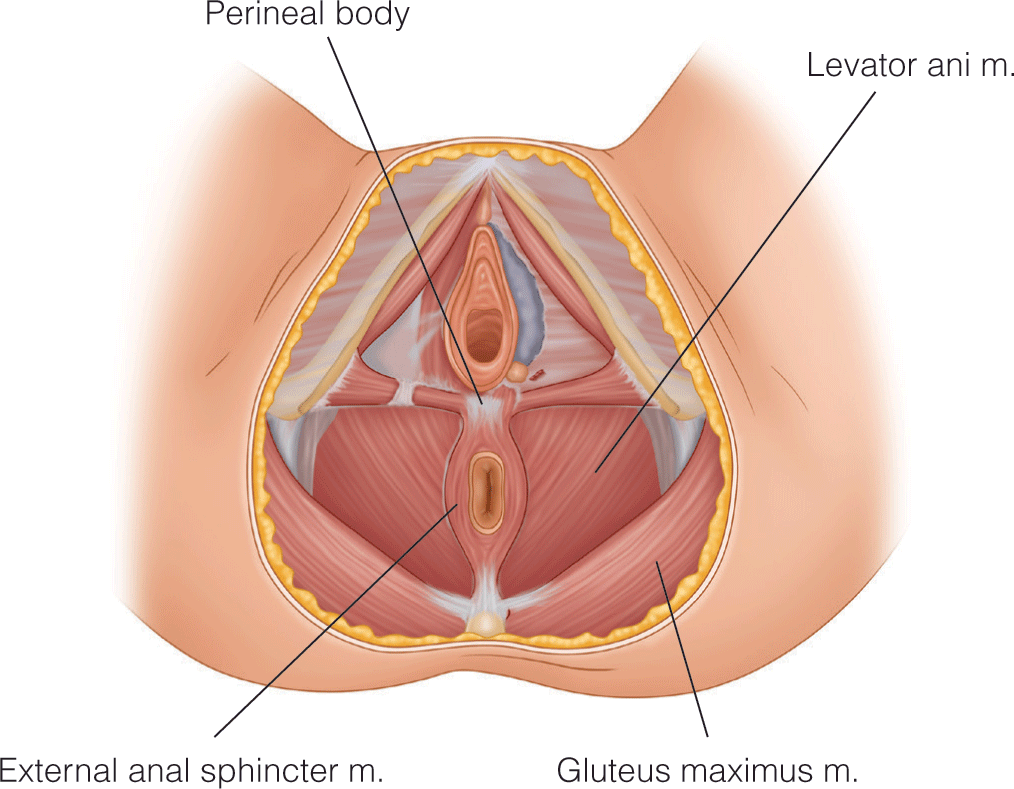
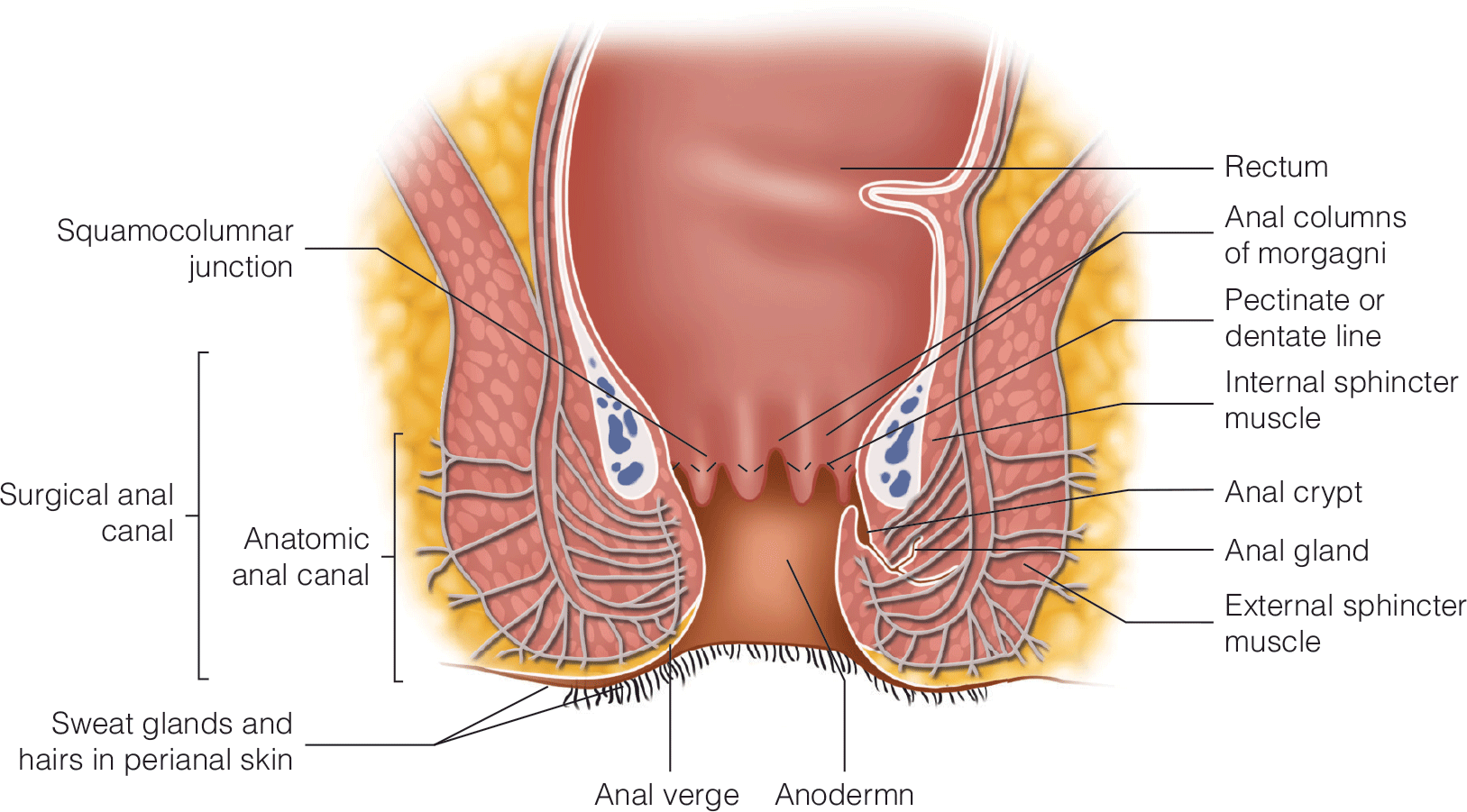
Surgical Management of Fecal Incontinence
- MRI defecography is obtained in real time as patient passes contrast during defecation. It is a noninvasive functional test, which can reveal anatomic defects including rectocele and rectal prolapse, the structure of surrounding pelvic organs and sphincter muscle anatomy. It is superior to endoanal ultrasonography in visualizing sphincter atrophy, which correlates with poor outcomes after sphincteroplasty, and can significantly influence surgical approach in patients who are operative candidates.
- Sacral nerve stimulation (SNS) has been shown to have excellent results in terms of improvement in fecal incontinence in up to 90% of patients and achievement of complete continence in 1/3 of patients after multiple years of follow-up. Additionally, SNS improves fecal incontinence in patients with external sphincter tears, pudendal neuropathy and preceding sphincteroplasty. Because of these encouraging results, SNS is becoming the first-line surgical therapy for patient’s refractory to medical management. As SNS has gained traction, some colorectal surgeons proceed directly to the first stage of SNS placement as a combined diagnostic and therapeutic modality.
- The Fenix system is an implantable device consisting of a ring of magnetized titanium beads that help keep the sphincter closed during defecation and can be forced open by bearing down during normal defecation. This device is currently under investigation, comparing its effectiveness with SNS in a large multicenter randomized controlled trial.



.png)






