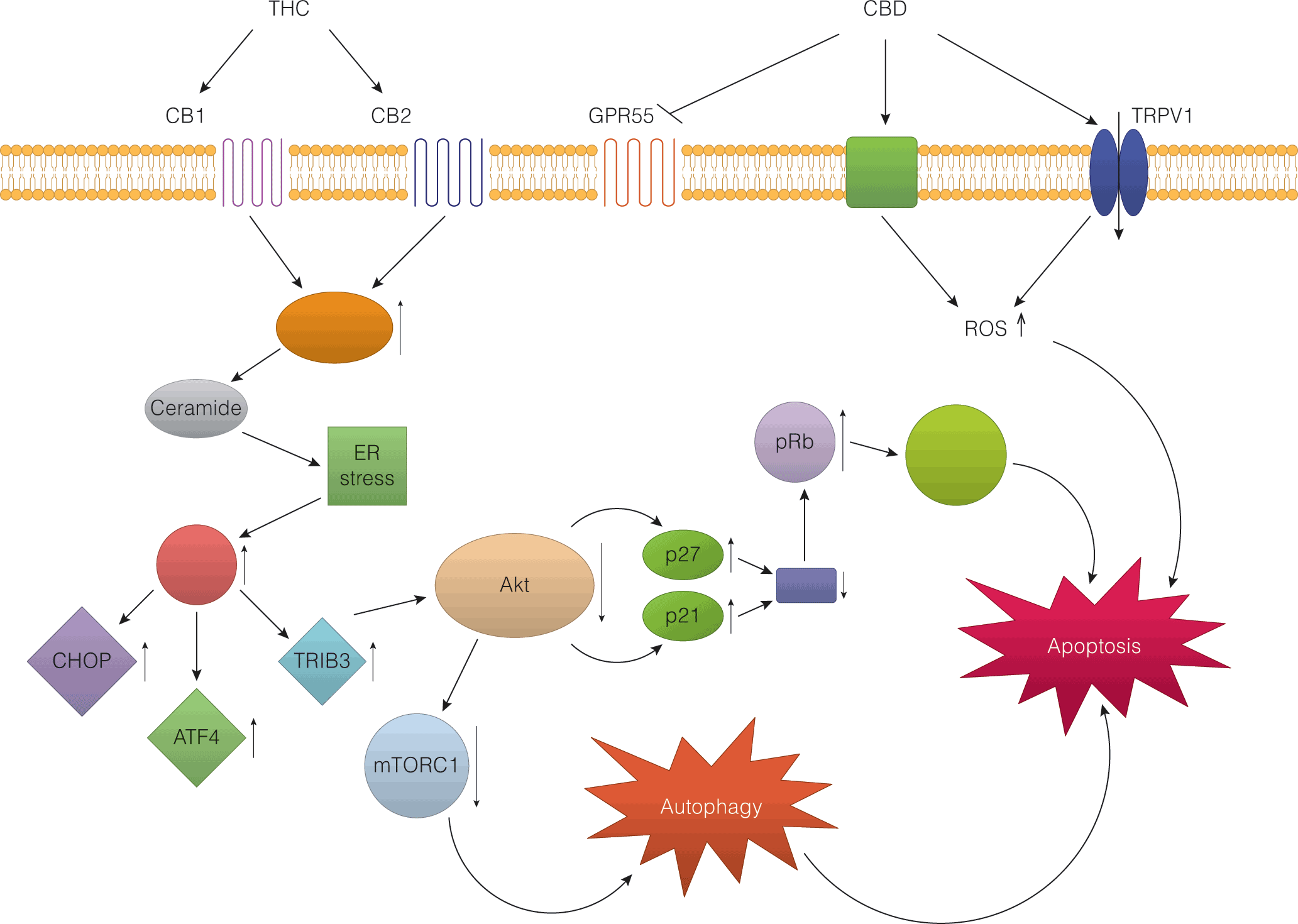
- Recreational cannabis use may be associated with development and progression of certain cancer cell types (eg, hepatocellular carcinoma, prostate cancer, testicular germ cell tumor)
- Cannabis has shown antineoplastic effect in halting progression of certain cancer types and inducing apoptosis of cancer cell lines
- Research to delineate the role of cannabinoid therapy is hampered by legislative hurdles (ie, schedule I agent)
- Cannabis use may have application in palliation of physiologic states brought on directly by cancer (cachexia) or indirectly by chemotherapy-induced effects ( nausea, neuropathic pain, cardiomyopathy)
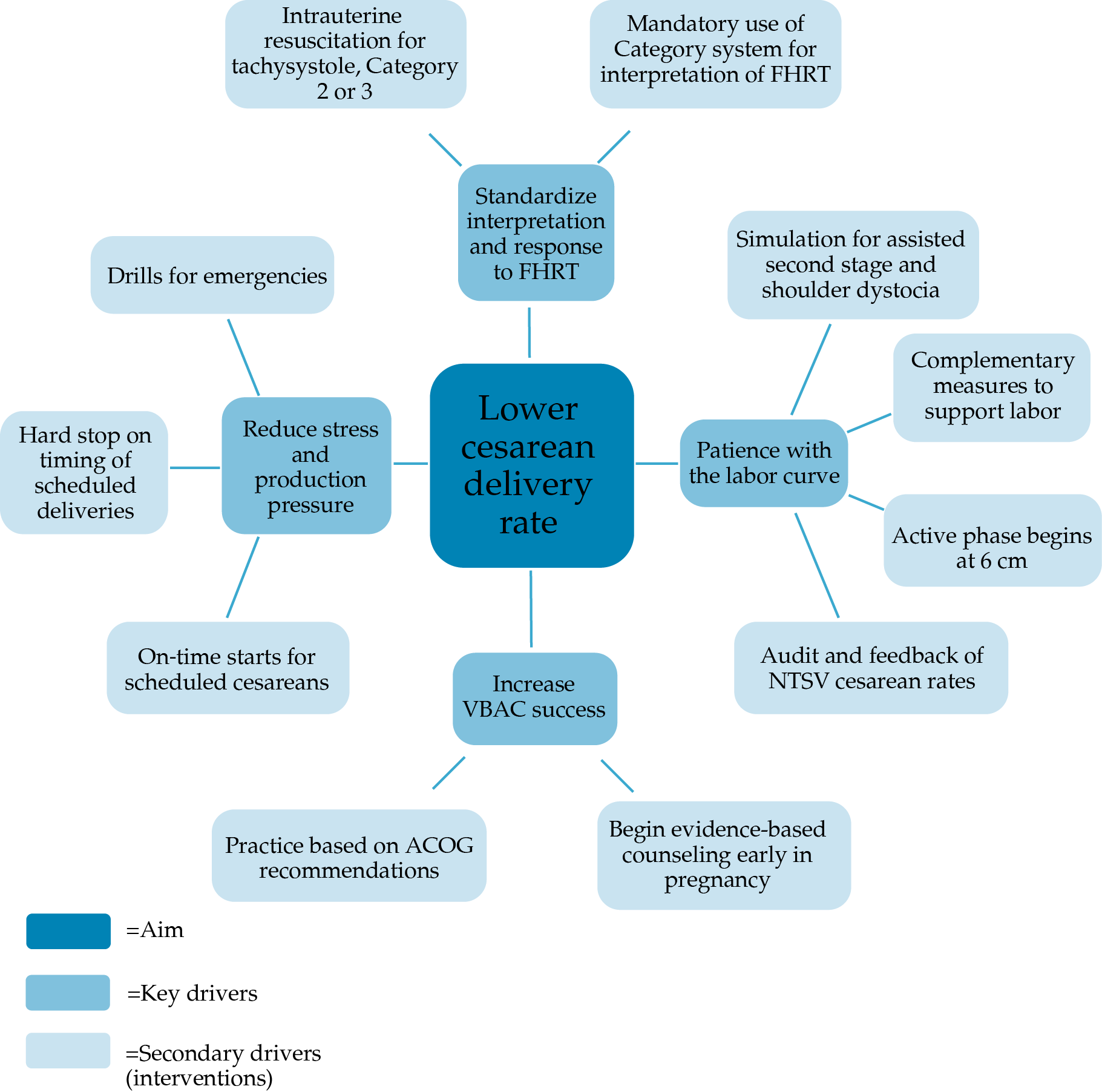
- Cesarean delivery is a significant contributor to maternal morbidity and mortality. The rise in cesarean delivery has not been associated with a decrease in cerebral palsy in offspring.
- A multi-strategy quality improvement approach that accounts for fetal heart tracing assessment, progress in labor, and environmental stress may lead to a reduction in cesarean delivery rates.
- Many cesarean deliveries occur because of subjective interpretation of fetal heart rate tracings. Standardization of interpretation of fetal heart rate tracings using NICHD-endorsed terminology may help to decrease the incidence of cesarean for “nonreassuring” fetal heart tracings
- Allowing patience with the labor curve may achieve increased numbers of safe vaginal deliveries. Redefining arrest and protraction could potentially decrease the cesarean rate and the resultant morbidity. Of particular importance for clinicians, active labor may not begin until 6cm of cervical dilation, and before diagnosing arrest of labor in the second stage, providers should allow for at least 2 hours of pushing in multiparous women and 3 hours in nulliparous women. ACOG and SMFM also endorse longer second stages on an individualized basis.
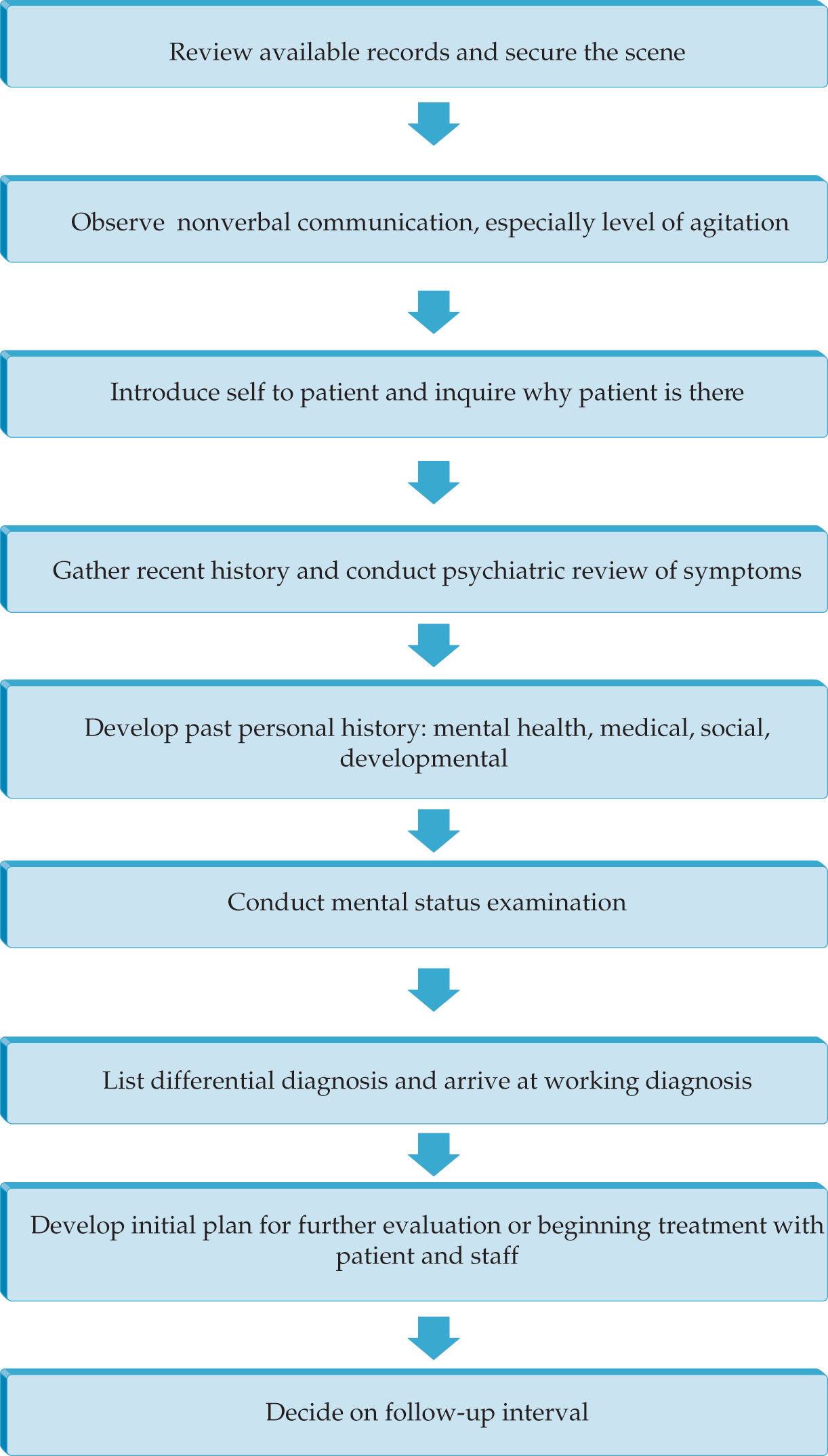
The Psychiatric Interview and Mental Status Examination
- Patient assessment precedes the development of the comprehensive treatment plan
- The interview must be adjusted to suit the patient and circumstance
- The mental status examination is the psychiatrist’s equivalent of the internist’s physical examination
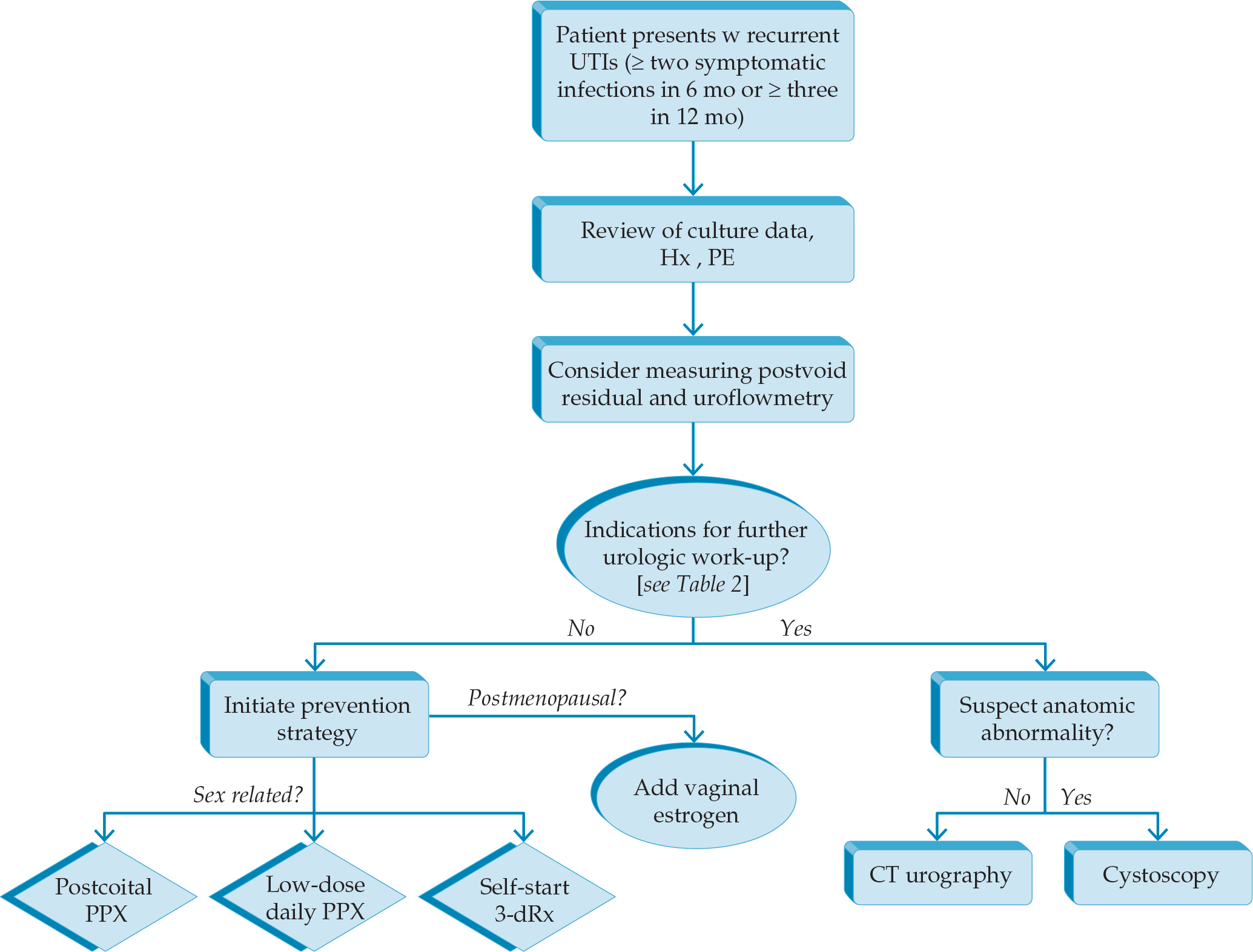
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
- In simple recurrent UTIs, urologic investigation beyond urine cultures may not be warranted.
- High risk patients warranting imaging or cystoscopy include hematuria, obstructive symptoms, structural abnormalities and immunocompromised.
- Behavioral changes, cranberry, probiotics, oral estrogens don’t reduce uti’s, vaginal estrogen does in postmenopausal women.
- Three strategies for antibiotic prevention: (1) low-dose daily (2) postcoital (3) patient-initiated treatment.
- 6-12 months of any prophylaxis (and vaginal estrogen >65 yo) reduces UTIs. UTIs return when antibiotics stop.

Patient with a History of Active Substance Abuse Requesting Opioids for Chronic Pain
- Recent data demonstrate the clinical, economic, and social burden of chronic pain and opioid abuse.
- Drug tests now have the ability to distinguish heroin from alternate opioid intoxication by recognizing the metabolite 6-monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM).
- Using the basis of medical ethical conduct to treat patients with chronic pain and prescribe opioid medications. These tenets include nonmaleficence, beneficence, justice, and autonomy.
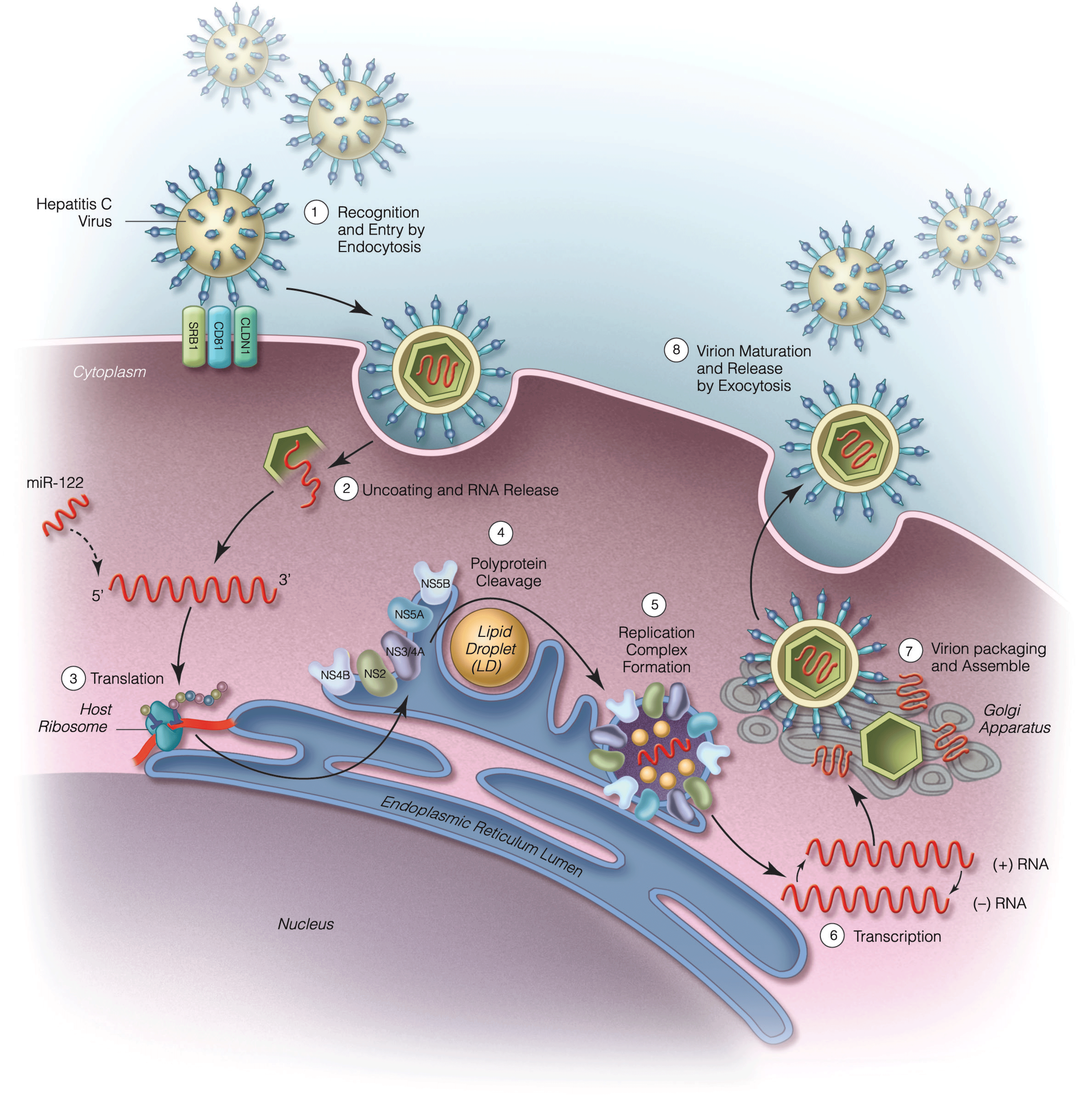
Viral Hepatitis C: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Transmission, And Natural History
- Changing incidence and prevalence of HCV
- Increasing burden of HCV-related liver disease
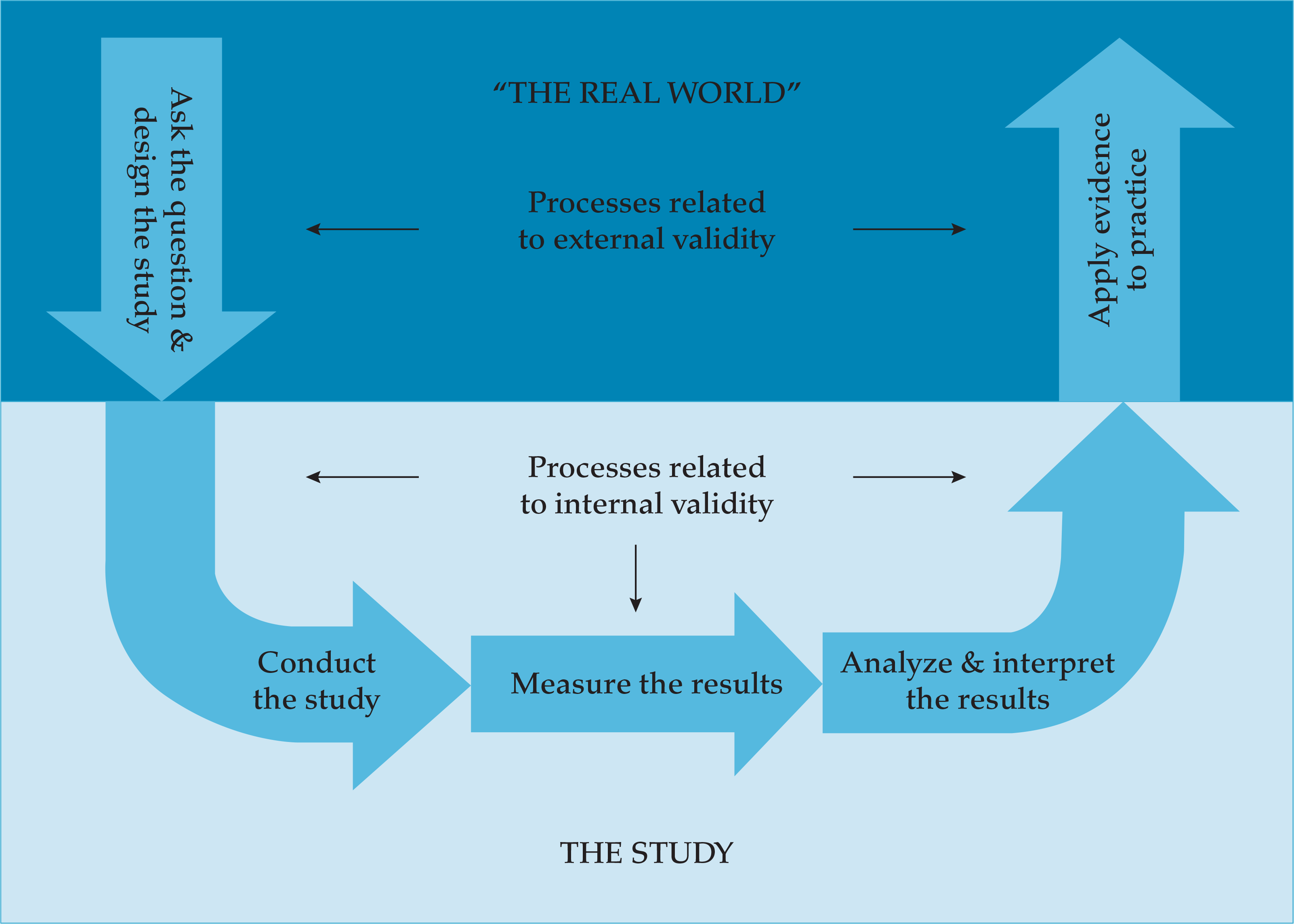
- Methods to appraise the strength of scientific evidence in surgery
- Overview of methods to evaluate the quality of research studies
- Methods to interpret and apply scientific evidence to clinical practice
- Different approaches in clinical and health services research
- Approaches to measuring the quality of care in surgery


.png)







