- There has been much interest in the development of breast cancer prevention strategies. Pharmacologic approaches are the most developed at this time. The nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) tamoxifen, a mainstay in the management of breast cancer, has also been tested as a chemopreventive agent.
- Screening strategies for breast cancer include the triad of breast self-examination (BSE), clinical breast examination by a health care professional, and screening mammography. Although widely touted as an important component of early detection, BSE is of uncertain value.
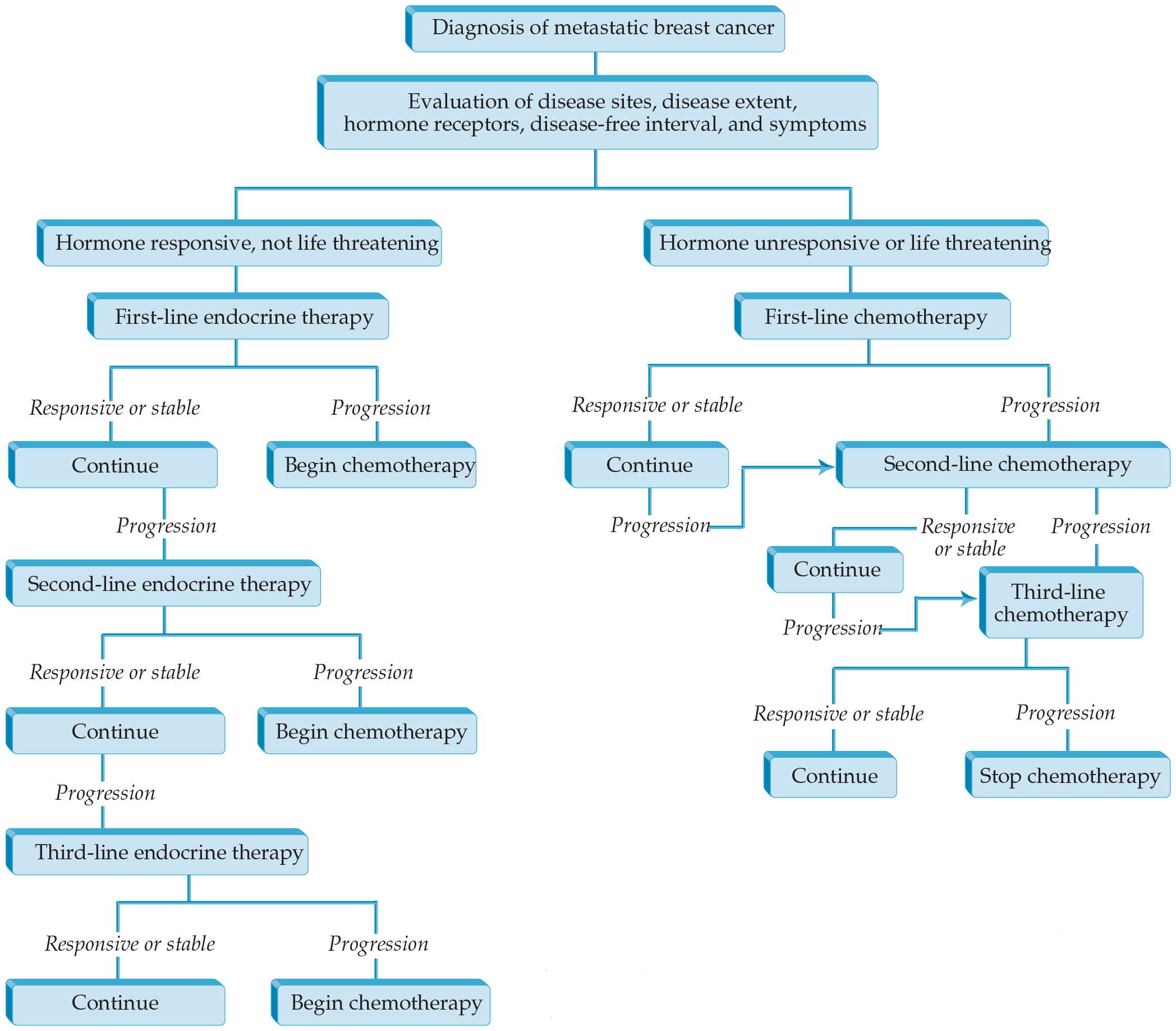
- Increased understanding of growth pathways of breast cancer has led to the identification of crucial nonendocrine pathways that are potential targets for therapy. One such target is the HER-2 protein, a transmembrane protein that is overexpressed in about 20% of breast cancers, generally because of gene amplification.
Latest Updates

- There has been much interest in the development of breast cancer prevention strategies. Pharmacologic approaches are the most developed at this time. The nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) tamoxifen, a mainstay in the management of breast cancer, has also been tested as a chemopreventive agent.
- Screening strategies for breast cancer include the triad of breast self-examination (BSE), clinical breast examination by a health care professional, and screening mammography. Although widely touted as an important component of early detection, BSE is of uncertain value.
- Increased understanding of growth pathways of breast cancer has led to the identification of crucial nonendocrine pathways that are potential targets for therapy. One such target is the HER-2 protein, a transmembrane protein that is overexpressed in about 20% of breast cancers, generally because of gene amplification.

- There has been much interest in the development of breast cancer prevention strategies. Pharmacologic approaches are the most developed at this time. The nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) tamoxifen, a mainstay in the management of breast cancer, has also been tested as a chemopreventive agent.
- Screening strategies for breast cancer include the triad of breast self-examination (BSE), clinical breast examination by a health care professional, and screening mammography. Although widely touted as an important component of early detection, BSE is of uncertain value.
- Increased understanding of growth pathways of breast cancer has led to the identification of crucial nonendocrine pathways that are potential targets for therapy. One such target is the HER-2 protein, a transmembrane protein that is overexpressed in about 20% of breast cancers, generally because of gene amplification.
Overview of Substance Use Disorders
- Discussion of the evolution of DSM substance use disorder diagnoses over time
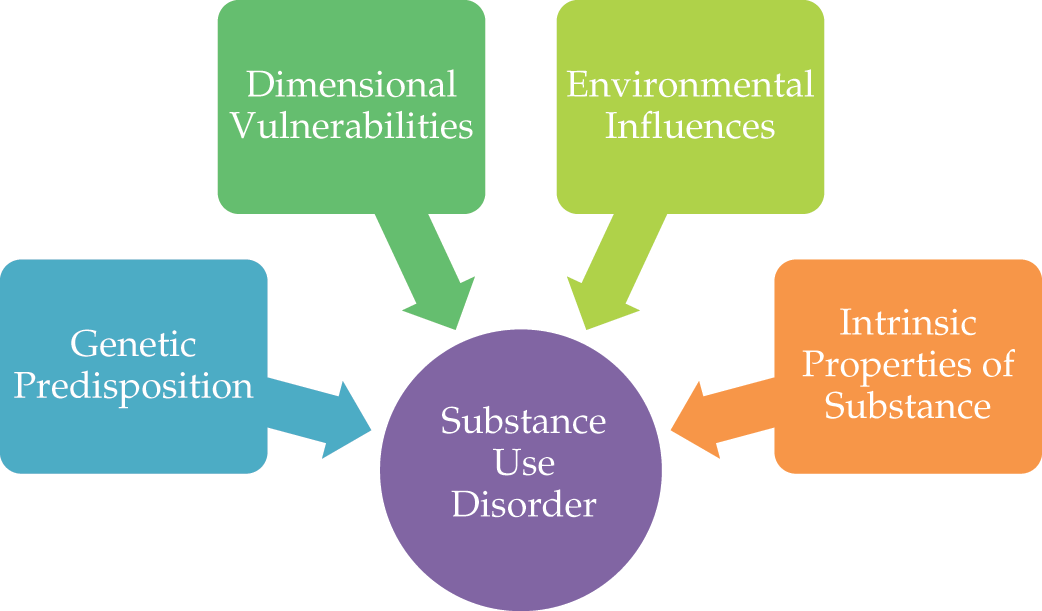
- Overview of the biological, environmental, and personal factors implicated in the development of substance use disorders
- Critical reviews of the current diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, and clinical presentation of the major substances of misuse

Overview of Substance Use Disorders
- Discussion of the evolution of DSM substance use disorder diagnoses over time
- Overview of the biological, environmental, and personal factors implicated in the development of substance use disorders
- Critical reviews of the current diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, and clinical presentation of the major substances of misuse
- Use of HVPG to accurately diagnose portal hypertension
- Child-Pugh score and MELD score in risk stratification and decision-making
- Fibroelastography, multidetecter row CT scan, and capsule endoscopy as emerging modalities in detection of varices.
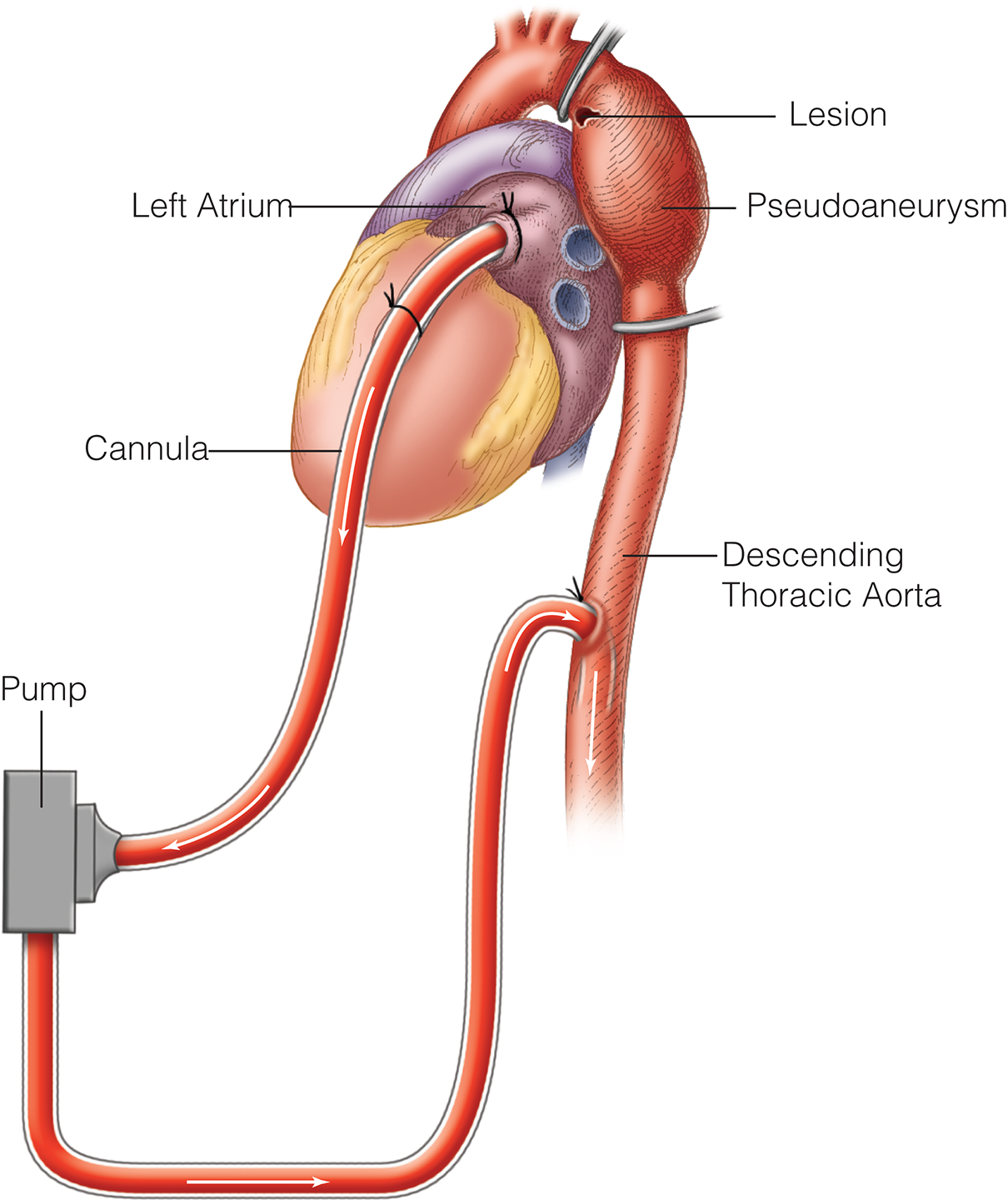
- BTAI is now the gold standard n treating patients with these problems
- The grade of injury with these lesions has been defined and there is controversy on which lesion should be treated and how emergently
- Recently in the US a device changed its IFU because of complications after TEVAR for BTAI. It was being used outside its IFU.
- Recent advancement on sizing and device differences between BTAI and other pathologies treated with TEVAR
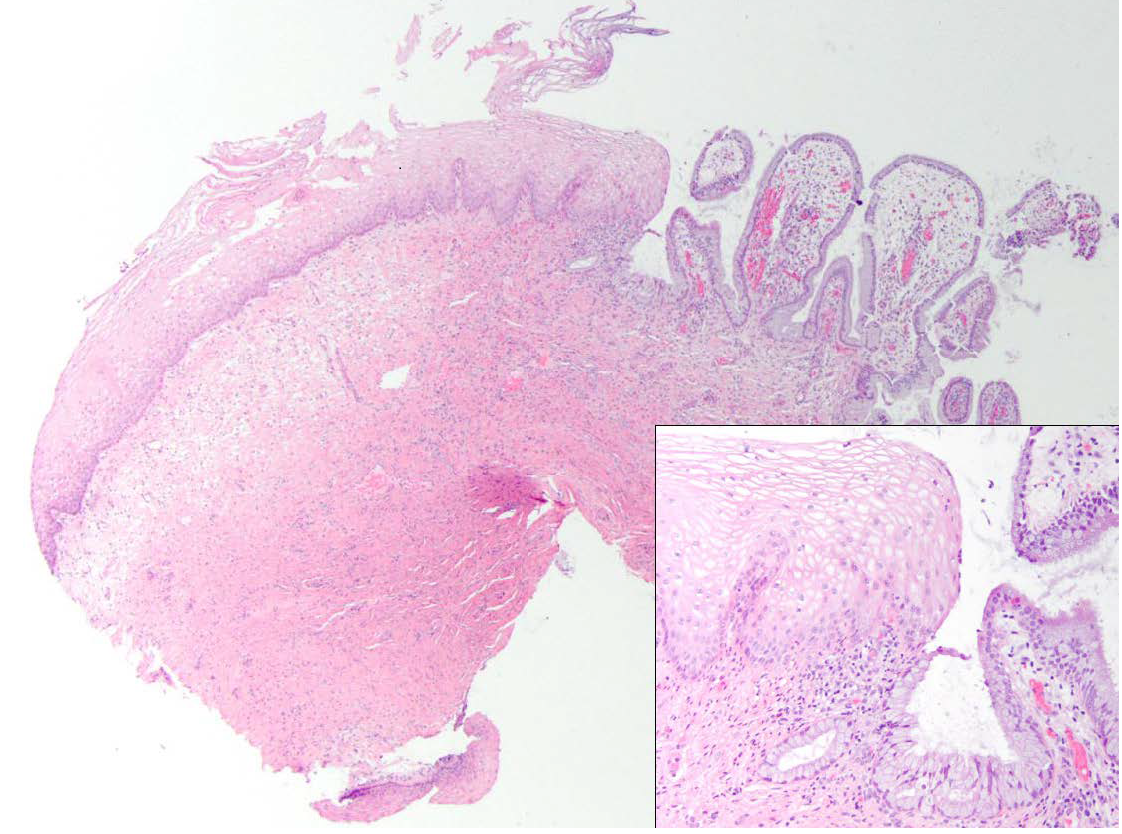
Cervical Dysplasia and Human Papillomavirus
- Large randomized trials of Pap and HPV cotesting found that after extended follow-up, the incidence of invasive cervical cancer was significantly lower in women initially screened with HPV-based testing compared with cytology alone.
- Screening that includes assessment of HPV status provides 60 to 70% greater protection against invasive cervical carcinomas compared with cytology alone.
- Vaccination rates for the HPV vaccine, approved in the United States since 2006, are well below national goals, and provider recommendation has been found to be the most important factor influencing a patient’s or parent’s decision as to whether or not to accept the HPV vaccine.


.png)







