Lymphatic Mapping and Sentinel Node Biopsy
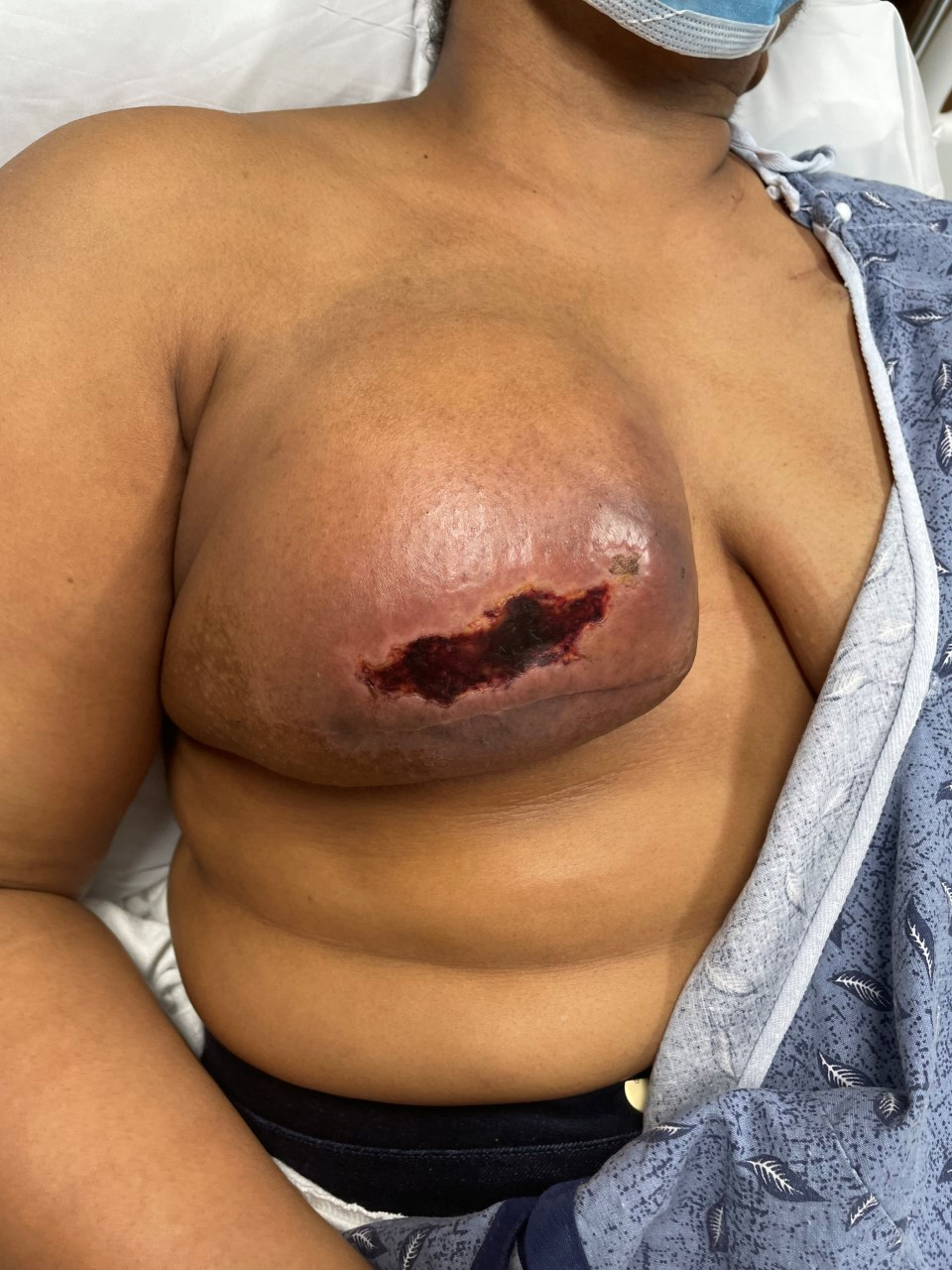
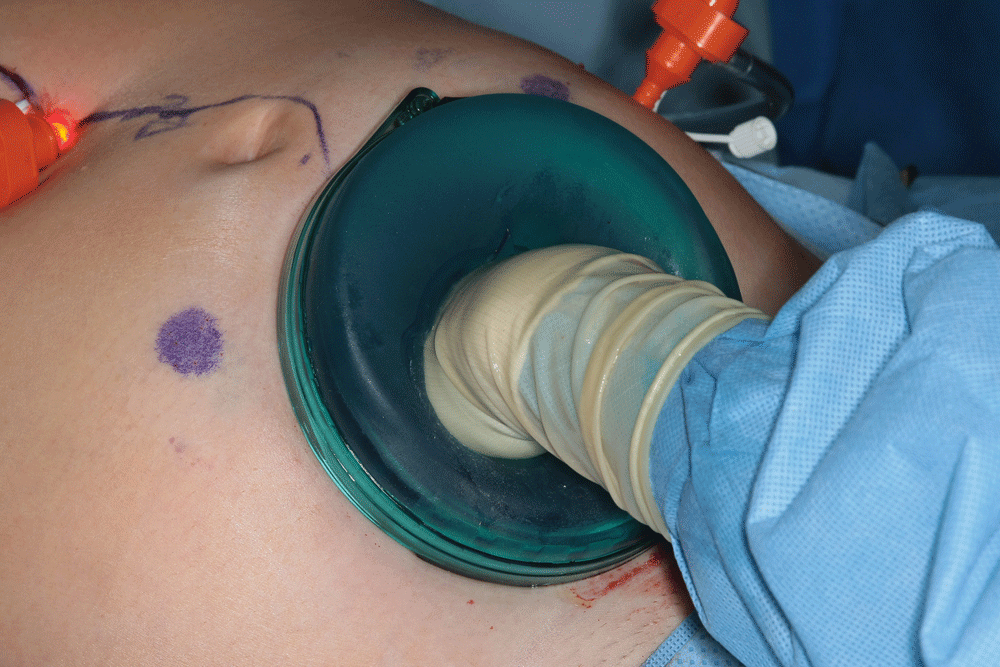
- The dual-tracer technique of lymphatic mapping has the highest accuracy rates, and most melanoma surgeons prefer this method. Methylene blue is generally avoided due to the high rate of skin necrosis at the site of injection. It should not be considered in melanoma patients in whom the injection site is not going to be excised and should not be considered in breast cancer patients unless a total mastectomy is being performed. Isosulfan blue is most commonly used but is associated with a rare incidence of anaphylaxis. Thus, isosulfan blue should never be used in a setting without direct anesthesia care provided.


.png)







