- Updating consensus guideline recommendations up to January 2016
- Adding a duplex scan image showing a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the diagnosis section
- Adding a computed tomographic (CT) scan showing a pulmonary embolism (PE)
- Showing the various types of approved inferior vena cava filters
- Adding five separate flow-chart figures depicting a stepwise management algorithm for the evaluation and treatment of DVT and PE
- Adding a section on catheter-associated upper extremity thrombosis
- Adding a section on extended prophylaxis, the use of non–vitamin K antagonists, updates on stockings
- Writing five new multiple-choice questions based on the review
Latest Updates
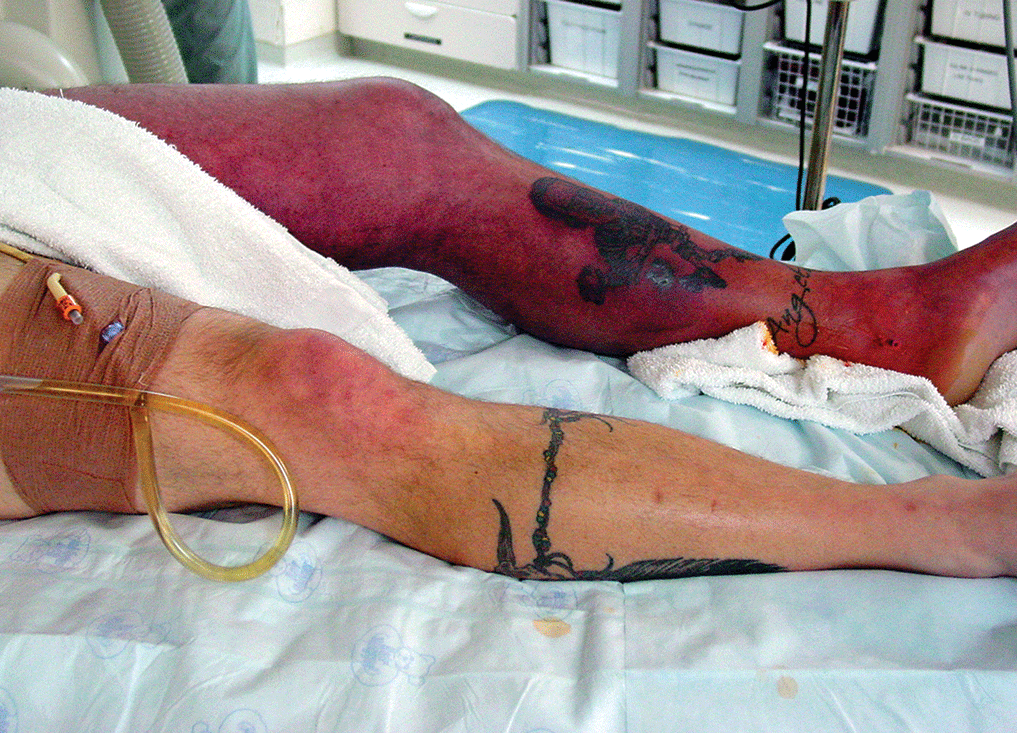
Principles of Initial Trauma Evaluation and Management
- There is a shift to change the definition of massive transfusion to focus on units per time as opposed to total units administered.
- While laparotomy is still considered the gold standard treatment for gunshot wounds to the abdomen, selective NOM of penetrating abdominal wounds is possible. NOM can only be performed in centers that have the staffing and resources to perform serial examinations and the ability to take the patient to the OR at any time should they decompensate.
- Resuscitation of the trauma patient, like much of critical care, is a sophisticated art of balancing the needs of competing organ systems in a patient with multiple injuries. Resuscitation of the trauma patient focuses on prevention of the lethal triad of trauma and secondary injury. The term refers to a triad of acidosis, coagulopathy, and hypothermia resulting from injury and blood loss.

- Catatonia was considered a subtype of schizophrenia in DSM-I through DSM-III-R.
- Catatonia is listed as a specifier in DSM-5 and ICD-10.
- Most persons with catatonia have a mood disorder, most commonly bipolar disorder.
- There is no known cause, but the condition is probably mediated by GABAergic neurotransmission.
- Catatonia is effectively treated with benzodiazepines and/or electroconvulsive therapy.
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Imaging modalities in the assessment of NAFLD
- Controlled attenuation parameter as a point of care measure for hepatic steatosis
- Proton density fat fraction as MRI based measure for hepatic steatosis
- Liver stiffness measurement on elastography as a correlate of hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis
- Active clinical trials in phase 2b and 3, yet no FDA approved therapy
- Intense lifestyle changes with 5-10% weight loss can improve fibrosis and steatosis
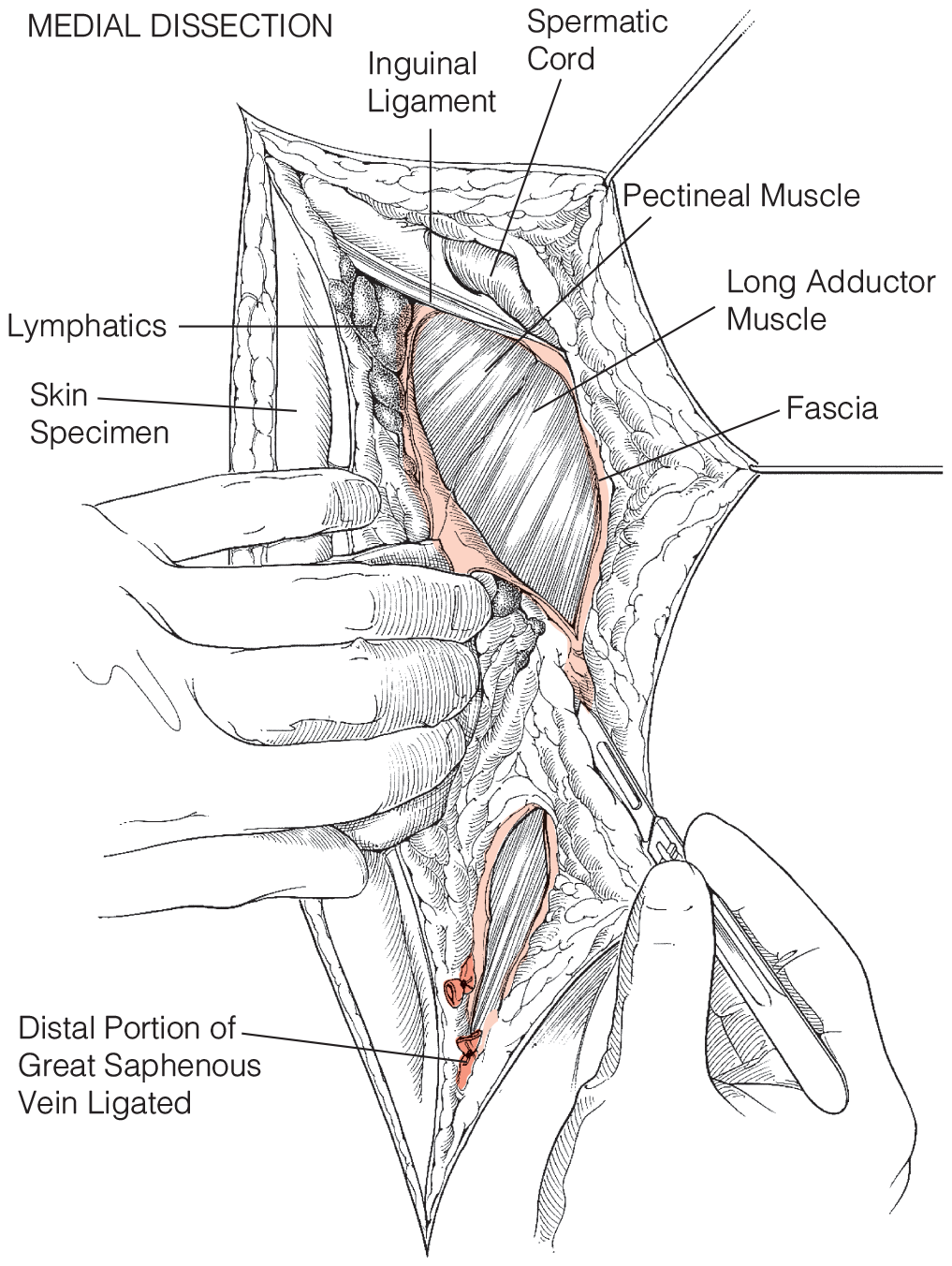
Surgical Management of Melanoma and Other Skin Cancers
- An interesting advance in the treatment of advanced basal cell carcinoma is the use of inhibitors of the sonic hedgehog pathway. The vast majority of basal cell carcinomas harbor genetic mutations in the hedgehog signaling pathway, which results in constitutive activation and basal cell proliferation.
- SLNB is generally not recommended unless the lesion is between 0.75 and 1.0 mm, high risk based on histologic features (e.g., ulcerated or with > 1 mitoses/mm2), or inadequately staged (e.g., positive deep margin).
- An important variable in the prognosis of melanoma is the thickness of the primary tumor as assessed using the Breslow system. Tumor thickness in the Breslow system is measured from the epidermal surface to the deepest point of the tumor with a calibrated ocular micrometer.
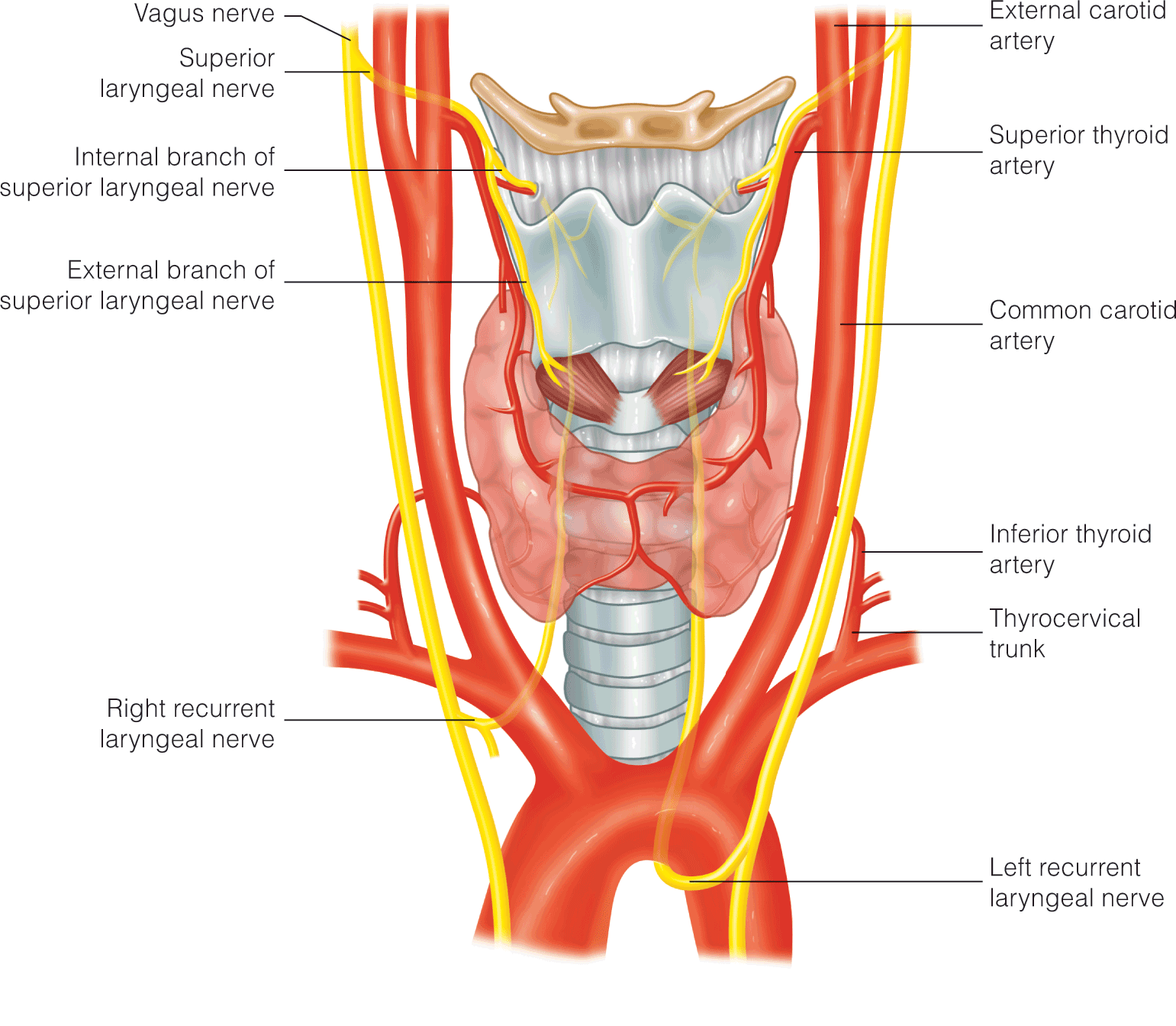
Thyroid/ Parathyroid Disease and Surgery
- Molecular tests for gene point mutations, insertions, deletions, fusions and expression alterations are available that can be used to help risk stratify intermediate risk differentiated thyroid cancers into either surgical management or observation .
- Stage IV anaplastic thyroid cancer requires aggressive approach for complete resection and prompt transition to adjuvant definitive-intention therapy to attain long-term survival.
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is being studied in clinical trials as alternative to high risk surgical patients and selected benign thyroid nodules.
- To avoid neck scar, consider robotic thyroidectomy with approaches including trans axillary (most common), bilateral axilla-breast, retro auricular, and transoral (requires CO2 gas insufflation, not a “clean” procedure) approaches for patients with indeterminate, likely benign lesions if BMI <35.
- Transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy can be considered for patients with a thyroid mass without evidence of lymph node metastases as retrospective review of 422 patients did not demonstrate significant difference in complications compared to open thyroidectomy group.

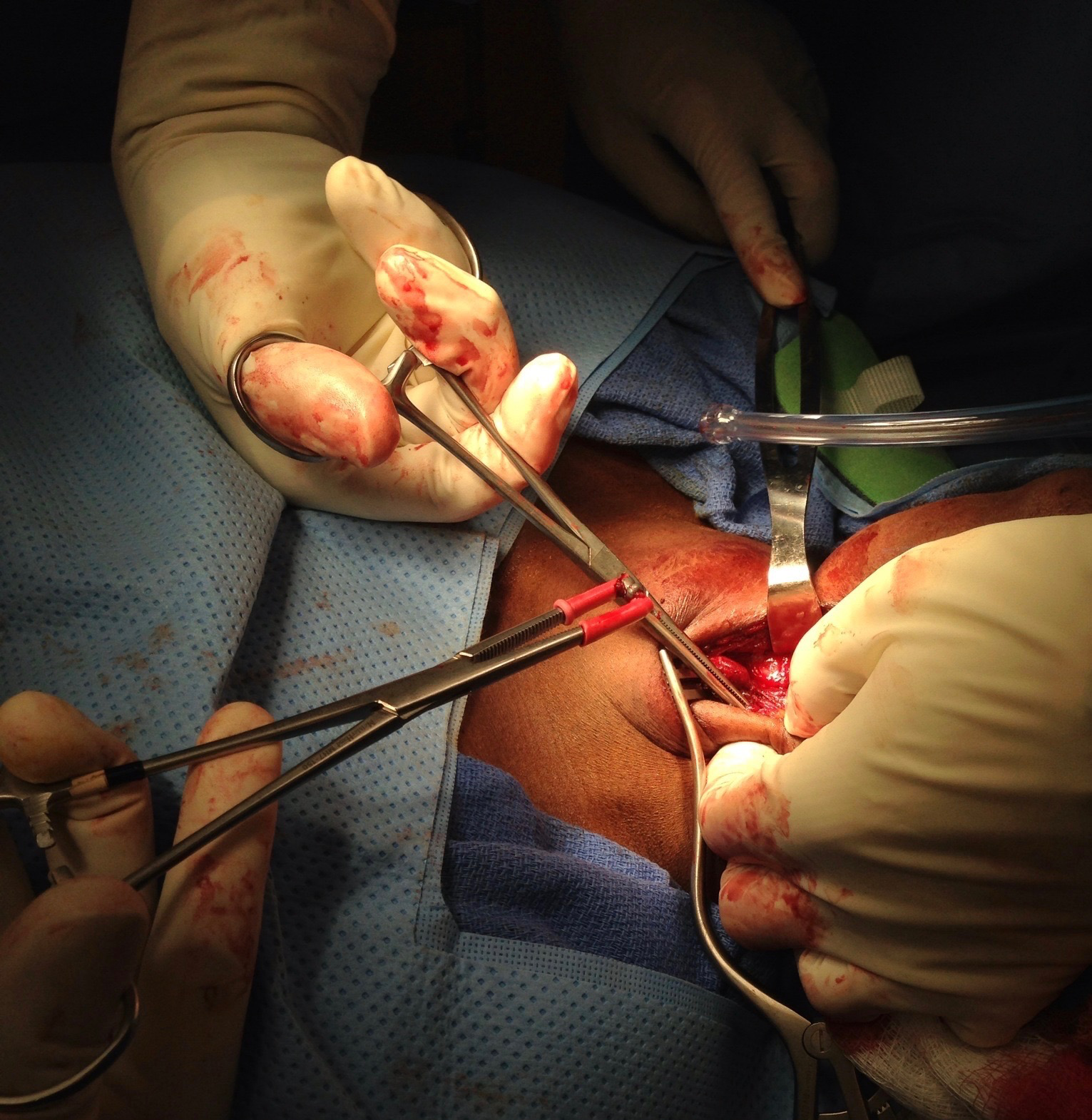
Principles of Initial Trauma Evaluation and Management
- There is a shift to change the definition of massive transfusion to focus on units per time as opposed to total units administered.
- While laparotomy is still considered the gold standard treatment for gunshot wounds to the abdomen, selective NOM of penetrating abdominal wounds is possible. NOM can only be performed in centers that have the staffing and resources to perform serial examinations and the ability to take the patient to the OR at any time should they decompensate.
- Resuscitation of the trauma patient, like much of critical care, is a sophisticated art of balancing the needs of competing organ systems in a patient with multiple injuries. Resuscitation of the trauma patient focuses on prevention of the lethal triad of trauma and secondary injury. The term refers to a triad of acidosis, coagulopathy, and hypothermia resulting from injury and blood loss.


.png)







