Macrovascular Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
Latest Updates
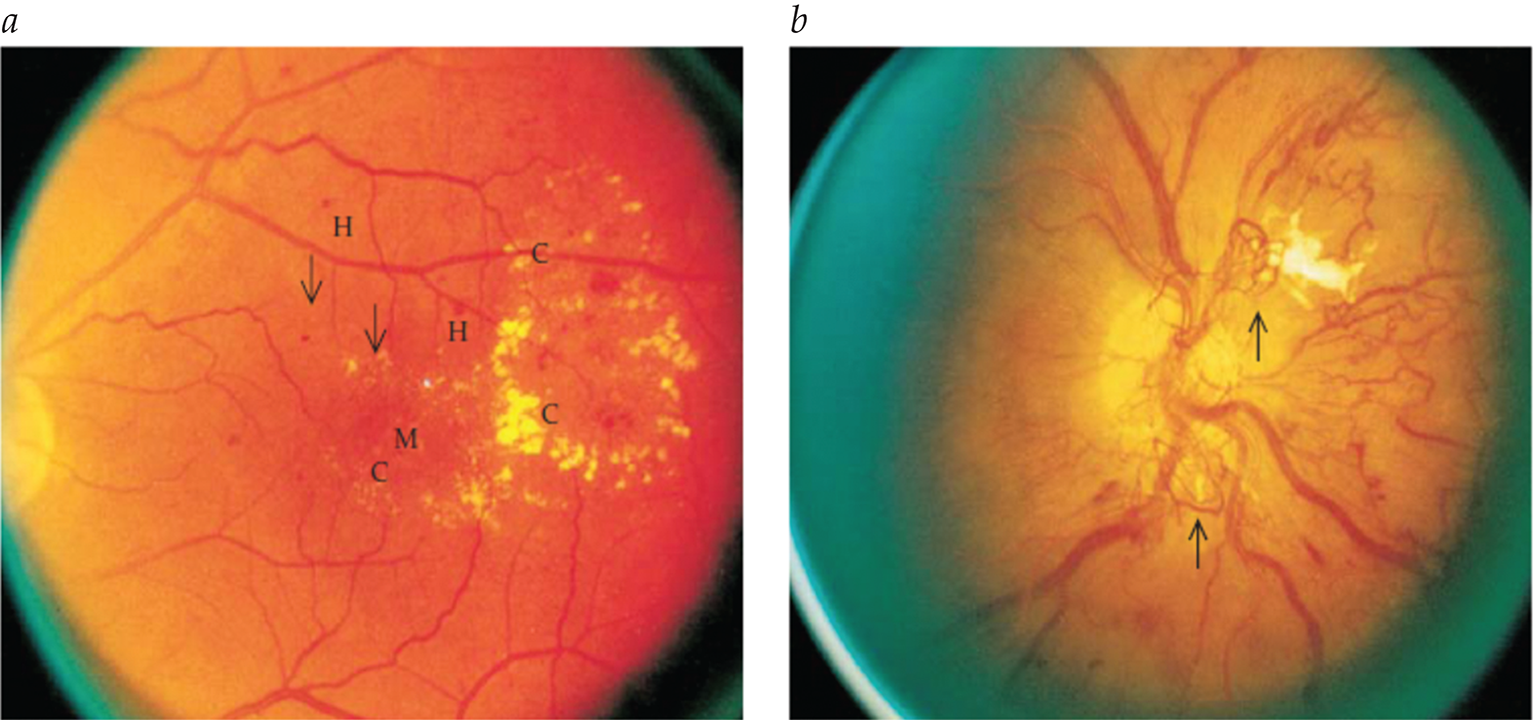
Microvascular Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
- Nonmydriatic fundus cameras with digital transmission enable efficient, remote retinopathy screening supervised by ophthalmologists.
- Two-step approach: significant lesions in digital retinal photographs prompt full ophthalmologist examinations.
- Cost-saving strategy for retinopathy screening, particularly beneficial in remote areas.
- Newer drugs (SGTLT 2 inhibitors, GLP-1 agonists, MR antagonists) offer added cardiovascular and renal benefits in diabetes.
- Chronic complications in diabetes require specialized management and consultation with appropriate specialists.
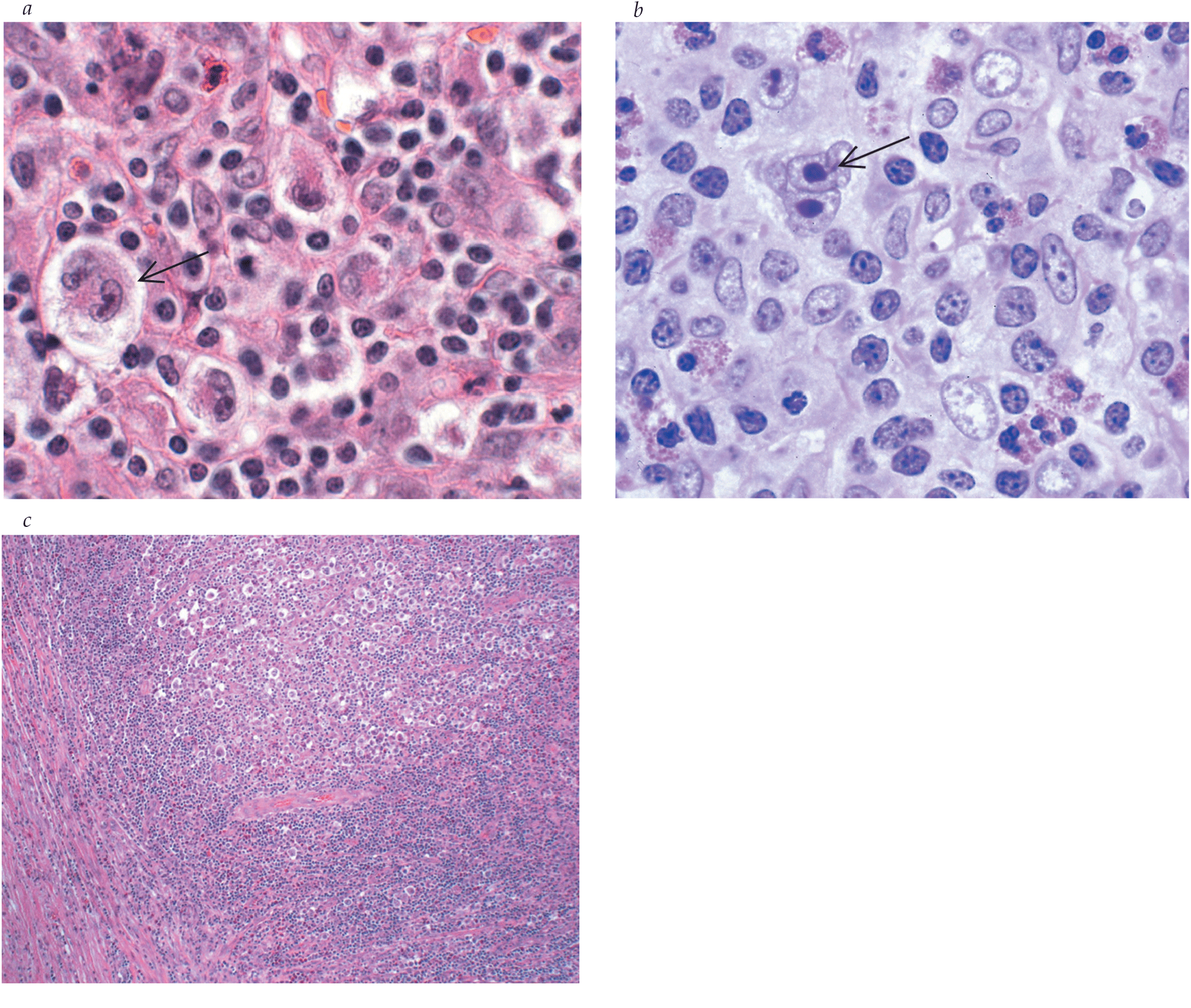
- Imaging studies for the initial evaluation of Hodgkin lymphoma should include a screening chest radiograph and computed tomography (CT) of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis (with intravenous contrast if possible). CT is the gold-standard imaging modality. Positron emission tomography (PET) is an important adjunct to CT for initial staging.
- An improved histopathologic classification, accurate staging, improved radiotherapy, and effective chemotherapeutic agents contribute to the high cure rate for Hodgkin lymphoma. For therapeutic success, care should be given by a multidisciplinary team with expertise in histopathology, diagnostic radiology, medical oncology, and radiation therapy.
- Because of the high cure rate of Hodgkin lymphoma, long-term toxicity of therapy is becoming increasingly important as the follow-up time for patients increases. The full toxicity profile of radiation is only now becoming apparent. The risk of several types of solid tumors is dramatically increased in patients who receive radiation therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Contemporary understanding of ventricular mechanics with identification of the structure and function of the ventricular myocardial band
- Detailed description of the anatomic proximity of cardiac structures and how knowledge of this proximity helps prevent intraoperative complications and damage to critical cardiac structures
- Comprehensive description of aortic root anatomy and mechanics and application of how this anatomy dictates performance of transcatheter aortic valve replacement
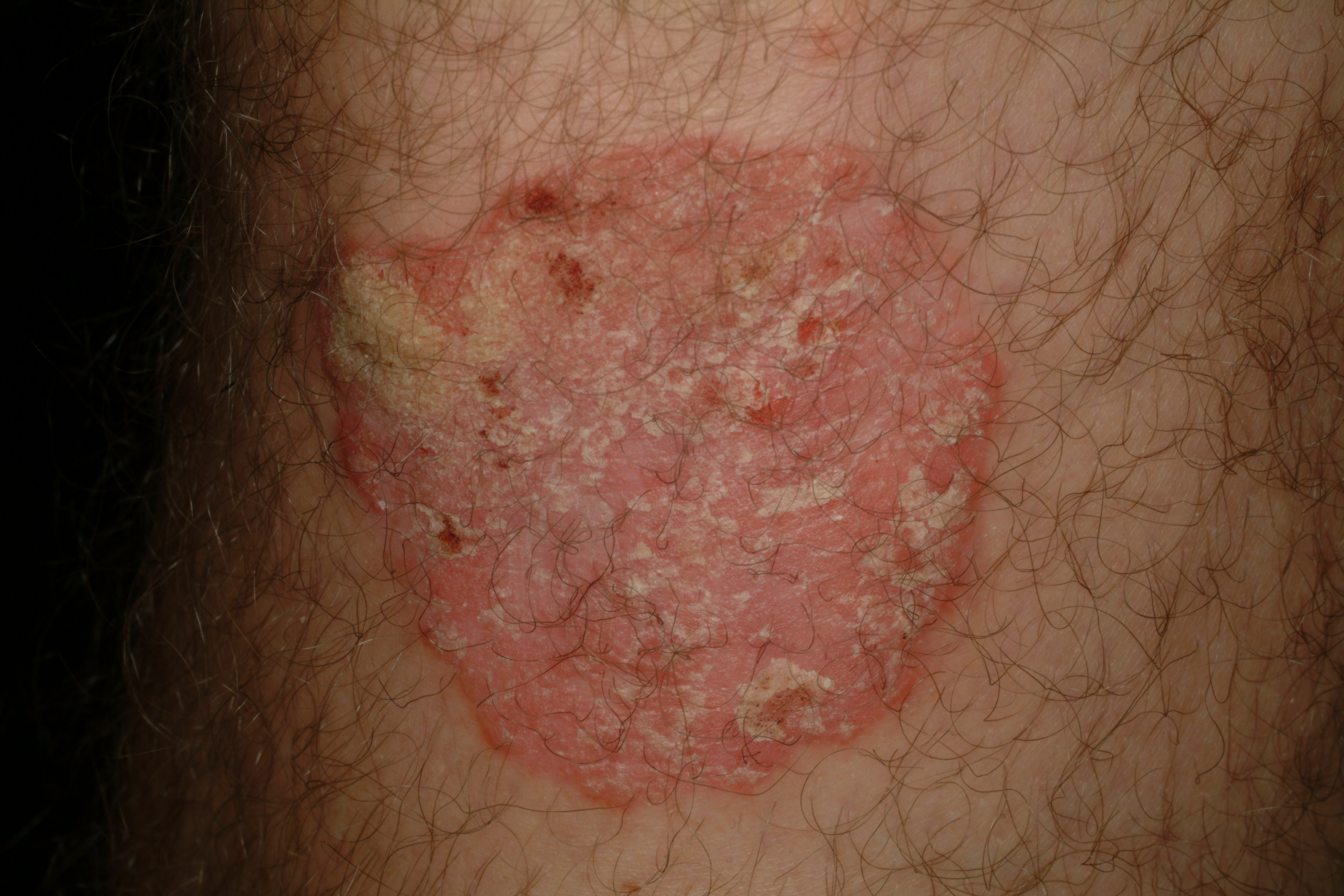
- Topical therapy is the mainstay of treatment for psoriasis, particularly in mild cases. Topical corticosteroids are the most commonly prescribed class of medication but are now often used together with topical calcipotriene, a vitamin D3 analogue, or topical tazarotene, a retinoid; both calcipotriene and tazarotene were approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of psoriasis.
- Emollients are an important part of any topical regimen for psoriasis. Application of petrolatum alone may be sufficient therapy for some patients. More elegant creams and lotions are helpful but are somewhat less effective than greasy ointments. Tar and salicylic acid shampoos are valuable in the treatment of patients with scalp involvement. These preparations are available without prescription.
- Short-term use of the antimetabolite methotrexate can be an extremely effective treatment of psoriasis. Methotrexate is indicated for patients who do not respond adequately to phototherapy and for patients with psoriatic arthritis. The source of methotrexate’s efficacy against psoriasis was once thought to be its antimitotic effect on proliferating macrophages and T cells.
Cardiac Arrhythmias, Acute Coronary Syndromes, and Heart Failure in the Surgical Patient
- To recognize and treat important cardiac arrhythmias in the surgical patient using the latest advances
- Most up to date guidelines in management of Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) in Surgical Patients
- Recent progress in management ofheart failure in postoperative and traumatic patients

- Contemporary understanding of ventricular mechanics with identification of the structure and function of the ventricular myocardial band
- Detailed description of the anatomic proximity of cardiac structures and how knowledge of this proximity helps prevent intraoperative complications and damage to critical cardiac structures
- Comprehensive description of aortic root anatomy and mechanics and application of how this anatomy dictates performance of transcatheter aortic valve replacement



.png)






