Microvascular Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
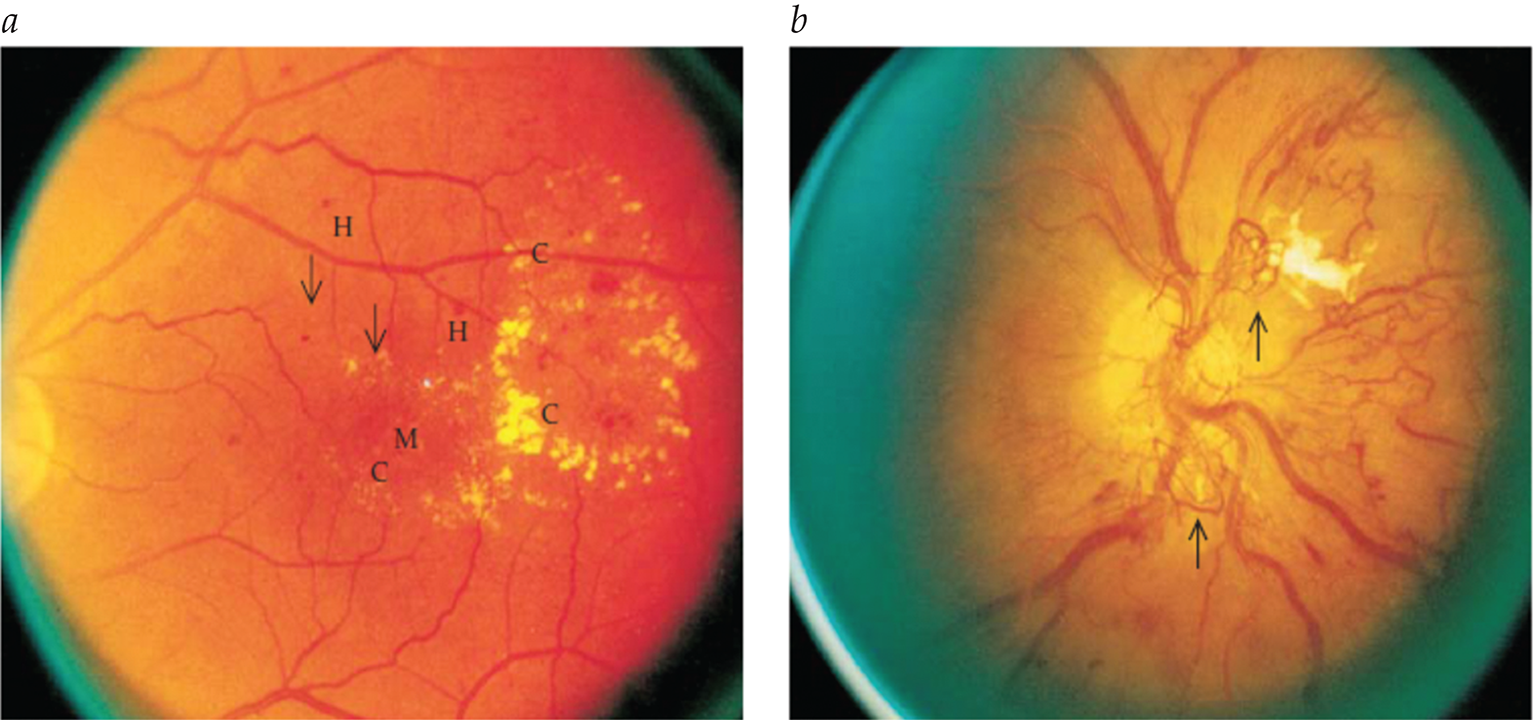
- Nonmydriatic fundus cameras with digital transmission enable efficient, remote retinopathy screening supervised by ophthalmologists.
- Two-step approach: significant lesions in digital retinal photographs prompt full ophthalmologist examinations.
- Cost-saving strategy for retinopathy screening, particularly beneficial in remote areas.
- Newer drugs (SGTLT 2 inhibitors, GLP-1 agonists, MR antagonists) offer added cardiovascular and renal benefits in diabetes.
- Chronic complications in diabetes require specialized management and consultation with appropriate specialists.



.png)






