Classification Systems for Lower Extremity Occlusive Disease
- The SVS runoff score provides a method for giving weight to those vessels contributing to the runoff. It was developed to anatomically stratify patients when designing studies to compare the outcome of lower extremity arterial bypass.
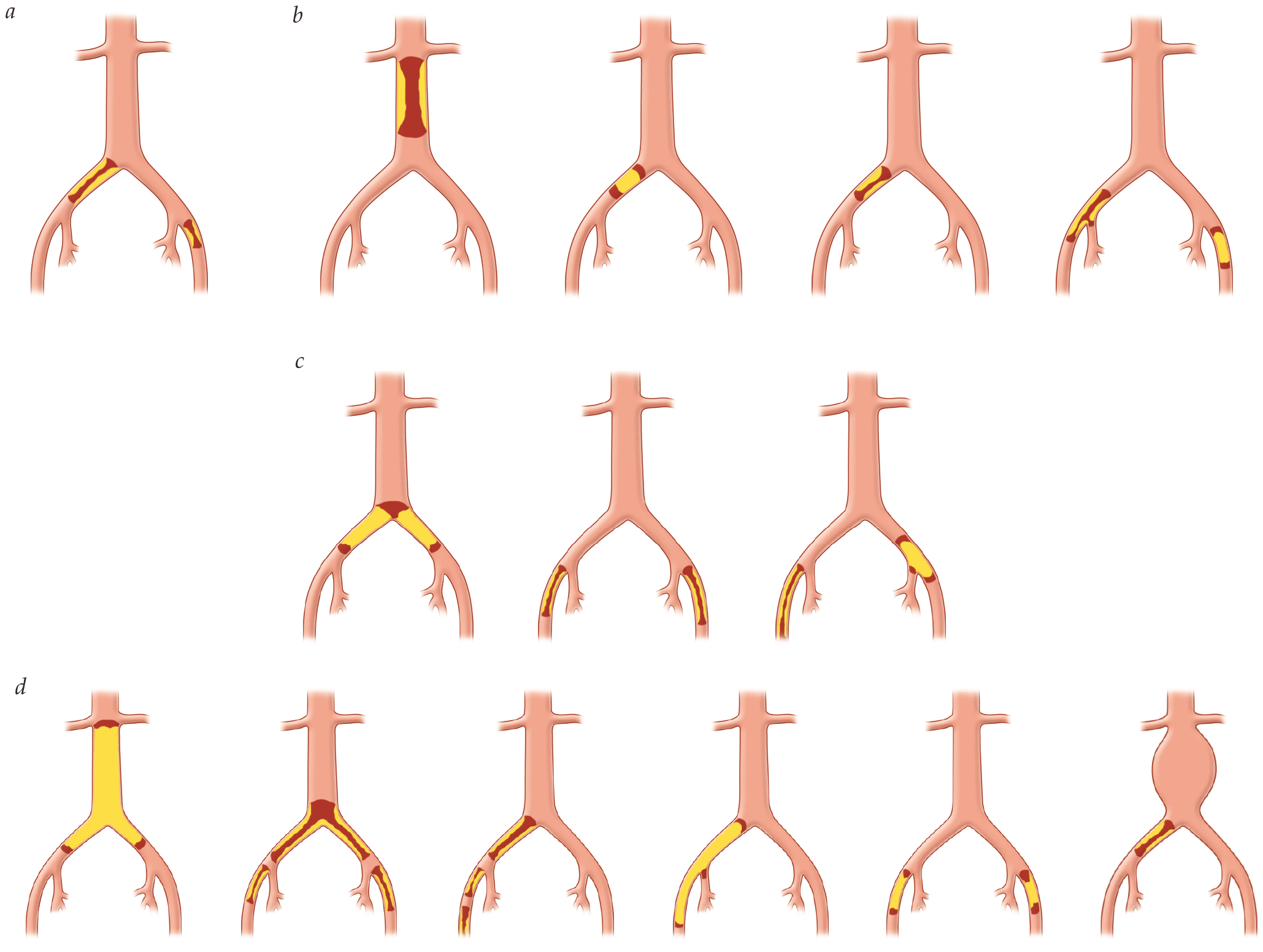
- The TASC classification system guides the clinical management of a patient by providing vascular specialists with a basic framework for determining whether the patient’s vascular disease pattern is best treated with endovascular intervention or with surgical revascularization. The TASC classification is also used to stratify cohorts in research studies evaluating treatment modalities.
- The Finnvasc score, Project of Ex-Vivo graft Engineering via Transfection (PREVENT) III (PIII) score, and BASIL Mortality Index are three tools designed to aid in decision making between open surgical revascularization and endovascular intervention. These tools stratify the risk of periprocedural morbidity and/or predict a patient’s probability for short-term, medium-term, and long-term survival.


.png)







