- Clinical gestalt can also accurately assess the pretest probability of PE.
- For patients with a low pretest probability of PE, the Pulmonary Embolism Rule-out Criteria can be used to rule out PE without further testing including no need to order a
- D-dimer.
- The YEARS protocol may be used to exclude a subset of patients from having a workup to rule out PE when their D-dimer is less than 1000 as opposed to 500.
- Novel or new oral anticoagulants are becoming the mainstay of treatment for the hemodynamically stable patient with PE.
- Intravenous alteplase, catheter-directed thrombolysis, surgical embolectomy, and catheter-directed embolectomy are treatment modalities for patients with PE who are hemodynamically unstable.
- For patients in imminent or actual PE-related cardiac arrest, current guidelines recommend a bolus regimen consisting of 50 mg IV t-PA given over two minutes and repeated after 15 minutes in the absence of return of spontaneous circulation.
- A subset of patients with PE can be treated as outpatients if their Simplified Pulmonary Severity Index is 0.
Latest Updates
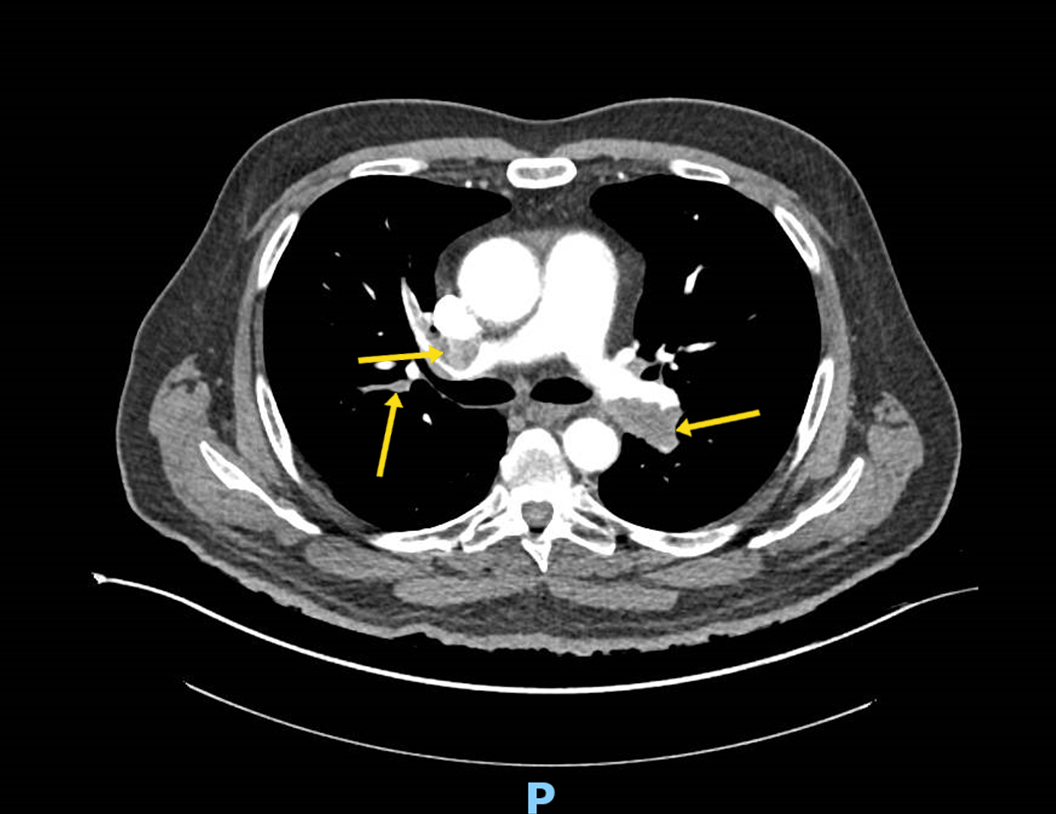
Management of Postpartum Hemorrhage
- In a 2015 population-based, cross-sectional study conducted by the United Kingdom Obstetric Surveillance System on women requiring massive postpartum transfusion for PPH, uterine atony was found to be responsible 40% of the time. Atony represents a large proportion of cases of PPH, and its incidence is on the rise. Over recent years, we have observed a significant rise in the rate of PPH attributed to uterine atony not only in the United States but also worldwide.
- Originally described in 1997, the B-Lynch compression suture is an effective and easily used tool for the management of PPH. This technique involves placing brace sutures over the fundus of the uterus to apply ongoing compression of the uterus.
- The correct ratio of packed red blood cells to fresh frozen plasma to platelets in the setting of obstetrical hemorrhage remains controversial. Most experts advocate for a 1:1:1 ratio in the setting of active bleeding, whereas others advocate for 6:4:1 or 2:1 (with platelets to be given after the first 4:2).

Management and Therapeutic Issues in the Dementias
- The cholinesterase inhibitors donepezil, galantamine, and rivastigmine have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of AD dementia.
- Patients with mild to moderate AD dementia are the appropriate candidates for cholinesterase inhibitor therapy. These patients need a designated caregiver to supervise the use of the medication.
- Support for and empowerment of the caregivers of dementia patients must be an integral part of management. The emotional and physical health of caregivers is critical to long-term outcomes.
Prevention and Diagnosis of Infection
- Microbiologic studies are critical for characterizing infections. Gram stains and cultures of wound tissue, pus, sputum, urine, and drainage effluent are generally very useful. Identification of not only the particular organism involved but also of its specific antimicrobial susceptibility has become common practice in most hospital clinical laboratories.
- Treatment of CAUTI requires removal or change of the catheter along with systemic antimicrobial therapy. The predominant microorganisms causing CAUTI in the ICU are enteric gram-negative bacilli, Candida species, enterococci, staphylococci, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Multidrug resistance is a significant problem in urinary pathogens
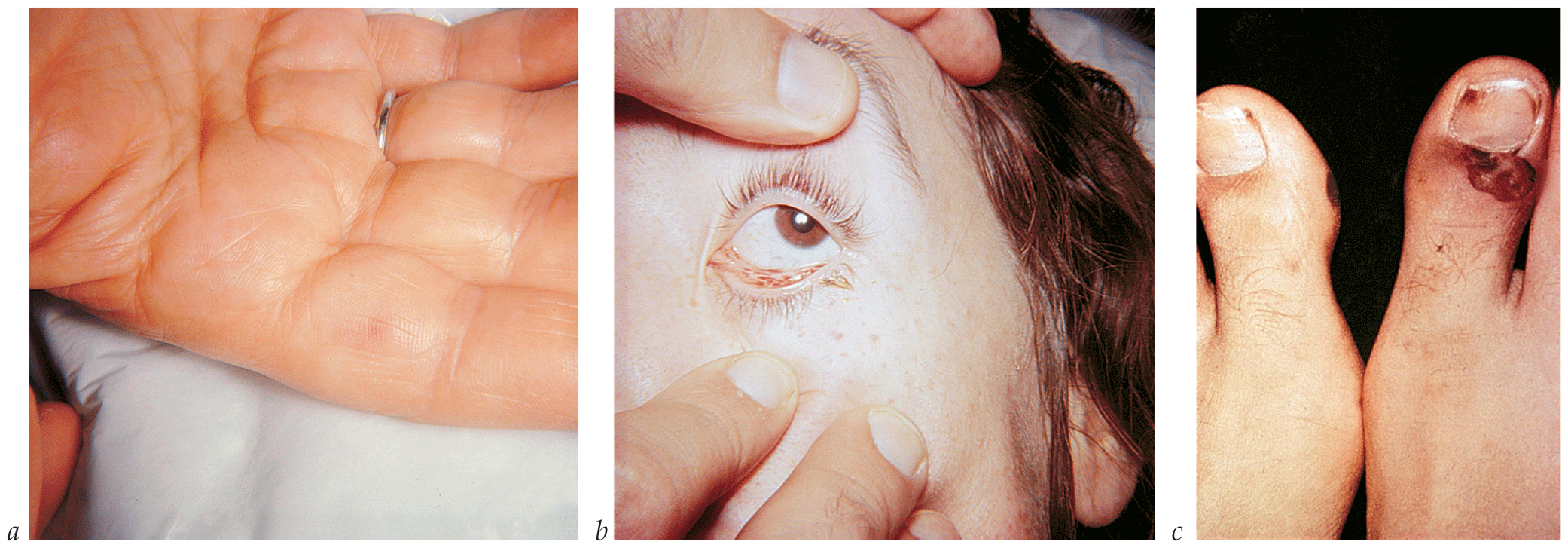
- Bactericidal antibiotics are used parenterally in high doses. With the exception of PVE caused by staphylococci, antimicrobial therapy for PVE caused by a specific organism uses the same drugs recommended for native valve endocarditis.
- Endocarditis caused by relatively penicillin-resistant (MIC = 0.2 to 0.5 µg/mL) viridans or other nonenterococcal streptococci is treated with a higher dose of penicillin G combined with gentamicin. If the strain is even more resistant to penicillin (MIC > 0.5 µg/mL), the infection is treated with one of the standard regimens for enterococcal endocarditis.
- Operative intervention to débride infected perivalvular tissue or to replace or reconstruct a dysfunctioning valve is important in the management of complicated infective endocarditis that involves either a native or a prosthetic valve. Overall, surgery is indicated in 25 to 40% of patients with infective endocarditis, and up to 45% of patients undergo surgery during the active phase of their disease.

Prevention and Diagnosis of Infection
- Microbiologic studies are critical for characterizing infections. Gram stains and cultures of wound tissue, pus, sputum, urine, and drainage effluent are generally very useful. Identification of not only the particular organism involved but also of its specific antimicrobial susceptibility has become common practice in most hospital clinical laboratories.
- Treatment of CAUTI requires removal or change of the catheter along with systemic antimicrobial therapy. The predominant microorganisms causing CAUTI in the ICU are enteric gram-negative bacilli, Candida species, enterococci, staphylococci, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Multidrug resistance is a significant problem in urinary pathogens

Prevention and Diagnosis of Infection
- Microbiologic studies are critical for characterizing infections. Gram stains and cultures of wound tissue, pus, sputum, urine, and drainage effluent are generally very useful. Identification of not only the particular organism involved but also of its specific antimicrobial susceptibility has become common practice in most hospital clinical laboratories.
- Treatment of CAUTI requires removal or change of the catheter along with systemic antimicrobial therapy. The predominant microorganisms causing CAUTI in the ICU are enteric gram-negative bacilli, Candida species, enterococci, staphylococci, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Multidrug resistance is a significant problem in urinary pathogens
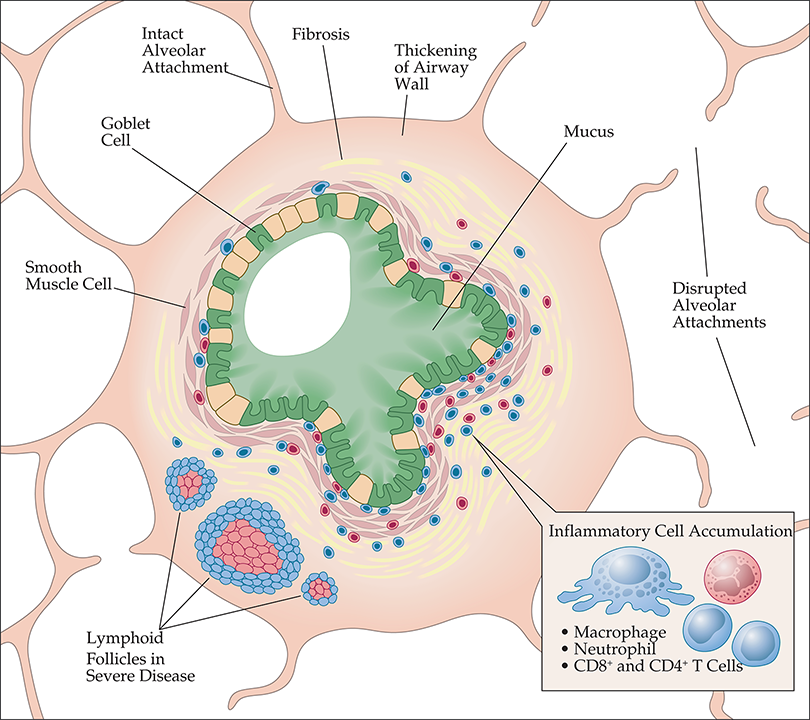
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- 2020 ATS and 2019 CTS practice guidelines delineating pharmacologic management of COPD.
- Introduced the new Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Combined COPD Assessment using symptoms of breathlessness, spirometric classification, and risk of exacerbation to evaluate patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and guide treatment
- Epidemiology section updated to reflect new data suggesting a decline in the age-adjusted prevalence of COPD, likely as a result of decreased smoking rates
- Multiple new common genetic risk factors associated with COPD described, including a recently discovered functional genetic variant
- Discussion about the long-term care of patients with COPD extensively revised to include the most recent trials assessing indications for long-acting inhaled bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids, among other therapies
- Recent evidence supporting lung cancer screening in patients with COPD reviewed


.png)







