Thoracic Injuries and Management Options
- Treatment of rib fractures is centered on pain control. Multimodality treatment utilizing non-narcotic medications is optimal.
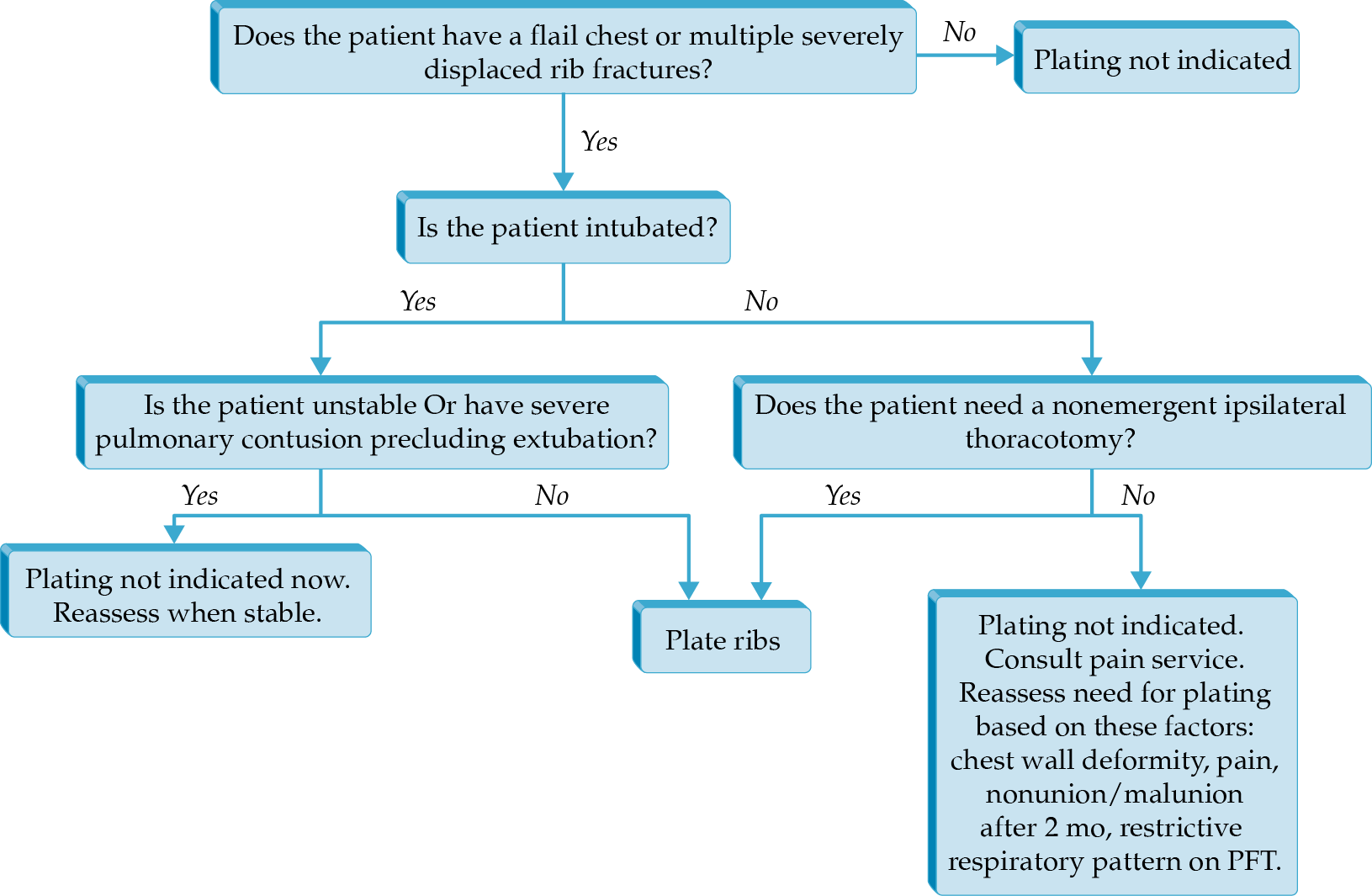
- Operative fixation of flail chest is associated with decreased respiratory failure, pneumonia, pain.
- Patients with type III or IV blunt aortic injury require repair, preferably using an endovascular approach.
- Most esophageal injuries require open repair. Time to repair is directly associated with mortality. Stenting has little role in repair.


.png)







