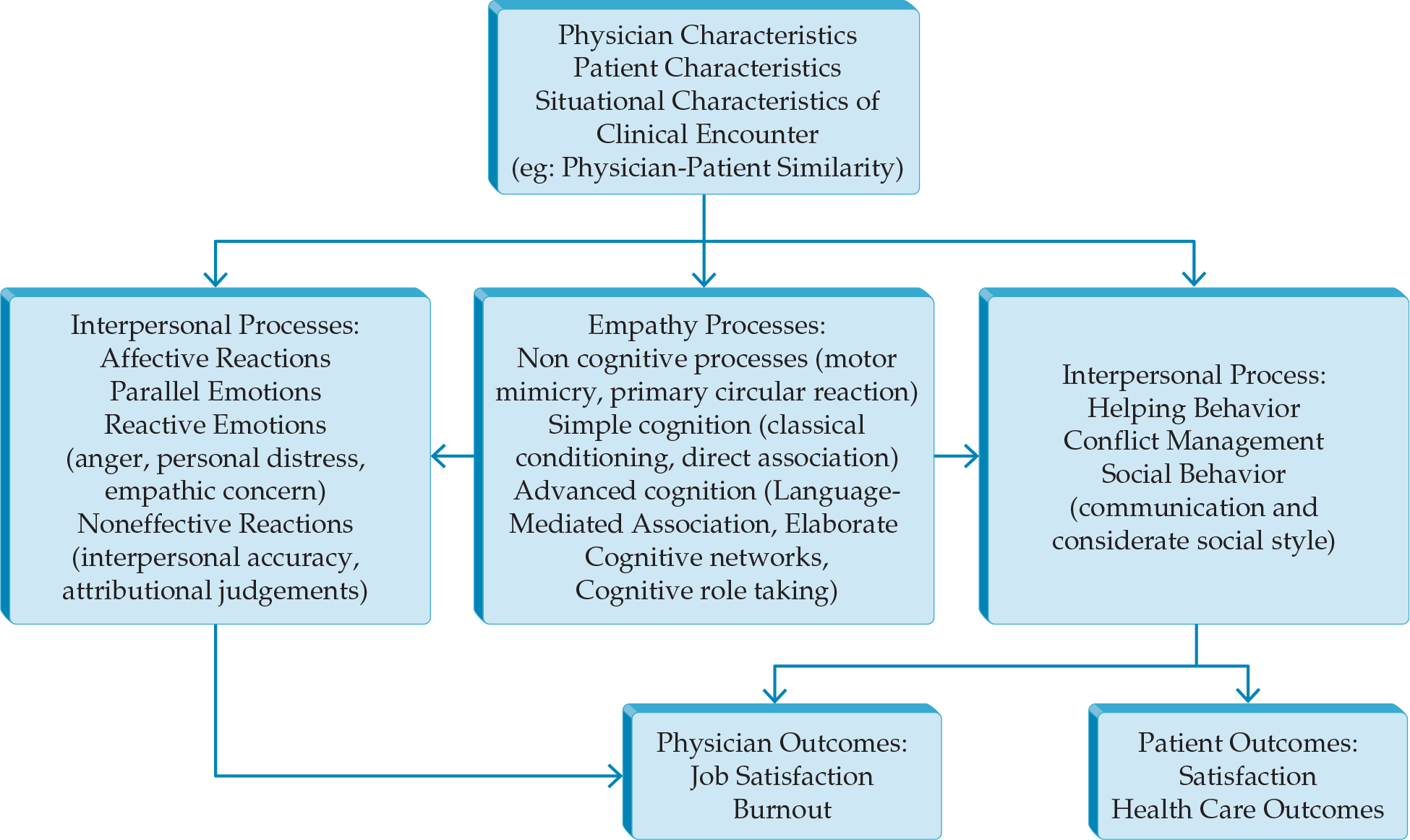
- Physicians need to be adept at communicating bad news in its entirety to patients to enable a decision-making process about disease management.
- Empathy is key in communicating bad news. Reactive rather than parallel empathy is more effective.
- Patients benefit from pairing hope to bad news but do not prefer that the bad news is underplayed.
- Models (SPIKES and Expanded Four Habits Model) are available to help structure this challenging interaction.
Latest Updates
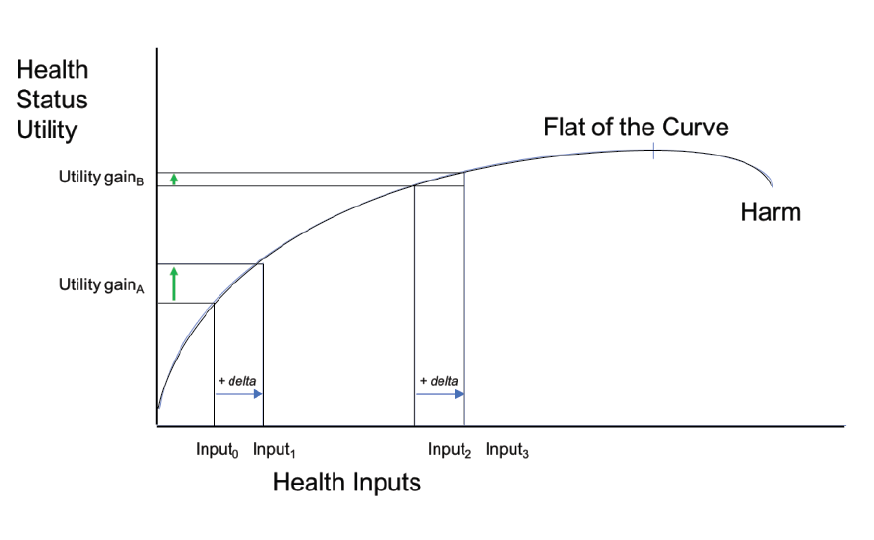
Health Economics: Select Concepts of the Health Production Function, Risk, and Insurance
- The select health economics concepts of the health production function, risk, and insurance are reviewed.

Health Economics: Select Concepts of the Health Production Function, Risk, and Insurance
- The select health economics concepts of the health production function, risk, and insurance are reviewed.

Health Economics: Select Concepts of the Health Production Function, Risk, and Insurance
- The select health economics concepts of the health production function, risk, and insurance are reviewed.
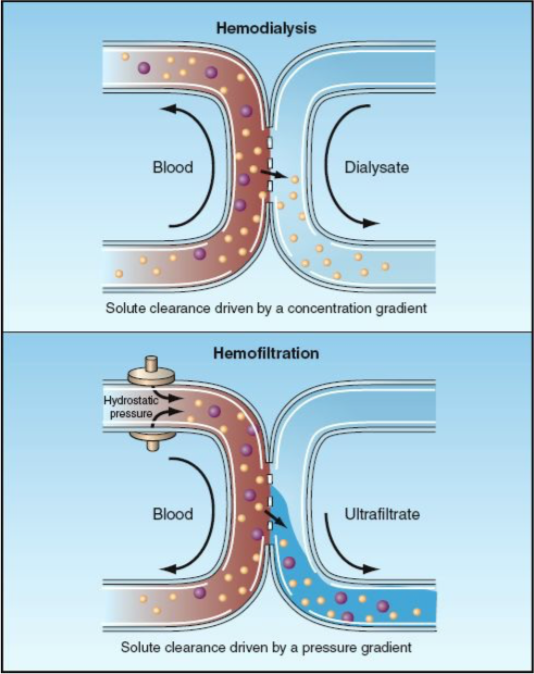
Pediatric Renal Replacement Therapy
- Efficiency of pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy
- Safety for methods of anticoagulation in renal replacement therapy
- Efficacy of access for renal replacement therapy
- Outcomes of renal replacement therapy in children
Surgical Management of Genitourinary Rhabdomyosarcoma
- The management of genitourinary rhabdomyosarcoma has gradually evolved from radical extirpative surgery to organ-sparing surgery with the aim of preserving organ function and improving the patient’s quality of life without compromising oncological outcomes.
- Primary resection of genitourinary rhabdomyosarcoma should not be attempted unless the tumor can be safely and completely resected in its entirety without considerable morbidity or loss of organ function.
- Symphysiotomy significantly facilitates the exposure and visibility to the prostate and posterior urethra in children with bladder or prostate rhabdomyosarcoma. Nerve-sparing technique should be the standard of care provided that local cancer control is not compromised.
- Residual masses post chemotherapy do not necessarily mean residual tumor. Maturing rhabdomyoblasts found on post-chemotherapy specimens can be managed with continued chemotherapy and observation with repeated imaging and biopsies.
- Routine retroperitoneal lymph node dissection can be avoided in children with paratesticular rhabdomyosarcoma younger than 10 years in the absence of gross lymphadenopathy on cross-sectional imaging.
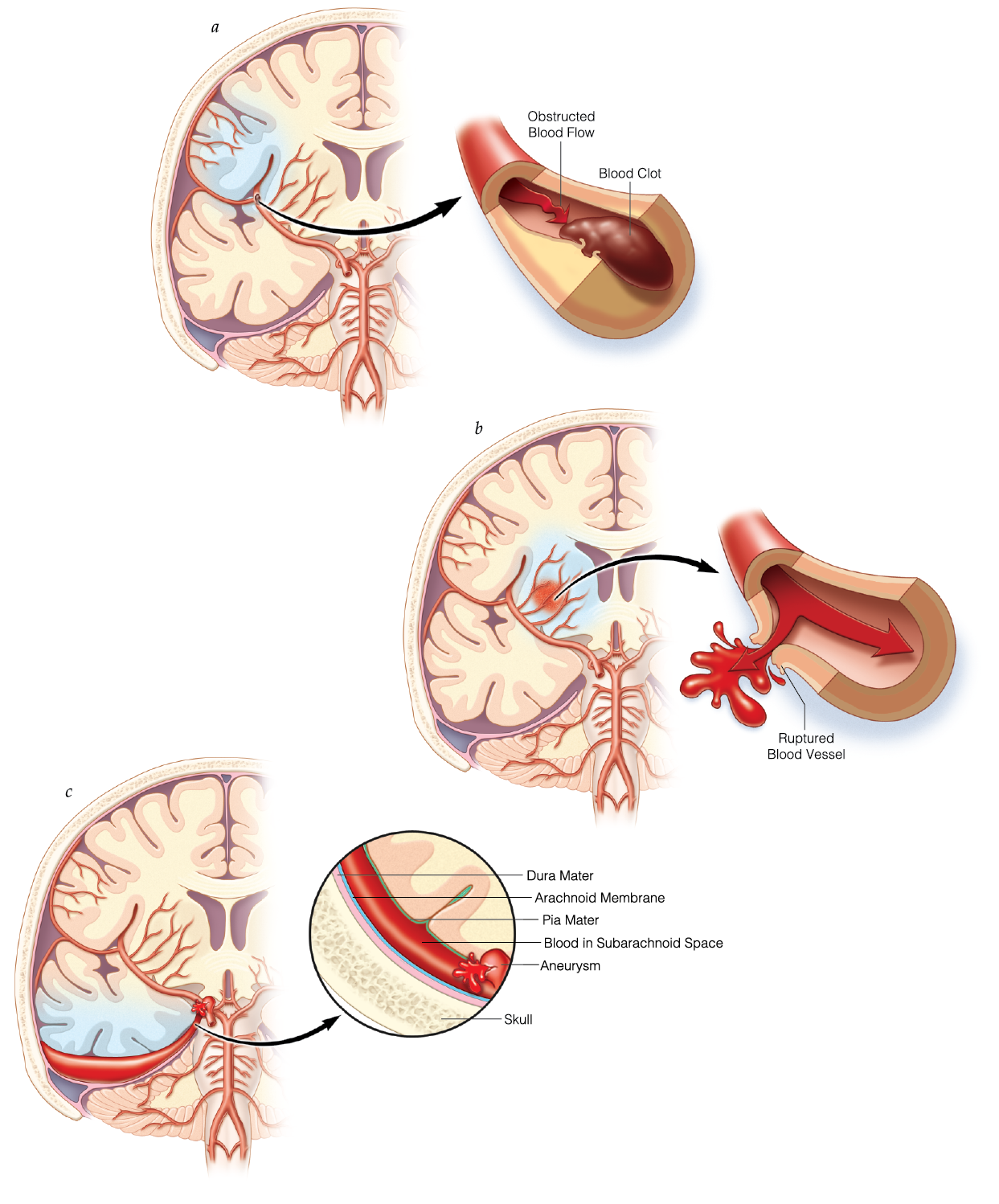
Acute Neurologic Events (Cerebrovascular Accidents, Subarachnoid Hemorrhage) and Complications
- Severity scoring, such as the National Institute of Health Stroke Scale, intracerebral hemorrhage score, Hunt and Hess and modified Fisher scores, informs acute care, long-term prognosis, and the study of acute cerebrovascular disease.
- Endovascular treatments and minimally invasive surgical techniques are revolutionizing the care of patients with acute stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Early withdrawal of life-sustaining therapies due to expected poor outcome results in a self-fulfilling prophecy; aggressive early care is prudent in all patients with severe stroke.
- Acute and long-term treatment of cerebrovascular disease has transformed to involve a multidisciplinary team composed of physicians from multiple specialties, nurses, physical therapists, and speech therapists.


.png)







